C27 - Penis, muscles of the male genital organs, prepuce, blood supply and innervation Flashcards
1
Q
Structures to mention
A
- Radix penis (Composed of the two crura and the bulbus penis)
- Crus penis (Proximal end of each corpus cavernosum penis. Attached to the arcus ischiadicus. Covered by m. Ischiocavernosus)
- Corpus penis (Shaft from the radix penis → glans penis
-
Dorsum penis (Surface opposite the facies urethralis)
- Sulcus dorsalis penis (eq)
-
Facies urethralis
- Sulcus urethralis ( containing corpus spongiosum and urethra)
- Flexura sigmoidea penis (su, Ru) (S-shaped bend)
- Pars libera penis (Distal to the attachment of the prepuce)
-
Glans penis (Head. Contains corpus spongiosum glandis
- Processus dorsalis glandis (eq)
- Pars longa glandis (ca) (Distal, cylindrical part)
- Bulbus glandis (ca)
- Corona glandis
- Collum glandis (Constriction proximal to the corona glandis)
-
Fossa glandis (eq) (Excavation around processus urethralis)
- Sinus urethralis (eq) (Dorsal diverticulum of fossa glandis)
-
Preputium (Foreskin, surrounding the pars libera penis when not erected)
- Lamina externa (External layer of the fold of the skin forming the prepuce)
- Raphe preputii (Medial ventral seam of prepuce. Continuous with raphe scroti)
- Ostium preputiale (where lamina externa is reflected as lamina interna)
- Cavum preputiale (Between the lamina interna and the pars libera penis)
-
Lamina interna (Internal layer of the fold of skin forming the prepuce. Attached to the penis at the proximal end of the pars libera, where it is continuous with the skin of the free end of penis and glans)
- Plica preputialis (eq)
- Anulus preputialis (eq) (Preputial ring. A thickened band of skin)
- Diverticulum preputiale (su) (Large dorsal sac connected with the cranial end of the preputial cavity)
- M. preputialis cranialis (Ø eq) (Cutaneous)
- M. preputialis caudalis (Ru)
- Corpus cavernosum penis (Vascular space of corpus cavernosum)
- Os penis (ca) (Ossified distal part of the fused corpora cavernosa in glans penis)
- Corpus spongiosum penis (Erectile tissue surrounding urethra)
- Corpus spongiosum glandis (Continuous with corpus spongiosum penis)
- Bulbus penis (Caudal expansion of the corpus spongiosum penis)
- Septum penis (Median septum between the corpsula cavernosa penis)
- Lig. suspensorium penis (Surrounds corpsula cavernosa and coprus spongiosum)
- Lig. fundiforme penis (Form median ventral surface of tendo prepubicus)
2
Q
Penis
Interspecies differences
A
- Dorsum penis
- Sulcus dorsalis penis (eq)
- Flexura sigmoidea penis (su, ru)
- Glans penis
- Processus dorsalis glandis (eq)
- Pars longa glandis (ca)
- Bulbus glandis (ca)
-
Fossa glandis (eq)
- Sinus urethralis (eq)
- Preputium
- Lamina interna
- Plica preputalis (eq)
- Anulus prepustalis (eq)
- Diverticulum preputiale (su)
- Lamina interna
- M. preputalis cranialis (ø eq)
- M. preputalis caudalis (ru)
- Os penis (ca)
Type of penis:
- Sus, ru: fibroelastic type
- Trabeculae predominate over cavernosus
- Ca, eq: musculocavernosum type
- Cavernous space predominant
Direction of penis
- Ø fe: directed cranially
- Fe: directed caudally
Muscles:
- M. preputalis cranialis (ø eq)
- M. preputalis caudalis (ru)
3
Q
Penis
Location
A
- Originates as two crura from arcus ischiadicus
- The crura converge to form radix penis
- The penis is suspended between the thighs on the ventral surface of the trunk

