Defining the Reproductive Tracts COPY Flashcards
Introduction to Defining the Reproductive Tracts:
- Unlike most other body systems the reproductive system is in ‘slumber’ until …
- It is composed of the primary sex organs (… and …) that produce the gametes and a associated structures such as glands, ducts and external …
- In the adult the reproductive structures are located in the … or … pelvis.
- Provides a link to the external environment via ….
- Function is …, … and … of germ cells

- Unlike most other body systems the reproductive system is in ‘slumber’ until puberty.
- It is composes of the primary sex organs (testes and ovaries) that produce the gametes and a associated structures such as glands, ducts and external genitalia.
- In the adult the reproductive structures are located in the true or lesser pelvis.
- Provides a link to the external environment via genitalia.
- Function is Production, storage and delivery of germ cells
Female Reproductive System
- Gonads = …
- Internal Ducts= U…, f…, c…, v…
- External Genitalia= v…- c…, … of vagina.
- Principle function of the Female Genital System
- To produce …- female gametes
- To produce … (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone)
- To transport … to the site of …
- … fertilized … to term
- Deliver …

- Gonads= Ovaries
- Internal Ducts= Uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina
- External Genitalia= Vulva- Clitoris, vestibule of vagina.
- Principle function of the Female Genital System
- To produce oocytes- female gametes
- To produce hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone)
- To transport oocyte to the site of fertilization
- Nourish fertilized oocyte to term
- Deliver fetus
Ovaries
- Appearance: … shaped and size
- Location: Develop … and remain in … cavity. Suspended by ligament of … and …
- Blood: Supplied by ovarian artery/vein within … ligament
- Nerve: Ovarian …

- Appearance: Almond shaped and size
- Location: Develop retroperitoneal and remain in abdominal cavity. Suspended by ligament of ovary and mesovarium
- Blood: Supplied by ovarian artery/vein within suspensory ligament
- Nerve: Ovarian plexus
Microscopic Anatomy - Reproductive Tracts
- A woman has around … gametes - only a fraction make it to maturation.
- Within each ovary are follicles. Within each follicle is a primary … and hormone producing support cells. Within the follicle the … matures before being released for fertilization.
- This development from … -> … follicles -> … follicles -> … follicle -> … follicle
- Within each ovary are follicles. Within each follicle is a primary … and hormone producing support cells. Within the follicle the … matures before being released for fertilization.
- Ovulation = secondary oocyte release from … follicle. The secondary oocyte is arrested in … of second … division.
- Remainder of follicle forms the … … – secretes progesterone
- … secrete androgens and … convert to oestrogen

- A woman has around 400,000 gametes- only a fraction make it to maturation.
- Within each ovary are follicles. Within each follicle is a primary oocyte and hormone producing support cells. Within the follicle the oocyte matures before being released for fertilization.
- This development from oocyte- Promordial follicles- Primary follicles- Secondary follicle-Graafain follicle
- Ovulation = secondary oocyte release from graafian follicle. The secondary oocyte is arrested in metaphase of second meiotic division.
- Corpus luteum – secretes progesterone
- Theca secrete androgens and granulosa convert to oestrogen
Uterine Tube
- Function: conduct …
- Structure: …cm long and divided into four parts from lateral to medial
- 1.I..
- 2.A…
- 3.I…
- 4.U…
- Normally the site of …
- VAN:
- branches from uterine + ovarian arteries and veins
- Innervation: … from ovarian (abdomen) and … from pelvic splanchnic n
- Function: conduct oocyte
- Structure: 10cm long and divided into four parts from lateral to medial
- 1.Infundibulum
- 2.Ampulla
- 3.Isthmus
- 4.Uterine
- Normally the site of fertilization
- VAN:
- branches from uterine + ovarian arteries and veins
- Innervation: symp from ovarian (abdomen) and parasymp from pelvic splanchnic n
4 Parts of the Uterine Tube
- What are they? (lateral to medial)
- Infundibulum (containing fimbriae)
- Ampulla
- Isthmus
- Intramural

