Autoimmune Diseases 1 Flashcards
Selection of adaptive immune lymphocytes
- Receptors of these cells produced by random somatic recombination events between VDJ gene segments - produce functional T and B cell receptors
- … … ensures receptors are useful (e.g. T cells - ensure they can recognise self-antigen in context of MHCII)
- … … reduces autoreactivity (Deletes T cells expressing receptors expressing very high affinity for self-antigen)
- Naive B and T cell receptors - repertoire
- Upon infection - expansion of best populations
- … of infection - Most die, some become memory cells
- Receptors of these cells produced by random somatic recombination events between VDJ gene segments - produce functional T and B cell receptors
- Positive selection ensures receptors are useful (e.g. T cells - ensure they can recognise self-antigen in context of MHCII)
- Negative selection reduces autoreactivity (Deletes T cells expressing receptors expressing very high affinity for self-antigen)
- Naive B and T cell receptors - repertoire
- Upon infection - expansion of best populations
- Resolution of infection - Most die, some become memory cells

Cytokine deviation (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- Change in T cell … eg Th1 to Th2 may reduce inflammation
- Change in T cell phenotype eg Th1 to Th2 may reduce inflammation
Classification of AID (autoimmune disease) with a few examples
- …-specific
- E.g. T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, Hashimotos thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia
- …-system
- E.g. Systemic lupus erythematosis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome
-
Organ-specific
- E.g. T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, Hashimotos thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia
-
Multi-system
- E.g. Systemic lupus erythematosis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome

Pathogenic mechanisms in AID: autoantibodies
- Type … hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes classification
- Refers to diseases where an antibody is clearly pathogenic ie causes disease/ tissue damage directly
- Criteria:
- Disease can be transferred between experimental animals by infusion of serum, or during gestation to cause problems in fetus/ neonate
- Removal of antibody by plasmapharesis is beneficial
- A pathogenic antibody can be identified and characterised
- Type II hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes classification
- Refers to diseases where an antibody is clearly pathogenic ie causes disease/ tissue damage directly
- Criteria:
- Disease can be transferred between experimental animals by infusion of serum, or during gestation to cause problems in fetus/ neonate
- Removal of antibody by plasmapharesis is beneficial
- A pathogenic antibody can be identified and characterised
Autoimmune diseases - in which adaptive immune responses to …-antigens contribute to … damage
Autoimmune diseases - in which adaptive immune responses to self-antigens contribute to tissue damage
Candidiasis is a key feature of what disease?
APACED (autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, candidiasis and ectodermal dystrophy) - Results from antibodies to IL-17 – this cytokine seems to be important in host defence against fungi at mucosal surfaces
Coeliac disease
- A very common inflammatory disease of the small bowel with gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal features
- Up to ….% UK population affected
- More common in …
- Majority undiagnosed
- Characteristics of an autoimmune disease, but unusually triggered by an exogenous … (gluten) in pre-disposed individuals
- Main manifestations are malabsorption (loose stool, weight loss, vitamin deficiency, anaemia, poor growth in children) but myriad others now recognised
- A very common inflammatory disease of the small bowel with gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal features
- Up to 1% UK population affected
- More common in women
- Majority undiagnosed
- Characteristics of an autoimmune disease, but unusually triggered by an exogenous antigen (gluten) in pre-disposed individuals
- Main manifestations are malabsorption (loose stool, weight loss, vitamin deficiency, anaemia, poor growth in children) but myriad others now recognised
Antibody-mediated autoimmune disease: autoimmune hyperthyroidism (Graves Disease)
- Symptoms of … (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, heat intolerance etc)
- Goitre
- Grave’s ophthalmopathy due to poorly-understood retro-orbital inflammation
- Has all the characteristics of an antibody-mediated disease:
- Neonatal … if mother is affected
- Serum transfers disease between experimental animals
- Antibody detected and characterised
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, heat intolerance etc)
- Goitre
- Grave’s ophthalmopathy due to poorly-understood retro-orbital inflammation
- Has all the characteristics of an antibody-mediated disease:
- Neonatal hyperthyroidism if mother is affected
- Serum transfers disease between experimental animals
- Antibody detected and characterised
List THREE examples of autoimmune diseases where the pathogenesis is definitely directly mediated by a pathogenic antibody.
- Grave’s disease
- Autoimmune cytopenias
- Myasthenia gravis
Pathogenic mechanisms in AID: autoantibodies
- Type II hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes classification
- Refers to diseases where an antibody is clearly … ie causes disease/ tissue damage directly
- Criteria:
- Disease can be transferred between experimental animals by infusion of serum, or during gestation to cause problems in fetus/ neonate
- Removal of antibody by plasmapharesis is beneficial
- A pathogenic antibody can be identified and characterised
- Type II hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes classification
- Refers to diseases where an antibody is clearly pathogenic ie causes disease/ tissue damage directly
- Criteria:
- Disease can be transferred between experimental animals by infusion of serum, or during gestation to cause problems in fetus/ neonate
- Removal of antibody by plasmapharesis is beneficial
- A pathogenic antibody can be identified and characterised
Antibody-mediated autoimmune disease: Grave’s thyroiditis
- Pituitary gland secretes TSH, acts on thryoid to induce release of thyroid hormones
- Thyroid hormones act on the pituitary to shut down production of TSH, suppressing further thyroid hormone synthesis (feedback suppression)
- Autoimmune B cell makes antibodies against … receptor that also stimulate thyroid hormone production
- Thyroid hormones shut down TSH production but have no effect on autoantibody production, which continues to cause … thryoid hormone production
- Pituitary gland secretes TSH, acts on thryoid to induce release of thyroid hormones
- Thyroid hormones act on the pituitary to shut down production of TSH, suppressing further thyroid hormone synthesis (feedback suppression)
- Autoimmune B cell makes antibodies against TSH receptor that also stimulate thyroid hormone production
- Thyroid hormones shut down TSH production but have no effect on autoantibody production, which continues to cause excessive thryoid hormone production

