Structure and Function of the Spinal Cord Flashcards
Anatomy of the spinal cord:
- Spinal cord extends from … to …
- Spinal cord narrows at … to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below … … vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves

Anatomy of the spinal cord:
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form … …
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to …
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find … … - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves
- Spinal cord extends from atlas to L1
- Spinal cord narrows at L1 to form conus medullaris
- Terminal filum (pia extension) attaches to coccyx
- Space below first lumbar vertebrae - lumbar cistern - will find cauda equina - dorsal and ventral roots of lumbar and sacral spinal nerves

Anatomy of the spinal cord (2)
- Sits protected within … column (in … canal)
- Surrounded by the …
- Sits protected within vertebral column (in vertebral canal)
- Surrounded by the meninges

Label the meninges


Spinal cord is divided into four regions:

Spinal cord - 4 regions:

… enlargement - innervation to upper limb and … enlargement - innervation to lower limb
Cervical enlargement - innervation to upper limb and lumbosacral enlargement - innervation to lower limb
Lumbar cistern contains what?
contains the cauda equina
Spinal Nerves
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- …. pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (… fibres) and ventral root (…. fibres)
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (afferent fibres) and ventral root (efferent fibres)

Spinal Nerves
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a … root (afferent fibres) and … root (efferent fibres)
- Spinal nerves connect the periphery to the spinal cord
- 31 pairs, each formed by a dorsal root (afferent fibres) and ventral root (efferent fibres)

Internal Anatomy (Spinal cord)
- Inner core, … matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, … matter
- … axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs
- Inner core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, white matter
- Myelinated axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs

Internal Anatomy (Spinal cord)
- … core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- … shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns (division of … shape)
- …, white matter
- Myelinated …
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs
- Inner core, grey matter
- Neuronal cell bodies
- H shaped
- Ventral, lateral and dorsal horns(division of H shape)
- Outer, white matter
- Myelinated axons
- White columns/tracts/funiculi
- Note the expanded grey matter at levels that supply the limbs

Grey matter organisation
- … horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- … horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- … horn - motor neurons
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - motor neurons

Grey matter organisation
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving … input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic … neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - … neurons
- Dorsal horn - neurons receiving sensory input
- Lateral horn - preganglionic sympathetic neurons (autonomic)
- Ventral horn - motor neurons

White matter organisation (1)
- Contains tracts
- Long … tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long … tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - … (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - crossed (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)

White matter organisation (1)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry … (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry … (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from … hemispheres - crossed (i.e. … cerebral hemisphere controls …. side of body)
- Contains tracts
- Long ascending tracts carry afferent (Sensory) impulses to centres within the brain
- Long descending tracts carry efferent (Motor) impulses from centres within brain
- Tracts to/from cerebral hemispheres - crossed (i.e. left cerebral hemisphere controls right side of body)

White matter organisation (2)
- … column contains ascending tracts
- … column contains descending and ascending tracts
- … column contains mainly descending tracts
- Dorsal column contains ascending tracts
- Lateral column contains descending and ascending tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly descending tracts

White matter organisation (2)
- Dorsal column contains … tracts
- Lateral column contains … and … tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly … tracts
- Dorsal column contains ascending tracts
- Lateral column contains descending and ascending tracts
- Ventral column contains mainly descending tracts

Ascending (sensory) tracts
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- …
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- …
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
Ascending (sensory) tracts
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from … the body (from …, joints, …)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from … the body (pain, …, …)
- Two types of sensory information carried in these tracts
- Proprioceptive
- Information originating from inside the body (from muscles, joints, tendons)
- Exteroceptive
- Information originating from outside the body (pain, temperature, touch)
Ascending tracts - anatomy
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via … root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or …
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the … …
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via dorsal root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or brainstem
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the cerebral cortex
- First order (primary sensory) neuron

Ascending tracts - anatomy
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- … order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via … root
- … order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or …
- … order neuron
- Projects to the … …
- … order (primary sensory) neuron
- Often three neurons in circuit:
- First order (primary sensory) neuron
- Enters spinal cord via dorsal root
- Second order neuron
- Ascends spinal cord or brainstem
- Third order neuron
- Projects to the cerebral cortex
- First order (primary sensory) neuron

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
- … touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- … (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with … information
- Fine touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- Proprioception (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with positional information

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
- Fine touch (from cutaneous …)
- Proprioception (from muscle …, … tendon organs, …)
- Provides brain with positional information
- Fine touch (from cutaneous mechanoreceptors)
- Proprioception (from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joints)
- Provides brain with positional information

What pathway provides brain with positional information?