The uterine tube is normally the site of …
fertilization
Innervation of the Uterine Tube
- Sympathethic from the … + …
- Parasympathetic from the …

- Sympathethic from the uterine + ovarian arteries and veins
- Parasympathetic from the pelvic splanchnic nerve
Uterus - Structure and Function
- Structure: … …-shaped muscular organ. Body – … shaped, upper 2/3rd Cervix – …, lower 1/3rd.
- Function: Site of … of … … and … development
- Has a uterine … that communicates to … via internal os

- Structure: Hollow pear-shaped muscular organ. Body – cone shaped, upper 2/3rd Cervix – cylindrical, lower 1/3rd.
- Function: Site of implantation of fertilized egg and foetus development
- Has a uterine cavity that communicates to vagina via internal os

Uterus - 3 Layered Wall
- … – outer … wall covering the uterus
- … – thick muscular layer, responsible for process of …
- … – inner mucous layer; site of …; thickness changes through … cycle

- Perimetrium – outer serous wall covering the uterus
- Myometrium – thick muscular layer, responsible for process of parturition
- Endometrium – inner mucous layer; site of implantation; thickness changes through menstrual cycle
Innervation of the Uterus
- Innervation: sympathetic from the … …(along uterine artery); parasympathetic via the … … … - Note: also vagina
- Touch and Pain - birth - via … afferents to S…-S…

- Innervation: symp from the hypogastric plexus (along uterine artery); parasymp via the pelvic splanchnic n. Note: also vagina
- Touch and Pain - birth - via somatic afferents to S2-S4
Position of the uterus
- The position of the uterus is normally considered as being … – the fundus and body point … relative to the cervix and …- the uterus is angled forward relative to the ….
- In ~…% of women the uterus is … – angled backwards
- The position of the uterus is normally considered as being anteflexed – the fundus and body point forward relative to the cervix and anteverted- the uterus is angled forward relative to the vagina.
- In ~20% of women the uterus is retroverted – angled backwards

Uterine Ligaments
- Ligament of …
- … ligament of uterus
- B… ligament
- Transverse … ligament
- U… ligament
- Peritoneal pouches-
- 1…. pouch
- 2…. pouch
- Ligament of ovary
- Round ligament of uterus
- Broad ligament
- Transverse cervical ligament
- Uterosacral ligament
- Peritoneal pouches-
- 1.Vesicouterine pouch
- 2.Rectouterine pouch

Cervix
- Inferior portion of uterus; … tube
- Thick muscular layer – support developing …
- Lumen – … canal
- Constricted openings at ends (os)
- Internal – communicating with …
- External – communicating with …
- Inferior portion of uterus; cylindrical tube
- Thick muscular layer – support developing foetus
- Lumen – cervical canal
- Constricted openings at ends (os)
- Internal – communicating with uterus
- External – communicating with vagina

Label the Diagram

- Mesosalpinx
- Mesovarium
- Ovarian Artery
- Ovarian Vein
- Suspensory Ligament
- Uterine Tube
- Ovary
- Broad Ligament
- Round Ligament
- Ovarian Ligament
- Cardinal Ligament (transverse cervical ligament)
- Uterosacral Ligament
- Vagina

The round ligament is a remnant of the embryonic …
The round ligament is a remnant of the embryonic gubernaculum
In females, there are two areas of note:
- … pouch (of Douglas) – double folding of the peritoneum between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus.
- … pouch – double folding of peritoneum between the anterior surface of the uterus and the bladder.
Rectouterine pouch (of Douglas) – double folding of the peritoneum between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus.
Vesicouterine pouch – double folding of peritoneum between the anterior surface of the uterus and the bladder.

