Congenital Heart Disease Symposium Flashcards
Fetal Lung Maturation
- Before birth lungs full of fluid containing c.., protein, mucus, s…
- Breathing movements begin before birth -> effectively aspiration of … fluid
- As preparation before delivery, fetus removes …% of fluid out from lungs
- Before birth lungs full of fluid containing chloride, protein, mucus, surfactant
- Breathing movements begin before birth -> effectively aspiration of amniotic fluid
- As preparation before delivery, fetus removes 60% of fluid out from lungs
Fetal Lung Maturation (2)
- Breathing movements essential for normal lung development (incl. respiratory muscles)
- Removal/expulsion of respiratory fluid
- Prelabour hormonal changes 40ml/kg to …ml/kg
- Compression of vaginal birth removes …
- A… secreted in labour promotes reabsorption of …
- Breathing movements essential for normal lung development (incl. respiratory muscles)
- Removal/expulsion of respiratory fluid
- Prelabour hormonal changes 40ml/kg to 10ml/kg
- Compression of vaginal birth removes 1/3
- Adrenaline secreted in labour promotes reabsorption 2/3
First Breath
- Motivators for baby to take first breath
- … change
- … stimulation
- … stimulation
- Lack of … supply
- … pressure in chest cavity from … after birth
- Motivators for baby to take first breath
- Temperature change
- Light stimulation
- Physical stimulation
- Lack of oxygen supply
- Negative pressure in chest cavity from recoil after birth
Adaptations at Birth
- … of pulmonary sacs
- Dilation of pulmonary vascular bed due to … in capillary pressure
- Inflation of pulmonary sacs
- Dilation of pulmonary vascular bed due to fall in capillary pressure

Developmental Circulation - Pre and Post Delivery

In the fetal circulation, vascular … are required to bypass the liver and non-functioning lungs.
In the fetal circulation, vascular shunts are required to bypass the liver and non-functioning lungs.
Shunts
- The lungs are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the … … between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation.
- Any blood that does not pass through the … … enters the pulmonary trunk, which is linked to the distal arch of aorta by the ductus ….
- These two separate shunts allow the circulation to bypass the lungs.
- The lungs are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the foramen ovale between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation.
- Any blood that does not pass through the foramen ovale enters the pulmonary trunk, which is linked to the distal arch of aorta by the ductus arteriosus.
- These two separate shunts allow the circulation to bypass the lungs.

Circulatory Changes at Birth
- Main circulatory changes include closure of:
- … Ovale
- Ductus …
- Ductus …
- … Vessels
- Main circulatory changes include closure of:
- Foramen Ovale
- Ductus Arteriosus
- Ductus Venosus
- Umbilical Vessels
Foramen Ovale
- The … are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the foramen ovale between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation
- At birth, these shunts need to … to allow the normal adult circulation to be established:
- Foramen ovale – intake of air leads causes pulmonary resistance to … The pressure within the left atrium is now … than the right.
- As blood cannot flow through the foramen ovale left to right, this effectively closes the shunt. It fuses shut in most individuals by the age of … year.
- The lungs are bypassed by two separate shunts, firstly the foramen ovale between the two atria, which is responsible for bypassing the majority of the circulation
- At birth, these shunts need to close to allow the normal adult circulation to be established:
- Foramen ovale – intake of air leads causes pulmonary resistance to fall. The pressure within the left atrium is now higher than the right. As blood cannot flow through the foramen ovale left to right, this effectively closes the shunt. It fuses shut in most individuals by the age of 1 year.

The Foramen Ovale usually shuts in most individuals by age …
1 year
Foramen Ovale - Circulation

Foramen Ovale - Changes at Birth
- Functional closure - … left atrial pressure / … right atrial pressure
- Flexible septum primum pressed against rigid septum secundum
- Closure initially …
- Functional closure - increased left atrial pressure / lower right atrial pressure
- Flexible septum primum pressed against rigid septum secundum
- Closure initially reversible

Foramen Ovale to Fossa Ovalis
- Apposition of septa leads to final fusion - fossa ovalis (..-.. months)
- Apposition of septa leads to final fusion - fossa ovalis (6-12 months)
Ductus Arteriosis
- Vessel connecting … trunk to … of …
- Vessel connecting pulmonary trunk to arch of aorta