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway - First order neurons
- Enter spinal cord and ascend dorsal column on same side within the:
- Fasciculus … (medial)
- Fasciculus … (lateral)
- Fibres ascend dorsal column uncrossed - … neurons in body
- First-order neurons synapse on second-order neurons in the …
- Axons are topographically organised
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- Information from … limb
- Fasciculus cuneatus terminates in nucleus cuneatus (cuneate)
- Information from … limb
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- 2 bumps- gracile tubercle and cuneate tubercle
- Enter spinal cord and ascend dorsal column on same side within the:
- Fasciculus gracilis (medial)
- Fasciculus cuneatus (lateral)
- Fibres ascend dorsal column uncrossed - Longest neurons in body
- First-order neurons synapse on second-order neurons in the medulla
- Axons are topographically organised
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- Information from lower limb
- Fasciculus cuneatus terminates in nucleus cuneatus (cuneate)
- Information from upper limb
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- 2 bumps- gracile tubercle and cuneate tubercle

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway - First order neurons
- Enter spinal cord and ascend dorsal column on same side within the:
- Fasciculus gracilis (…)
- Fasciculus cuneatus (…)
- Fibres ascend dorsal column … - Longest neurons in body
- First-order neurons synapse on second-order neurons in the medulla
- Axons are topographically organised
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in … … (gracile)
- Information from lower limb
- Fasciculus cuneatus terminates in … … (cuneate)
- Information from upper limb
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in … … (gracile)
- 2 bumps- gracile … and cuneate …
- Enter spinal cord and ascend dorsal column on same side within the:
- Fasciculus gracilis (medial)
- Fasciculus cuneatus (lateral)
- Fibres ascend dorsal column uncrossed - Longest neurons in body
- First-order neurons synapse on second-order neurons in the medulla
- Axons are topographically organised
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- Information from lower limb
- Fasciculus cuneatus terminates in nucleus cuneatus (cuneate)
- Information from upper limb
- Fasciculus gracilis terminates in nucleus gracilis (gracile)
- 2 bumps- gracile tubercle and cuneate tubercle

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway - Second-order neurons
- Cross in … and ascend to …
- Form medial … (ribbon-like)
- Cross in medulla and ascend to thalamus
- Form medial lemniscus (ribbon-like)

Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway - Third-order neurons
- Project from thalamus to … cortex
- Project from thalamus to somatosensory cortex
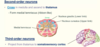
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway - summary

Damage to dorsal column
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord - E.g in multiple sclerosis
- Loss of … discrimination + … on sameside
- Symptoms include sensory … - Loss of coordination and balance without visual cues (i.e. no positional information)
- Clinical test: … sign
- Severe swaying on standing with eyes closed/feet together
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord - E.g in multiple sclerosis
- Loss of tactile discrimination + proprioception on sameside
- Symptoms include sensory ataxia - Loss of coordination and balance without visual cues (i.e. no positional information)
- Clinical test: Romberg’s sign
- Severe swaying on standing with eyes closed/feet together

Damage to dorsal column
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord - E.g in multiple sclerosis
- Loss of tactile discrimination + proprioception on … side
- Symptoms include sensory ataxia - Loss of … and … without visual cues (i.e. no positional information)
- Clinical test: Romberg’s sign
- … swaying on … with eyes closed/feet together
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord - E.g in multiple sclerosis
- Loss of tactile discrimination + proprioception on sameside
- Symptoms include sensory ataxia - Loss of coordination and balance without visual cues (i.e. no positional information)
- Clinical test: Romberg’s sign
- Severe swaying on standing with eyes closed/feet together

Spinothalamic tract
- … (From nociceptors)
- ..
- … touch
- Pain (From nociceptors)
- Temperature
- Crude touch