Vagina
- Function: Canal for … fluid, … canal, receives …/…
- Musculomembranous tube (…-…cm)
- Superiorly two recesses (…)
- Opens into … inferiorly
- Function: Canal for menstrual fluid, birth canal, receives penis/ejaculate
- Musculomembranous tube (7-9cm)
- Superiorly two recesses (fornix)
- Opens into vestibule inferiorly

External Genitalia - Female
- Consists of: … pubis, labia …, labia …, c…, bulb of …, … glands.
- Clitoris - erectile organ consists of: r…, body and g…
- Bulb of vestibule- erectile tissue over b… muscle
- Vestibular glands- secrete …
- Labia … encloses the … (openings for vagina and urethra) and the …
- Blood supply/drainage: … artery (erectile) & vein
- Innervation: branches of … and … n (e.g. dorsal n of clitoris)
- Consists of: mons pubis, labia majoria, labia minoria, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular glands.
- Clitoris- erectile organ consists of: root, body and glans
- Bulb of vestibule- erectile tissue over bulbospongiosus muscle
- Vestibular glands- secrete mucus
- Labia minora encloses the vestibule (openings for vagina and urethra) and the clitoris
- Blood supply/drainage: pudendal artery (erectile) & vein
- Innervation: branches of genitofemoral and pudendal n (e.g. dorsal n of clitoris)

Vasculature - Female Reproductive Tracts
- Ovarian (…) artery
- … artery
- … artery
- Internal … artery
- Ovarian (gonadal) artery
- Uterine artery
- Vaginal artery
- Internal pudendal artery

Female External Genitalia - Blood supply/drainage and Innervation
- Blood supply/drainage: … artery (erectile) & vein
- Innervation: branches of … and … n (e.g. dorsal n of clitoris)
- Blood supply/drainage: pudendal artery (erectile) & vein
- Innervation: branches of genitofemoral and pudendal n (e.g. dorsal n of clitoris)
Pregnancy
- Changes to the uterus and vagina from … and increasing size of the ….
- 1.Uterus expands from 50g to …g
- 2.Uterus extends to the x….
- 3.Centre of … is altered-increased lumbar ….
- 4 …. joint and pubic … relaxes
- 5.With uterine expansion the ovaries and uterine tubes are displaced …. The cervix becomes … and ….

- Changes to the uterus and vagina from hormones and increasing size of the uterus.
- 1.Uterus expands from 50g to 950g.
- 2.Uterus extends to the xiphisternum.
- 3.Centre of gravity is altered-increased lumbar lordosis.
- 4.Sacroiliac joint and pubic symphysis relaxes
- 5.With uterine expansion the ovaries and uterine tubes are displaced laterally. The cervix becomes softer and swollen.
Male Reproductive System
- Gonads = …
- Internal Ducts= Efferent …, E.., Vas .., … glands (e.g. prostate), U…
- External Genitalia= … and …
- Principle Functions of the Male Genital System:
- 1.To produce … -Male gametes
- 2.To produce … - Mostly testosterone
- 3.To facilitate fertilization- C…
- Gonads= testis
- Internal Ducts= Efferent ductules, Epididymis, Vas deferens, Accessory glands (e.g. prostate), Urethra
- External Genitalia=Penis and scrotum
- Principle Functions of the Male Genital System:
- 1.To produce spermatozoa-Male gametes
- 2.To produce androgens- Mostly testosterone
- 3.To facilitate fertilization- Copulation

Testis
- Appearance: Small egg-shaped oval organ …cm long …-…cm thick
- Location: The testis begin in the … region in week 12 and by week 32 arrive in the ….
- In the adult they should be located in the Scrotum suspended by the … cord
- Blood: Supplied by … artery- veins form the … plexus
- Nerve = … plexus (abdomen)
- Appearance: Small egg-shaped oval organ 4cm long 2-3cm thick
- Location: The testis begin in the lumbar region in week 12 and by week 32 arrive in the scrotum.
- In the adult they should be located in the Scrotum suspended by the spermatic cord
- Blood: Supplied by Testicular artery- veins form the pampiniform plexus
- Nerve:spermatic plexus (abdomen)

