A28 - Mammary gland, blood supply and innervation Flashcards
1
Q
Give the usual number of mammae in:
- Ca
- Fe
- Sus
- Cow
- Eq
(also give the number in different locations)
A
- Ca: 10 (8-12 complexes, 5-20 units per complex that have separate ostium papillae on tip of teat)
- Fe: 8
- Sus: 14 (14 complexes)
- Cow: 4 (4 complex, single unit in each)
- Eq: 2 (2 complex, 2 units per complex)

2
Q
What does the mammary comlex consist of?
A
-
Corpus mammae
- Consisting of skin, glandular tissue, and connective tissue
- Attached at its base to the ventral surface of the trunk and, and continued apically by papilla mammae
-
Papilla (teat)
- Projection of the ventral surface of each mamma through which milk is withdrawn
- Car, sus: nipple
- Ru, eq: teat
3
Q
What is the mammary gland covered by?
A
External fascia
4
Q
Suspension of the mammary gland
A
-
Suspensory apparatus:
- Superficialanddeeplayer ofexternal fascia of the trunk
-
Lateral laminae (dense connective tissue) & medial laminae (elastic)
- Lamella suspensoriae extends between the mammillary complexes
- Sulcus intermammarius: separates complex row (adjacent mammae)
There are seven different tissues that provide support for the udder (ru):
-
Skin
- Covering the gland
- Most superficial
-
Superficial fascia
- Attaches skin to underlying the tissue
-
Coarse areolar
- Forms loose bond between the dorsal surface of the front quarters and the abdominal wall
-
Subpelvic tendon
- Not actually part of the suspensory apparatus, but gives rise to the superficial and deep lateral suspensory ligaments
- Attached tot he pelvic bone at several points
-
Lateral suspensory ligament
- Composed of fibrous (and elastic) tissue
- Arising from subpelvic tendon
- Attaches to areolar tissue
-
Deep lateral suspensory ligament (lamellae)
- Arises from subpelvic tendon
- Extends bown over the udder and almost enveloping it
-
Median suspensory ligament
- Most important part of the suspensory system in cows
- Composes of 2 adjacent heavy yellow elastic sheets that arise from the abdominal wall → medial flat surface of the two udder halves
- Able to stretch somewhat as the gland fills with milk to allow for the increased weight of the gland
5
Q
Draw the mammary gland
A

6
Q
Blood supply
Arteries
A
Abdominal & inguinal complex:
- Tr. pudendoepigastricus → a. pudenda externa → a. epigastrica caudalis superficialis → a. mammaria caudalis
Thoracic complex:
- A. subclavia → a. thoracica interna → a. epigastrica cranialis → a. mammaria cranialis
- Ca: additional blood supply from a. thoracica lateralis
- Sus: additional blood supply from a. thoracica lateralis
- Eq:
- Main artery is a. pudenda externa → a. mammillaris cranialis + caudalis (anastamoses with a. epigastrica cranialis
- A. pudenda interna gives branches to udder caudally
7
Q
Blood supply
Veins
A
- V. pudenda interna + v. subcutaneous abdominalis → v. epigastrica cranialis → v. thoracica interna → v. cava caudalis
- V. subcutaneous abdominalis:
- “Milk vein”
- Large in good milkers
8
Q
Innervation
A
- Types:
- Sensory
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
- Additional neurohormonal reflex arch
- Suckling stimulates hormones that trigger milk production
- Thoracic complexes:
- Nn. intercostales
- Abdominal and inguinal complexes:
- N. iliohypogastricus
- N. ilioinguinalis
- N. genitofemoralis
- Inguinal:
- N. pudenda
9
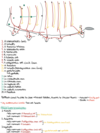
Q
Draw the blood supply, innervation and lymphatic system
A