Spinothalamic tract - First-order neurons
- Enter dorsal horn and form tract of …
- Collateral branches given off at tip of dorsal horn
- Run up or down 1-2 spinal segments
- Synapse in … … with second-order neurons
- Enter dorsal horn and form tract of Lissauer
- Collateral branches given off at tip of dorsal horn
- Run up or down 1-2 spinal segments
- Synapse in dorsal horn with second-order neurons

Spinothalamic tract - First-order neurons
- Enter dorsal horn and form tract of Lissauer
- … branches given off at … of dorsal horn
- Run up or down 1-2 spinal segments
- … in dorsal horn with second-order neurons
- Enter dorsal horn and form tract of Lissauer
- Collateral branches given off at tip of dorsal horn
- Run up or down 1-2 spinal segments
- Synapse in dorsal horn with second-order neurons

Spinothalamic tract - Second-order neurons
- Cross in dorsal horn at each level
- Ascend in … column to thalamus
- Fibres from lower limb - … in tract
- Fibres from upper limb - … in tract
- Cross in dorsal horn at each level
- Ascend in anterolateral column to thalamus
- Fibres from lower limb - lateral in tract
- Fibres from upper limb - medial in tract

Spinothalamic tract - Second-order neurons
- Cross in dorsal horn at each level
- Ascend in anterolateral column to …
- Fibres from … limb - lateral in tract
- Fibres from … limb - medial in tract
- Cross in dorsal horn at each level
- Ascend in anterolateral column to thalamus
- Fibres from lower limb - lateral in tract
- Fibres from upper limb - medial in tract

Spinothalamic tract - Third-order neurons
- Project from … to … cortex
- Project from thalamus to somatosensory cortex

Spinothalamic tract summary

Damage to anterolateral column
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Loss of pain, temperature and crude touch on … side
- … tract injury (E.g. cord … due to herniated disk)
- Loss of lower limb pain first (Fibres sit ….)
- … tract injury (E.g. grey matter tumour)
- Loss of upper limb pain first (fibres sit ….)
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Loss of pain, temperature and crude touch on opposite side
- Outer tract injury (E.g. cord compression due to herniated disk)
- Loss of lower limb pain first (Fibres sit laterally)
- Inner tract injury (E.g. grey matter tumour)
- Loss of upper limb pain first (fibres sit medially)

Damage to anterolateral column
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Loss of …, … and … touch on opposite side
- Outer tract injury (E.g. cord compression due to … disk)
- Loss of … limb pain first (Fibres sit laterally)
- Inner tract injury (E.g. grey matter …)
- Loss of … limb pain first (fibres sit medially)
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Loss of pain, temperature and crude touch on opposite side
- Outer tract injury (E.g. cord compression due to herniated disk)
- Loss of lower limb pain first (Fibres sit laterally)
- Inner tract injury (E.g. grey matter tumour)
- Loss of upper limb pain first (fibres sit medially)

Spinocerebellar tracts
- Unconscious muscle … (From muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs) - for smooth muscle …
- Unconscious muscle proprioception (From muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs) - for smooth muscle coordination

Spinocerebellar tracts
- Only two neurons in pathway
- Comprises of 3 main tracts
- E.g. … and … spinocerebellar tracts
- Carries … information from trunk and lower limb
- E.g. … and … spinocerebellar tracts
- Tracts terminate in the cerebellum on the same side (Left cerebellum controls left side of body)
- Only two neurons in pathway
- Comprises of 3 main tracts
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Carries proprioceptive information from trunk and lower limb
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Tracts terminate in the cerebellum on the same side (Left cerebellum controls left side of body)
Spinocerebellar tracts
- Only two neurons in pathway
- Comprises of 3 main tracts
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Carries proprioceptive information from … and … limb
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Tracts terminate in the cerebellum on the … side (Left cerebellum controls … side of body)
- Only two neurons in pathway
- Comprises of 3 main tracts
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Carries proprioceptive information from trunk and lower limb
- E.g. anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts
- Tracts terminate in the cerebellum on the same side (Left cerebellum controls left side of body)
Posterior Spinocerebellar tract
- First-order neurons
- Synapse in … horn
- Second-order neurons
- … in lateral column to cerebellum - Very … axons
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on … side
- Although rarely damaged in isolation
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on … side
- First-order neurons
- Synapse in dorsal horn
- Second-order neurons
- Ascend in lateral column to cerebellum - Very fast axons
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on same side
- Although rarely damaged in isolation
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on same side