Pathogenic mechanisms in AID: T cells
- Type … hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-dependent mechanisms
- T cells activate macrophages and other elements of innate immunity
- CD8 T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate autoreactive T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are …, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an …
- Type IV hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-dependent mechanisms
- T cells activate macrophages and other elements of innate immunity
- CD8 T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate autoreactive T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are sensitised, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an adjuvant
Antibody-mediated disease: autoimmune cytopenias
- Causing anaemia and mild form of …
- Can affect any part of blood compartment - affecting platelets = autoimmune …
- Causing anaemia and mild form of jaundice
- Can affect any part of blood compartment - affecting platelets = autoimmune thrombocytopaenia

Pathogenic mechanisms in AID: T cells
- Type IV hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-… mechanisms
- T cells activate … and other elements of innate immunity
- CD8 T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate … T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are sensitised, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an adjuvant
- Type IV hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-dependent mechanisms
- T cells activate macrophages and other elements of innate immunity
- CD8 T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate autoreactive T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are sensitised, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an adjuvant
Genetics and autoimmunity
- Evidence for importance:
- … monogenic disorders of the immune system that are associated with autoimmune diseases
- … models rely on genetically susceptible strains eg NOD mouse
- Enrichment in families, mostly attributable to HLA associations
- Environment clearly also important
- Evidence for importance:
- Rare monogenic disorders of the immune system that are associated with autoimmune diseases
- Mouse models rely on genetically susceptible strains eg NOD mouse
- Enrichment in families, mostly attributable to HLA associations
- Environment clearly also important

… represents a failure of tolerance
Autoimmunity represents a failure of tolerance
What syndrome develops as a result of failure migration 3th/ 4th branchial arches?
DiGeorge syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome are all examples of …-… autoimmune diseases
Systemic lupus erythematosis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome are all examples of multi-system autoimmune diseases
Antibody-mediated autoimmune disease: myasthenia gravis
- Muscle … and …
- Eyelids, facial muscles, chewing, talking and swallowing most often affected
- Muscle weakness and fatigability
- Eyelids, facial muscles, chewing, talking and swallowing most often affected

