Principles of Articulation Flashcards
(121 cards)
Articulation =
a joint
Joint =
From latin junctura - a joining
Arthrosis: An arthrosis is a …
Arthrosis: An arthrosis is a joint
An articulation or joint or arthrosis is a point of contact between:
- neighbouring bones
- bone and cartilage
- bone and teeth
Joint classification - Structural classification
- Presence or absence of a … cavity and the type of connective tissue
- Described as either fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial
- Presence or absence of a synovial cavity and the type of connective tissue
- Described as either fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial
Joint classification - Structural classification
- Presence or absence of a synovial cavity and the type of connective tissue
- Described as either f… , c… or s…
- Presence or absence of a synovial cavity and the type of connective tissue
- Described as either fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of … permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- … (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- … (immovable)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
-
Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
-
Synarthrosis (immovable)
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- … (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- … (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (…)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (… moveable)
- Synarthrosis (…)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
Joint classification - Functional classification
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (… moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Based on the degree of movement permitted:
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
- Amphiarthrosis (partially moveable)
- Diarthrosis (freely moveable)
- Synarthrosis (immovable)
Fibrous Joints
- No … cavity
- Held together by a fibrous … tissue
- Permits little or no movement (synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis)
- Three types of fibrous joint:
- 1) Suture
- 2) Syndesmosis
- 3) Interosseous membrane
- No synovial cavity
- Held together by a fibrous connective tissue
- Permits little or no movement (synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis)
- Three types of fibrous joint:
- 1) Suture
- 2) Syndesmosis
- 3) Interosseous membrane
Fibrous Joints
- No synovial cavity
- Held together by a fibrous connective tissue
- Permits little or no movement (termed…/…)
- Three types of fibrous joint:
- 1) Suture
- 2) Syndesmosis
- 3) Interosseous membrane
- No synovial cavity
- Held together by a fibrous connective tissue
- Permits little or no movement (synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis)
- Three types of fibrous joint:
- 1) Suture
- 2) Syndesmosis
- 3) Interosseous membrane
What movement do fibrous joints permit?
little or no movement - synarthrosis/amphiarthrosis
What are the three types of fibrous joints?
Suture, Syndesmosis, Interosseous membrane
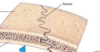
Fibrous joints - Suture
- Unite … bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
*
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
Fibrous joints - Suture
- Unite skull bones
- … layer of dense connective tissue
- … in shape
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
*
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age

Fibrous joints - Suture
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- … edges provide …, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
- Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
*
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age

Fibrous joints - Suture
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (…)
- … of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
- Unite skull bones
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Irregular
- Interlocking edges provide strength, permit no movement (Synarthrosis)
-
Ossification of a suture forms a synostosis
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
*
- e.g left and right sides of frontal bones fuse - 6yrs of age
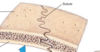
Ossification of a suture forms a …
synostosis
suture fibrous joints unite … bones
skull bones
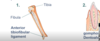
Fibrous joints - Syndesmosis
- … connective tissue than seen in a suture
- Crosses a … density than a suture
- Connective tissue typically arranged into bundles (ligament)
- Typically permit slight movement (…)
- examples - anterior tibiofibular ligament and gomphosis joint, also known as a dentoalveolar
- More connective tissue than seen in a suture
- Crosses a greater density than a suture
- Connective tissue typically arranged into bundles (ligament)
- Typically permit slight movement (amphiarthrosis)
- examples - anterior tibiofibular ligament and gomphosis joint, also known as a dentoalveolar
Fibrous joints - Syndesmosis
- More connective tissue than seen in a suture
- Crosses a greater density than a suture
- Connective tissue typically arranged into bundles (…)
- Typically permit … movement (amphiarthrosis)
- examples - anterior tibiofibular ligament and gomphosis joint, also known as a dentoalveolar
- More connective tissue than seen in a suture
- Crosses a greater density than a suture
- Connective tissue typically arranged into bundles (ligament)
- Typically permit slight movement (amphiarthrosis)
- examples - anterior tibiofibular ligament and gomphosis joint, also known as a dentoalveolar