Posterior Spinocerebellar tract
- First-order neurons
- Synapse in dorsal …
- Second-order neurons
- … in lateral column to … - Very fast axons
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Uncoordinated … limb muscular activity on same side
- Although … damaged in isolation
- Uncoordinated … limb muscular activity on same side
- First-order neurons
- Synapse in dorsal horn
- Second-order neurons
- Ascend in lateral column to cerebellum - Very fast axons
- Lesion on one side of spinal cord
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on same side
- Although rarely damaged in isolation
- Uncoordinated lower limb muscular activity on same side

Descending tracts
- Brain … … spinal cord
- Control of … activity
- Many descending tracts
- Grouped into pyramidal or extrapyramidal
- Brain down towards spinal cord
- Control of muscular activity
- Many descending tracts
- Grouped into pyramidal or extrapyramidal
Descending tracts
- Brain down towards spinal cord
- Control of … activity
- Many descending tracts
- Grouped into … or …
- Brain down towards spinal cord
- Control of muscular activity
- Many descending tracts
- Grouped into pyramidal or extrapyramidal
Corticospinal tract
- Great … motor pathway
- Pyramidal tract
- 2 neurons in circuit:
- … motor (premotor) neurons
- From cerebral cortex to ventral horn
- … motor neurons
- From ventral horn to skeletal muscle
- … motor (premotor) neurons
- Great voluntary motor pathway
- Pyramidal tract
- 2 neurons in circuit:
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
- From cerebral cortex to ventral horn
- Lower motor neurons
- From ventral horn to skeletal muscle
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
Corticospinal tract
- Great voluntary motor pathway
- … tract
- 2 neurons in circuit:
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
- From … cortex to … horn
- Lower motor neurons
- From … horn to skeletal muscle
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
- Great voluntary motor pathway
- Pyramidal tract
- 2 neurons in circuit:
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
- From cerebral cortex to ventral horn
- Lower motor neurons
- From ventral horn to skeletal muscle
- Upper motor (premotor) neurons
Pyramidal tract
- Upper motor axons pass through the … of the …
- Upper motor axons pass through the pyramids of the medulla
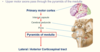
Pyramids of decussation
- Within the pyramids of the medulla, nerve fibres …
- 80% cross midline - … corticospinal tract
- 20% on same side - … corticospinal tract
- Within the pyramids of the medulla, nerve fibres decussate
- 80% cross midline - lateral corticospinal tract
- 20% on same side - anterior corticospinal tract

Pyramids of decussation
- Within the pyramids of the …, nerve fibres decussate
- …% cross midline - lateral corticospinal tract
- …% on same side - anterior corticospinal tract
- Within the pyramids of the medulla, nerve fibres decussate
- 80% cross midline - lateral corticospinal tract
- 20% on same side - anterior corticospinal tract

Lower motor neuron
- Excellent topographical organisation of lower motor neurons in ventral horn
- Medial = t…
- Anterolateral = … limb segments
- Posterolateral = … limb segments
- Excellent topographical organisation of lower motor neurons in ventral horn
- Medial = trunk
- Anterolateral = proximal limb segments
- Posterolateral = Distal limb segments

Lower motor neuron
- Excellent topographical organisation of lower motor neurons in ventral horn
- … = trunk
- … = proximal limb segments
- … = Distal limb segments
- Excellent topographical organisation of lower motor neurons in ventral horn
- Medial = trunk
- Anterolateral = proximal limb segments
- Posterolateral = Distal limb segments

Motor neuron disease
- Disruption of the corticospinal tract
- Upper motor neuron disease - Degeneration of upper motor neurons
- Spastic … (… muscle tone)
- … tendon reflexes
- No significant muscle …
- E.g. following a stroke
- Stroke - … pyramids - symptoms opposite side, … pyramids = same side
- Disruption of the corticospinal tract
- Upper motor neuron disease - Degeneration of upper motor neurons
- Spastic paralysis (increased muscle tone)
- Overactive tendon reflexes
- No significant muscle atrophy
- E.g. following a stroke