4
Q
Peins
Give the main divisions of the penis
A
-
Radix penis
- __2 crura penis (formed by 2 columns of cavernous tissue)
- Corpus penis
- __Corpus cavernosum
- Corpus spongiosum
-
Glans penis
- __Os penis (ca) (modification of corpus cavernosum)
- Corpus spongiosum
5
Q
Penis
Corpus spongiosum
A
- Originates at the pelvic outlet with the sudden enlargement of spongy tissue around pelvic part of urethra
- The expansion forms bulbus penis?
- Corpus spongiosum extends beyond the distal end of corpus cavernosus to form glans penis
- Glans penis carries the external opening of the urethra (ø ru)
6
Q
Penis
Corpus cavernosus
A
- There are two different types of penis, related to the structure of corpus cavernosus:
-
Ru, sus: fibroelastic type
- Exhibits flexura sigmoidea penis
- Small blood space
- Ca, eq: musculocavernous type
- Large blood space
-
Ru, sus: fibroelastic type
7
Q
Penis
Corpus penis
A
- Surrounds urethra
- Begins at the pelvic outlet with bulbus penis, which is divided into left halves
- Bulbus penis is covered by m. bulbospongiosus
- The dorsal surface of corpus penis is marked by sulcus dorsalis penis
- The ventral surface of corpus penis is marked by sulcus ventralis penis
- These sulci accommodate urethra and icorpus spongiosum
8
Q
Penis direction
A
Directed cranially
Ø fe: caudally
9
Q
Penis
Draw cross sections of the penis
A

10
Q
Prepuce
A
- Prepuce is a fold of skin that covers the free end of the penis in retracted stat
- Eq: have an additional fold, allowing for considerable lengthening of the penis during erection
- M. preputalis cranialis (ø eq): retracts the prepuce → exposing apex of the penis
- M. preputalis caudalis (ru): protract the penis
Structures
- Lamina externa
- Raphe preputii
- Ostium preputiale
- Cavum preputiale
-
Lamina interna
- Plica preputialis (eq)
- Anulus preputialis (eq)
- Diverticulum preputiale (su)
- M. preputalis cranialis (ø eq)
- M. preputalis caudalis (ru)
Figure: prepuce and glans of the stallion

11
Q
Muscles of the pens
- List the muscles of the penis
- Draw the muscles of the penis
A
- M. bulbospongiosus
- M. ischocavernosus
- M. retractor penis
- M. urethralis
- M. preputalis cranialis (ø eq)
- M. preputalis caudalis (ru)

12
Q
Muscles of the pens
M. bulbospongiosus
A
- Thick circular muscle
- Continous with m. urethralis
- Surrounds the urethra and bulbis penis, extends to the proximal end of the shaft of the penis
- Eq: continues to glans penis
- Action: pulsatile contraction during ejaculation
13
Q
Muscles of the pens
M. ischiocavernosus
A
- Paired
- Origin: arcus ischiadicus and tuber ischiadicum
- Encloses the crura at radix penis
- Extends to the proximal end of corpus penis
- Action: raises erect penis
14
Q
Muscles of the pens
M. retractor penis
A
- Paired
- Smooth muscles
- Origin: From the caudal vertebrae → through perineum around anus to reach penis
-
Ending:
- Fibroelastic type (ru, su): Caudal to the arch of flexura sigmoidea
- Musculocavernous type (ca, eq): Follows m. bulbospongiosus to the apex of the penis
- Action: Retract the penis onto the prepuce
15
Q
Muscles of the pens
M. urethralis
A
- Ca, eq: Surrounds pelvic part of urethra
- Su, ru: Covers the ventral and lateral surfaces of the urethra
16
Q
Muscles of the pens
M. prepuralis cranialis
A
- Ø eq
- Derivated from m. cutaneous trunci
- Origin: Lateral to processus xiphoideus
- Ending: Lamina interna of prepuce
- Action: Retracts the prepuce → exposing apex of the penis
17
Q
Muscles of the penis
M. preputalis caudalis
A
- Ru
- Derived from m. cutaneous trunci
- Origin: abdominal fascia
- Ending: Lamina externa of prepuce
- Action: Retractor of prepuce (expose the penis)
18
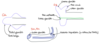
Q
Blood supply
A
Penis:
-
A. iliaca interna
-
A. pudenda interna
-
A. penis
- A. bulbi penis (to corpus spongiosum)
- A. profunda penis (to corpus cavernosum)
- A. dorsalis penis (to tip of penis)
-
A. penis
-
A. pudenda interna
Prepuce:
- A. pudenda externa → r. preputalis
19
Q
Innervation
A
- Penis and prepuce:
- Plexus lumbalis → n. pudenda
- Muscles of the penis:
- N. retractor caudalis
- N. perinealis profunca
-
Autonomic innervation:
- Sympathetic: pelvic plexus
- Parasympathetic: pelvic nerves