Testis ducts
- Sperm travel – exiting the testis:
- … tubules – coiled tubules; sperm is produced
- … testis – straight tubules (‘rete’ = net)
- … ductules – ducts leaving (efferent) testis
- … – transport and storage of sperm
- … … – thin muscular tube about 45 cm long
- Sperm travel – exiting the testis:
- Seminiferous tubules – coiled tubules; sperm is produced
- Rete testis – straight tubules (‘rete’ = net)
- Efferent ductules – ducts leaving (efferent) testis
- Epididymis – transport and storage of sperm
- Vas deferens – thin muscular tube about 45 cm long

Microscopic (Semifiniferous tubules)
- Each testis is subdivided into approx - … pyramid shaped lobules contain seminiferous tubules
- Function- production of … (spermatogenesis)
- Structure- highly …, lined by seminiferous epithelium
- Tunica propria-loose C.T, fibroblasts and myoid cells
- Stroma-surrounds semifiniferous tubules, loose C.T, vascular and houses small clusters of large interstitial cells of …
- … Cells - sit between seminiferous tubules
- Stretch from basal lamina to the lumen, linked by … junctions
- •Enfold developing spermatozoa-acting to
- Protect them from … in the blood
- Provide …
- … excess cytoplasm
- Secrete … binding protein
- Secrete i..
- Add fluid to the l..
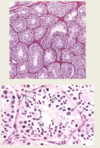
- Each testis is subdivided into approx. 250 pyramid shaped lobules contain seminiferous tubules
- Function- production of spermatozoa (spermatogenesis)
- Structure- highly tortuous, lined by seminiferous epithelium
- Tunica propria-loose C.T, fibroblasts and myoid cells
- Stroma-surrounds semifiniferous tubules, loose C.T, vascular and houses small clusters of large interstitial cells of Leydig
-
Sertoli Cells - sit between seminiferous tubules
- Stretch from basal lamina to the lumen, linked by tight junctions
- Enfold developing spermatozoa-acting to
- Protect them from antibodies in the blood
- Provide nutrients
- Phagocytose excess cytoplasm
- Secrete androgen binding protein
- Secrete inhibin
- Add fluid to the lumen
Inguinal Canal - (Not testing in 203)
- Formed between … and … inguinal ring
- Male contains ductus …, testicular artery, veins and nerves
- Female contains … ligament
- Hernia: Basic info:
- Weakness in muscle and surrounding tissue.
- Variety of causes, including congenital
- 1 in 50 boys get a hernia. 98% of inguinal hernia affect men.
- Surgery to correct.
- Formed between deep and superficial inguinal ring
- Male contains ductus deferens, testicular artery, veins and nerves
- Female contains round ligament
- Hernia: Basic info:
- Weakness in muscle and surrounding tissue.
- Variety of causes, including congenital
- 1 in 50 boys get a hernia. 98% of inguinal hernia affect men.
- Surgery to correct.
Spermatogenesis
- … sperm per gram of testis per second!
- Mature spermatozoa-highly specialized cell
- Involves extensive and elaborate … during development
- It involves … and …
- Takes … days
- Spermatids transformed into …
- 600 sperm per gram of testis per second!
- Mature spermatozoa-highly specialized cell
- Involves extensive and elaborate remodelling during development
- It involves mitosis and meiosis
- Takes 64 days
- Spermatids transformed into spermatozoa