- The Ductus Arteriosus protects lungs against circulatory … - shunts …% of blood away from the lungs
- The Ductus Arteriosus protects lungs against circulatory overload - shunts 90% of blood away from the lungs
- Blood required for lung development - need that 10%
Ductus Arteriosus - Changes at Birth
- Closure mediated by … - from lung during initial inflation (Requires high O2)
- Initial closure at ..-.. hours, full anatomical closure may take 1-3 months
- … by muscular …
- Closure mediated by bradykinin - from lung during initial inflation (Requires high O2)
- Initial closure at 6-48 hours, full anatomical closure may take 1-3 months
- Constriction by muscular contraction
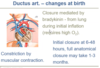
Ductus arteriosus – muscular wall … to close after birth (a process mediated by …).
Ductus arteriosus – muscular wall contracts to close after birth (a process mediated by bradykinin).
The circulatory shunts are summarised in the table below:
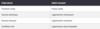
Ligamentum Arteriosum
- Lumen of ductus … obliterated to form ligamentum arteriosum
- Lumen of ductus arteriosus obliterated to form ligamentum arteriosum
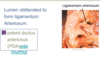
Umbilical Arteries
- Branches of fetal iliac arteries - carry … blood to placenta
- … blood returns from placenta via umbilical veins (and ductus) to fetal heart
- Branches of fetal iliac arteries - carry deoxygenated blood to placenta
- Re-oxygenated blood returns from placenta via umbilical veins (and ductus) to fetal heart

Birth
- Umbilical arteries and veins …
- Loss of … and associated blood flows
- … of umbilical vessels
- Prox. Umbilical arteries - internal iliac, fibrosis of rest - medical umbilical ligament
- Umbilical arteries and veins constrict
- Loss of placenta and associated blood flows
- Clamping of umbilical vessels
- Prox. Umbilical arteries - internal iliac, fibrosis of rest - medical umbilical ligament

At birth - … veins constrict but remain patent for some time
At birth - Umbilical veins constrict but remain patent for some time
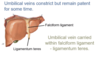
At birth - Ductus … undergoes gradual … - obliterated ligamentum - venosus in liver fissure
At birth - Ductus Venosus undergoes gradual fibrosis - obliterated ligamentum - venosus in liver fissure

What is Patent Ductus Venosus?
- If the ductus venosus fails to occlude after birth, it remains patent (open), and the individual is said to have a patent ductus venosus
- Little consequence in first months
- Liver and cardiac problems

Postnatal Changes

What is a Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)?
- Every baby is born with a ductus arteriosus. After birth, the opening is no longer needed and it usually narrows and closes within the first few days.
- Sometimes, the ductus doesn’t close after birth.
Neonatal Heart Failure
- Associated with:
- Signs classically right and left as adults
- Tachy…
- Metabolic …
- Hepato…
- Peripheral …
- … is crucial
- B… - paediatric history
- Associated with:
- Signs classically right and left as adults
- Tachpnoea
- Metabolic acidosis
- Hepatomegaly
- Peripheral oedema
- Weight is crucial
- Behaviour - paediatric history
Common Congenital Anomalies

Strictly 4 types ASD
- No murmurs, until tricuspid regurg
*

Aortic Stenosis
- … … Murmur
- Associated with another anomalies
- … syndrome
- … palate
- … heart failure
- Ejection Systolic Murmur
- Associated with another anomalies
- Williams syndrome
- Cleft palate
- Left heart failure

Cardiac Anomalies
- Associated with many genetic/syndromes
- Downs, Williams, 22q deletion (V/C/F)
- … - ,,, stands for vertebral defects, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal fistula, renal anomalies, and limb abnormalities
- Up to …% detected antenatally
- Associated with many genetic/syndromes
- Downs, Williams, 22q deletion (V/C/F)
- VACTERL - VACTERL stands for vertebral defects, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal fistula, renal anomalies, and limb abnormalities
- Up to 60% detected antenatally
Coarctation of the Aorta

Coarctation of Aorta Presents as:
- Overwhelming bi ventricular …
- Large change upper/lower limb BP
- NO / weak …
- Duct dependant lesion
- Overwhelming bi ventricular failure
- Large change upper/lower limb BP
- NO / weak femorals
- Duct dependant lesion