Motor neuron disease
- Disruption of the … tract
- Upper motor neuron disease - Degeneration of upper motor neurons
- Spastic paralysis (increased muscle tone)
- Overactive tendon reflexes
- No significant muscle atrophy
- E.g. following a …
- Stroke - above pyramids - symptoms … side, below pyramids = … side
- Disruption of the corticospinal tract
- Upper motor neuron disease - Degeneration of upper motor neurons
- Spastic paralysis (increased muscle tone)
- Overactive tendon reflexes
- No significant muscle atrophy
- E.g. following a stroke
- Stroke - above pyramids - symptoms opposite side, below pyramids = same side

Lower motor neuron disease:
- Degeneration of lower motor neurons
- Flaccid paralysis (… muscle tone)
- … tendon reflexes
- Muscle …
- E.g. spinal muscular atrophy (A), Guillain-Barre syndrome (B)
- Degeneration of lower motor neurons
- Flaccid paralysis (no muscle tone)
- No tendon reflexes
- Muscle atrophy
- E.g. spinal muscular atrophy (A), Guillain-Barre syndrome (B)

Lower motor neuron disease:
- … of lower motor neurons
- Flaccid paralysis (no muscle tone)
- No tendon reflexes
- Muscle atrophy
- E.g. spinal muscular … (A), …-… syndrome (B)
- Degeneration of lower motor neurons
- Flaccid paralysis (no muscle tone)
- No tendon reflexes
- Muscle atrophy
- E.g. spinal muscular atrophy (A), Guillain-Barre syndrome (B)

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Selectively affects lower and upper motor neurons
- Progressive muscle weakness and atrophy but mind intact
- Symptoms initially in limb or bulbar signs (speech and swallowing difficulties)
- … present when upper motor neurons affected
- … life span (about … years - due to … failure)
- Affects ..-.. in 100,000
- Selectively affects lower and upper motor neurons
- Progressive muscle weakness and atrophy but mind intact
- Symptoms initially in limb or bulbar signs (speech and swallowing difficulties)
- Spasticity present when upper motor neurons affected
- Short life span (about 5 years - due to respiratory failure)
- Affects 4-5 in 100,000

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Selectively affects lower and upper motor neurons
- Progressive muscle … and … but mind …
- Symptoms initially in … or bulbar signs (… and … difficulties)
- Spasticity present when … motor neurons affected
- Short life span (about 5 years - due to respiratory failure)
- Affects 4-5 in 100,000
- Selectively affects lower and upper motor neurons
- Progressive muscle weakness and atrophy but mind intact
- Symptoms initially in limb or bulbar signs (speech and swallowing difficulties)
- Spasticity present when upper motor neurons affected
- Short life span (about 5 years - due to respiratory failure)
- Affects 4-5 in 100,000

Extrapyramidal tracts
- Do not pass through the pyramids
- Many extrapyramidal tracts:
- Rubrospinal (From … nucleus (midbrain))
- Reticulospinal (From … formation (pons))
- Vestibulospinal (From … nuclei - medulla))
- Important for maintaining … and regulating … movements
- Lesions to extrapyramidal tracts cause movement disorders
- e.g. dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements), dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions)
- Do not pass through the pyramids
- Many extrapyramidal tracts:
- Rubrospinal (From red nucleus (midbrain))
- Reticulospinal (From reticular formation (pons))
- Vestibulospinal (From vestibular nuclei - medulla))
- Important for maintaining posture and regulating involuntary movements
- Lesions to extrapyramidal tracts cause movement disorders
- e.g. dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements), dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions)

Extrapyramidal tracts
- Do not pass through the …
- Many extrapyramidal tracts:
- Rubrospinal (From red nucleus (…))
- Reticulospinal (From reticular formation (…))
- Vestibulospinal (From vestibular nuclei - …))
- Important for maintaining posture and regulating involuntary movements
- … to extrapyramidal tracts cause movement disorders
- e.g. … (involuntary muscle movements), … (involuntary muscle contractions)
- Do not pass through the pyramids
- Many extrapyramidal tracts:
- Rubrospinal (From red nucleus (midbrain))
- Reticulospinal (From reticular formation (pons))
- Vestibulospinal (From vestibular nuclei - medulla))
- Important for maintaining posture and regulating involuntary movements
- Lesions to extrapyramidal tracts cause movement disorders
- e.g. dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements), dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions)

Summary of structure and function of the spinal cord