Ductus Deferens Gross Anatomy
- Flow as from the perspective of sperm leaving the testis.
- Structure: Tube continuous with epididymis that is joined by duct seminal gland => … duct
- Location: Ascends in spermatic cord- which contains: vas deferens, Blood (testicular) and lymphatic vessels, cremaster muscle, nerves (e.g. branch of genitofemoral). Passes through the Inguinal canal- superficial ring first then canal- then deep inguinal ring. Deferens travels posteriorly, crosses over external iliacs and towards the back of bladder
- Function: to enable movement of sperm from testis to urethra for deposit into female tract.
- VAN: Arteries: those that primarily supply the lower bladder – inferior vesical – and rectum – middle rectal. Venous: blood follow the arteries and so have the same name.
- Flow as from the perspective of sperm leaving the testis.
- Structure: Tube continuous with epididymis that is joined by duct seminal gland => ejaculatory duct
- Location: Ascends in spermatic cord- which contains: vas deferens, Blood (testicular) and lymphatic vessels, cremaster muscle, nerves (e.g. branch of genitofemoral). Passes through the Inguinal canal- superficial ring first then canal- then deep inguinal ring. Deferens travels posteriorly, crosses over external iliacs and towards the back of bladder
- Function: to enable movement of sperm from testis to urethra for deposit into female tract.
- VAN:Arteries: those that primarily supply the lower bladder – inferior vesical – and rectum – middle rectal. Venous: blood follow the arteries and so have the same name.

Ductus Deferens - VAN
- Arteries: those that primarily supply the lower … – inferior … – and … – middle …
- Venous: blood follow the … and so …
- Arteries: those that primarily supply the lower bladder – inferior vesical – and rectum – middle rectal
- Venous: blood follow the arteries and so have the same name.
Accessory Glands
- … duct is joined by … glands:
- … vesicles – 5cm elongated organ; just inferior to rectovesical pouch; secretes alkaline fluid + fructose + coagulate
- … – blunt inverted cone; 3 x 4 cm; located at base of bladder; secretes prostatic fluid (20% total volume)
- … glands – pea sized glands; a.k.a. Cowpers glands; located inferior to prostate; secretion assists lubrication of ducts
-
Deferens duct is joined by accessory glands:
- Seminal vesicles – 5cm elongated organ; just inferior to rectovesical pouch; secretes alkaline fluid + fructose + coagulate
- Prostate – blunt inverted cone; 3 x 4 cm; located at base of bladder; secretes prostatic fluid (20% total volume)
- Bulbourethral glands – pea sized glands; a.k.a. Cowpers glands; located inferior to prostate; secretion assists lubrication of ducts
Seminal Vesicles
- Structure: … tubes in sac, bound by adventitia, Epithelium folded, … affect height and secretion of the epithelium
- Location: Posterior aspect of the …
- Function: Secrete- f…, amino acids, p…, citric and ascorbic acids that nourish …
- VAN: Wall of sac contains smooth muscle, which when stimulated by sympathetic nerves expels fluid out-ejaculation. Blood: Inf vesicle + prostatic vessels (int iliac a)

- Structure: Coiled tubes in sac, bound by adventitia, Epithelium folded, androgens affect height and secretion of the epithelium
- Location: Posterior aspect of the bladder
- Function: Secrete- fructose, amino acids, prostaglandins, citric and ascorbic acids that nourish spermatozoa
- VAN: Wall of sac contains smooth muscle, which when stimulated by sympathetic nerves expels fluid out-ejaculation. Blood: Inf vesicle + prostatic vessels (int iliac a)
Seminal Vesicles - VAN
- Wall of sac contains … muscle, which when stimulated by … nerves expels fluid out-…
- Blood: … vesicle + … vessels (int iliac a)
- Wall of sac contains smooth muscle, which when stimulated by sympathetic nerves expels fluid out-ejaculation
- DBlood: Inf vesicle + prostatic vessels (int iliac a)

