Multiple Pregnancies Flashcards
Incidence of Twin Pregnancy (per 1000 deliveries)
- …-… Far East
- …-… Europe
- …-… Nigeria
- 2-7 Far East
- 9-20 Europe
- 20-45 Nigeria
Multiple Births - England & Wales

Twinning rates - Netherlands
1978 - first IVF baby

Triplets and higher order births E&W (per 1000 maternities)
- law limited no of embryos put back - avoid triplets if possible - explains the fall

Aetiology of Multiple Pregnancy
- E…
- Increasing … …
- Increasing …
- … Hx
- … treatment
- All factors for ‘super ovulation’
- Ethnicity
- Increasing Maternal Age
- Increasing Parity
- Family Hx
- Fertility treatment
- All factors for ‘super ovulation’
Multiple Pregnancy - Need to know…
- Zygosity - how many …
- Chorionicity - how many …
- Amnionicity - how many …
- Zygosity - how many eggs
- Chorionicity - how many placentas
- Amnionicity - how many amniotic saces
Monozygous twin pregnancy - the twins are…
Monozygous twin pregnancy - the twins are identical (1 egg)
Dizygous twin pregnancy - the twins are …
Dizygous twin pregnancy - the twins are non-identical (2 eggs)
What proportion of twin pregnancies are monozygous?
1/3 (identical)
What proportion of twin pregnancies are dizygous?
2/3 (non-identical)
Early Primordia - 14 days

Folding of the embryo in Week 4

The Endometrium and Fetal Membranes

Dizygotic twins
- How many eggs?
- Identical/Non-identical Twins?
- Accounts for … of all twin pregnancies
- How many eggs? - 2
- Accounts for 2/3 of all twins
- non-identical

Monozygotic Twins
- How many eggs?
- Identical/Non-identical Twins?
- Accounts for … of all twin pregnancies
- 1 egg
- Identical
- 1/3
Monozygotic Twins - 3 Different Outcomes
- DCDA / MCDA / MCMA
- Splitting at 2 cell stage: DCDA (seperate chorions, amnions and placentae)
- OR
- Splitting in early blastocyst yields 2 inner cell masses but common chorion, seperate amnions and joined placentae MCDA
- OR
- Later splitting yields 2 embryos from one inner cell mass - common chorion, amnion and ‘joined’ placentae MCMA

What is a dichorionic diamniotic (DCDA) twin pregnancy?
a type of twin pregnancy where each twin has its own chorionic and amniotic sacs (can be as a result of dizygotic twin or monzygotic twin)
- So, DCDA twins can be identical or non-identical
What are monochorionic, diamniotic twins?
Monochorionic, diamniotic (MCDA) twins are the product of a single fertilized ovum (egg), resulting in genetically identical offspring. MCDA twins share a single placenta (blood supply) but have separate amniotic sacs.

What is a monochorionic monoamniotic (MCMA) twin pregnancy?
This rare type of identical twins not only share a placenta, but also share the same amniotic sac (pocket of fluid).

Twin pregnancy - Dichorionic
- All dizygous twins are dichorionic
- Dichorionic twins must be diamniotic
- Dichorionic = separate circulations
- 1:3 monozygous twins are dichorionic
Twin pregnancy - Monochorionic
- Monozygous twins may be monochorionic (2/3) or dichorionic
- MC have vascularly joined placentae
- MC twins 3x increased loss rate
- MC twins usually diamniotic
Diagnosis of Twin Pregnancy
- Size of …
- By … scan
- Up to …% at delivery worldwide
- Uterine size
- Ultrasound scan
- Up to 50% at delivery worldwide
What type of pregnancy?
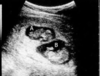
dichorionic pregnancy
What type of pregnancy?

monochorionic diamniotic - only one chorion
What type of pregnancy?

rare - MCMA (monochorionic monoamniotic)
Multiple pregnancy - Complications
- “Everything except post-dates”
- Symptoms of pregnancy
- Anaemia
- Hypertension
- Intrauterine growth restriction
- Pre-term labour
- Delivery problems
- Perinatal mortality
Twin pregnancy - Mortality
- Stillbirth – defined as after …. weeks
- Early neonatal – first … days
- Neonatal – in first … days
- Perinatal mortality – … risk + early … risk
- Infant – first …
- Rates shown are per 1000 births
- Stillbirth – after 24 weeks
- Early neonatal – first 7 days
- Neonatal – in first 28 days
- Perinatal mortality – SB risk + early neonatal risk
- Infant – first year
- Rates are per 1000 births
- Twins and triplets - higher risk as shown

Twin pregnancy - First trimester management
- Discuss … for … anomalies
- Determine …
- Discuss … … if triplets or more
- Discuss screening for chromosomal anomalies
- Determine chorionicity
- Discuss fetal reduction if triplets or more
Twin pregnancy - Second trimester management
- Detection of fetal …
- Serial scans for growth for all
- – DC monthly from … weeks
- Serial scans for TTTS (Transfusion syndrome) if … twins
- 2 weekly 16-28 weeks then monthly
- Maternal …
- Detection of fetal abnormality
- Serial scans for growth for all
- –DC monthly from 24 weeks
- Serial scans for TTTS if MC twins
- 2 weekly 16-28 weeks then monthly
- Maternal complications
Twin pregnancy - Monochorionic twins
- More fetal …
- More fetal … restriction
- Twin to twin …
- More fetal malformation
- More fetal growth restriction
- Twin to twin transfusion

What is Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) ?
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) is a rare pregnancy condition affecting identical twins or other multiples. TTTS occurs in pregnancies where twins share one placenta (afterbirth) and a network of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients essential for development in the womb. (MC twins, second trimester risk)
Monochorionic twin pregnancy - Twin to twin transfusion
- Unbalanced placental vascular a…
- Donor twin is …, decreased liquor
- High … (esp recipient)
- Rx - laser or amnio-reduction
- Early delivery by …
- Unbalanced placental vascular anastamoses
- Donor smaller, decreased liquor
- High mortality (esp recipient)
- Rx - laser or amnio-reduction
- Early delivery by caesarean

Twin pregnancy - Third trimester management
- Scanning as in … trimester
- Monitor … …
- …-… labour
- … planning
- Scanning as in 2nd trimester
- Monitor blood pressure
- Pre-term labour
- Delivery planning
Twin pregnancy - Delivery planning
- 37-38 weeks for … twins
- –vaginal birth or caesarean
- Presentation of twin I
- 36-37 weeks for … twins
- ?all … twins by caesarean?
- Pregnancy complications
- 37-38 weeks for DC twins
- – can be via vaginal birth or caesarean
- Presentation of twin I
- 36-37 weeks for MC twins
- ?all MC twins by caesarean?
- Pregnancy complications
Twin pregnancy - Labour management
- Monitoring … twins
- Problems delivering twin …
- Risk of … bleed
- Monitoring both twins
- Problems delivering twin II
- Risk of postpartum bleed
Twin pregnancy - Puerperium
- … difficulties
- … & … support
- Feeding difficulties
- Emotional & social support
Puerperium is …
the period of about six weeks after childbirth during which the mother’s reproductive organs return to their original non-pregnant condition
Multiple pregnancy - Higher order multiples
- Consider fetal …
- Determine …
- High risk of … labour
- Deliver preterm by …
- Postpartum …
- Difficult … & after
- Consider fetal reduction
- Determine chorionicity
- High risk of preterm labour
- Deliver preterm by caesarean
- Postpartum haemorrhage
- Difficult puerperium & after