Selection of adaptive immune lymphocytes
- Receptors of these cells produced by random somatic recombination events between … gene segments - produce functional T and B cell receptors
- Positive selection ensures receptors are useful (e.g. T cells - ensure they can recognise self-antigen in context of MHCII)
- Negative selection reduces … (Deletes T cells expressing receptors expressing very high affinity for self-antigen)
- Naive B and T cell receptors - repertoire
- Upon infection - expansion of best populations
- Resolution of infection - Most …, some become … …
- Receptors of these cells produced by random somatic recombination events between VDJ gene segments - produce functional T and B cell receptors
- Positive selection ensures receptors are useful (e.g. T cells - ensure they can recognise self-antigen in context of MHCII)
- Negative selection reduces autoreactivity (Deletes T cells expressing receptors expressing very high affinity for self-antigen)
- Naive B and T cell receptors - repertoire
- Upon infection - expansion of best populations
- Resolution of infection - Most die, some become memory cells

T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, … thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia are all examples of …-… autoimmune diseases
T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, … thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia are all examples of organ-specific autoimmune diseases
DiGeorge syndrome
- Failure migration 3th/ 4th branchial arches
- Full phenotype:
- Absent … (low calcium, tetany)
- … palate
- … heart defects
- Thymic … (low T cell numbers, immunodeficiency)
- Microdeletions chromosome 22
- Variable presentation
- May affect any of above in isolation
- Huge spectrum of immunodeficiency from mild-SCID-like
- Autoimmunity is also common
- Failure migration 3th/ 4th branchial arches
- Full phenotype:
- Absent parathyroids (low calcium, tetany)
- Cleft palate
- Congenital heart defects
- Thymic aplasia (low T cell numbers, immunodeficiency)
- Microdeletions chromosome 22
- Variable presentation
- May affect any of above in isolation
- Huge spectrum of immunodeficiency from mild-SCID-like
- Autoimmunity is also common
T cell-mediated autoimmunity: autoimmune hypothyroidism (Hashimotos thyroiditis)
- Commonest cause of hypothyroidism in industrialised countries
- Particularly women over …
- Autoimmune … of thyroid: organ infiltrated by CD4 and CD8 T cells
- Commonest cause of hypothyroidism in industrialised countries
- Particularly women over 30
- Autoimmune destruction of thyroid: organ infiltrated by CD4 and CD8 T cells

DiGeorge syndrome
- Failure … 3th/ 4th branchial arches
- Full phenotype:
- Absent parathyroids (low …, tetany)
- Cleft palate
- Congenital heart defects
- … aplasia (low T cell numbers, immunodeficiency)
- Microdeletions chromosome …
- Variable presentation
- May affect any of above in isolation
- Huge spectrum of immunodeficiency from mild-SCID-like
- … is also common
- Failure migration 3th/ 4th branchial arches
- Full phenotype:
- Absent parathyroids (low calcium, tetany)
- Cleft palate
- Congenital heart defects
- Thymic aplasia (low T cell numbers, immunodeficiency)
- Microdeletions chromosome 22
- Variable presentation
- May affect any of above in isolation
- Huge spectrum of immunodeficiency from mild-SCID-like
- Autoimmunity is also common
NOTE: there are myriad inflammatory diseases (sarcoidosis, inflammatory bowel disease etc) that clearly involve the immune system but are not classified as autoimmune diseases, because they have not been demonstrated to involve … immune responses to … antigens
NOTE: there are myriad inflammatory diseases (sarcoidosis, inflammatory bowel disease etc) that clearly involve the immune system but are not classified as autoimmune diseases, because they have not been demonstrated to involve adaptive immune responses to self antigens
- The adaptive immune system is prone to autoimmunity
- Rigorous negative selection would mean a … risk of autoimmunity, but a … repertoire and therefore … susceptibility to infection
- Permissive negative selection would mean a … repertoire and therefore a … risk of infection but a … risk of autoimmunity
- Always be some potentially auto reactive T-cells produced - Peripheral … mechanisms used to keep this process in check - if this fails, autoimmunity = … …
- The adaptive immune system is prone to autoimmunity
- Rigorous negative selection would mean a low risk of autoimmunity, but a poor repertoire and therefore increased susceptibility to infection
- Permissive negative selection would mean a broad repertoire and therefore a lower risk of infection but a higher risk of autoimmunity
- Always be some potentially auto reactive T-cells produced - Peripheral tolerance mechanisms used to keep this process in check - if this fails, autoimmunity = autoimmune diseases