Prostate
- Structure: Largest accessory gland of reproductive system (3cm long), 2/3 …. 1/3 …
- Location: Prostatic ducts open into prostatic …
- Function: Support …
- VAN: Supplied by … arteries and veins, Innervated by sympathetic from inferior … and parasympathetic from … nerves
- TURP
- Structure: Largest accessory gland of reproductive system (3cm long), 2/3 glandular. 1/3 fibromuscular
- Location: Prostatic ducts open into prostatic urethra
- Function: Support sperm
- VAN: Supplied by prostatic arteries and veins, Innervated by sympathetic from inferior hypogastric and parasympathetic from pelvic splanchnic nerves
- TURP - Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgery used to treat urinary problems that are caused by an enlarged prostate
What is TURP?
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgery used to treat urinary problems that are caused by an enlarged prostate
Bulbourethral glands
- Structure: Paired gland, Pea shaped, Open into spongy …
- Location: in external … …
- Function:.. of urethra
- VAN: Blood: … vesicle + … vessels (int iliac a)
- Structure: Paired gland, Pea shaped, Open into spongy urethra
- Location: in external urethral sphincter
- Function:lubrication of urethra
- VAN: Blood: Inf vesicle + prostatic vessels (int iliac a)

Composition of Ejaculate
- Sperm accounts for about …-…%
- Seminal vesicles about …-…%
- Prostate secreting …-…%
- Bulbourethral glands …%
- Sperm accounts for about 2-5%
- Seminal vesicles about 60-70%
- Prostate secreting 20-30%
- Bulbourethral glands 1%
Penis Gross Anatomy
- Structure: Consists of root, body and glans, body contains 3 … bodies
- Paired corpora … and 1 corpus …
- Location: … aspect of the pelvis
- Function:
- VAN: Supplied by internal … arteries and external … veins. Innervated by S2/4 … nerve, … nerve to penis, … nerve

- Structure: Consists of root, body and glans, body contains 3 cylindrical bodies
- Paired corpora cavernosa and 1 corpus spongiosum
- Location: Anterior aspect of the pelvis
- Function:
- VAN: Supplied by internal pudendal arteries and external pudendal veins. Innervated by S2/4 Pudendal nerve, dorsal nerve to penis, ilioinguinal nerve

Penis Microscopic Anatomy
- Each cavernous body is encapsulated by tough fibrous sheath (Tunica …)
- Interior of each cavernous body -> irregular … spaces, lined by endothelium, with dense … tissue and … muscle
- Each cavernous body is encapsulated by tough fibrous sheath (Tunica Albuginea)
- Interior of each cavernous body-irregular vascular spaces, lined by endothelium, with dense fibroelastic tissue and smooth muscle

Male Urethra
- Divided into three parts:
- P…
- M…
- P…
- Divided into three parts:
- Prostatic
- Membranous
- Penile

Erection, Emission and Ejaculation
- Erection- … arteries-supply the corpora-in flaccid state A/V shunts
- Increased … nerve supply, increases blood flow- diverted to vascular spaces
- Increased pressure in erectile tissue thus … venous return
- Emission - semen is delivered to the prostatic …, prostatic … added.
- Emission results from … activity.
- Ejaculation - semen expelled through …
- Inhibition of … supply-return to flaccid state
- Erection- Deep arteries-supply the corpora-in flaccid state A/V shunts
- Increased parasympathetic nerve supply, increases blood flow- diverted to vascular spaces
- Increased pressure in erectile tissue thus decreasing venous return
- Emission- semen is delivered to the prostatic urethra, prostatic fluid added.
- Emission results from sympathetic activity.
- Ejaculation-semen expelled through urethra
- Inhibition of sympathetic supply-return to flaccid state
Male Reproductive Tracts - Clinical Cases
- Testicular Torsion
- Cryptorchidism
- Patent processus vaginalis
- Hydrocele
- Hematocele
- Testicular Torsion
- Cryptorchidism
- Patent processus vaginalis
- Hydrocele
- Hematocele
Female Reproductive Tracts - Clinical Cases
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Prolapse
- Genital Warts
- Vulvitis
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Prolapse
- Genital Warts
- Vulvitis
Innervation - Erection, Emission, Ejaculation
- Erection - point =
- Emission = shoot =
- Erection - point = parasympathetic
- Emission = shoot = sympathetic


