Practical topic 25 Flashcards
Heart (20 cards)
What covers the heart?
Pericardium
Give the layers of the pericardium
- Fascia
- Pleura
- Pericardium fibrosum
- Pericardium serosum
- Lamina parietalis
- Lamina visceralis
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
Continuation of pericardium fibrosum to…
- Sternum:
- Lig. sternopericardium (Ru: 2)
-
Diaphragm:
- Lig. phrenicopericardium (ca, su)
Where is the papillary muscles located in the right ventricle?
-
M. papillaris subarteriosus
- On the septum
- At base of the supraventricular crest
-
M. papillaris parvi
- On the septum
- Next to sulcus interventricularis subsinosus
-
M. papillaris magnus
- On the parietal wall
- The biggest one
Where is the tricuspid valves located?
Give the name of the cusps
Right ventricle:
-
Cuspis septalis
- Originate from interventricular septum
- On septum
-
Cuspis parietalis
- From parietal wall
- Between m. papillaris parvi and magnus
-
Cuspis angularis
- Between m. papillaris magnus and subarteriosus
Where is the semilumar valves located?
Give the name of the cusps
Right ventricle:
-
Valva semilunaris sinister
- Towards sulcus interventricularis paracoronalis
-
Valva semilunaris dexter
- Just above crista semilunaris
- Valva semilunaris intermedia
Where is the mm. pectinati located?
Left atrium and right atrium
Where is the papillary muscles located in the left ventricle?
On the parietal wall:
- M. papillaris subauricularis
- M. papillaris subatrialis
Where is the bicuspid valves located?
In the left ventricle, papillary muscles attached to them:
- Cuspis parietalis
- Cuspis septalis
Give the pathway of the blood flow
Venous/deoxygenated blood to RA
→ RV
→ Pulmonary trunk (arteries)
→ Lungs to be supplied with oxygen
→ Oxygenated blood through pulmonary veins
→ LA
→ LV
→ Aorta
→ Systemic circulation

- Probe: lig. arteriosum
- Tr. pulmonalis
- Arcus aortae
- A. plumonalis sinistra (left)
- Conus arteriosus
- Right ventricle
- Right auricle
- Right atrium
- Left auricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- Sulcus coronarius

- Tr. pulmonales
- Conus arteriosus
- Right ventricle
- A. pulmonalis dextra (right)
- A. pulmonalis sinistra (left)
- Right auricle
- Arcus aortae
- Sulcus interventricularis paraconalis
- Left auricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- Sulcus coronarius

- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- Cusps (of left atrioventicular opening)
- Chordae tendineae
- M. papillaris
- Trabeculae carnae
- Tricuspid valve (semilunar cusps) of the aortic valve
- A. coronaria dextra (right)
- Tr. pulmonalis
- Right and left side v. pulminalis
- A. circumflexa
- Greate cardiac vein in sulcus coronarius

This is the heart as we viewed it from the left side of the dog
A. Right auricle
B. Left auricle
C. Left atrium
D. Right ventricle
E. Tr. pulmonalis
F. A. pulmonalis
G. Left ventricle
H. Arcus aortae
I. Tr. brachiocephalicus
J. A. subclavia sinistra (left)
K. Sulcus interventricluaris

This is the heart as we viewed it from the right side of the dog
A. Vena cava cranialis
B. Vena cava caudalis
C. V. azygous (right??)
D. V. pulmonalis
E. Right auricle
F. Right atrium
G. Sulcus coronarius
H. Right ventricle

The right atrium has been opened up
A. Vena cava cranialis
B. Vena cava caudalis
C. M. pectinati (of the auricle)
D. Tuberculum intervenosum
E. Fossa ovale
F. Sinus coronarius
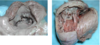
- Left: looking down through the atrioventricular valve from the right atrium to the right ventricle
- Right: right ventricular wall opened up
A. Right atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendinae
C. Mm. papillaris
D. Trabecula carnae
E. Trabecula septomarginalis

Right ventricular wall opened
A. Right atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendinae
C. Mm. papillaris
D. Trabeculae carnae
E. Trabeculae septomarginalis

Left: apex is towards you
Right:
A. Left atrioventricular valve
B. Chordae tendinae
C. Mm. papillaris (which chordae tendinae attaches to)
D. Trabecula carnae (on the ventricular septal wall)
E. Arotic valve
F. trabecula septomarginalis

From the view as if looking into the left thorax
A. Lig. arteriosum
B. A. Pulmonalis
C. Aorta
D. Tr. brachiocephalicus
E. A. subclavia sinistra (left)