Monogenic disorders and autoimmunity: APACED
(autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, candidiasis and ectodermal dystrophy)
- AIRE gene regulates ectopic expression of tissue-specific antigens in thymus
- AIRE mutations result in … of negative selection
- Strongly associated with organ-specific auutoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, alopecia, autoimmune adrenal disease etc)
- Candidiasis also a key feature of the disease
- Results from antibodies to IL-… – this cytokine seems to be important in host defence against fungi at mucosal surfaces
- AIRE gene regulates ectopic expression of tissue-specific antigens in thymus
- AIRE mutations result in failure of negative selection
- Strongly associated with organ-specific auutoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, alopecia, autoimmune adrenal disease etc)
- Candidiasis also a key feature of the disease
- Results from antibodies to IL-17 – this cytokine seems to be important in host defence against fungi at mucosal surfaces

HLA and coeliac
- Virtually all affected individuals express:
- HLA-DQ…
- HLA-DQ8
- ………or both
- Virtually all affected individuals express:
- HLA-DQ2
- HLA-DQ8
- ………or both
Spontaneous urticaria manifests with … and …
Spontaneous urticaria manifests with hives and swelling
Strong association between the expression of … molecules and some autoimmune diseases
Strong association between the expression of HLA molecules and some autoimmune diseases
Antibody-mediated autoimmune disease: autoimmune hyperthyroidism (Graves Disease)
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, heat intolerance etc)
- A G…
- Grave’s ophthalmopathy due to poorly-understood retro-orbital inflammation
- Has all the characteristics of an antibody-mediated disease:
- Neonatal hyperthyroidism if mother is affected
- … transfers disease between experimental animals
- Antibody … and …
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism (tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, heat intolerance etc)
- Goitre
- Grave’s ophthalmopathy due to poorly-understood retro-orbital inflammation
- Has all the characteristics of an antibody-mediated disease:
- Neonatal hyperthyroidism if mother is affected
- Serum transfers disease between experimental animals
- Antibody detected and characterised
What is IPEX?
- Monogenic disorders and autoimmunity: IPEX (immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-Linked)
- Exceedingly rare X Linked mutation affecting Forkhead p3 (FoxP3) gene
- Abrogates production of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells
What disease is present in bottom photo?


HLA and coeliac
- Dietary … (wheat, rye and barley) is degraded by gut tissue transglutamine 2 enzyme during digestion to produce … peptides
- HLA DQ2/ 8 molecules can present these … peptides to T cells if the appropriate T cell receptors are present
- Dietary gliadin (wheat, rye and barley) is degraded by gut tissue transglutamine 2 enzyme during digestion to produce gliadin peptides
- HLA DQ2/ 8 molecules can present these gliadin peptides to T cells if the appropriate T cell receptors are present

HLA and coeliac
- Dietary gliadin (wheat, rye and barley) is degraded by gut tissue … 2 enzyme during digestion to produce gliadin peptides
- HLA DQ2/ 8 molecules can present these gliadin peptides to T cells if the … T cell receptors are present
- Dietary gliadin (wheat, rye and barley) is degraded by gut tissue transglutamine 2 enzyme during digestion to produce gliadin peptides
- HLA DQ2/ 8 molecules can present these gliadin peptides to T cells if the appropriate T cell receptors are present

Immunological hierarchy (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- CD4 T cell will not be activated unless antigen is presented in an ‘inflammatory’ context with … ligation
- CD4 T cell will not be activated unless antigen is presented in an ‘inflammatory’ context with TLR ligation
The adaptive immune system is prone to …
The adaptive immune system is prone to autoimmunity
- Rigorous negative selection would mean a low risk of autoimmunity, but a poor repertoire and therefore increased susceptibility to infection
- Permissive negative selection would mean a broad repertoire and therefore a lower risk of infection but a higher risk of autoimmunity
- Always be some potentially auto reactive T-cells produced - Peripheral tolerance mechanisms used to keep this process in check - if this fails, autoimmunity = autoimmune diseases
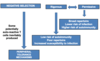
Clonal exhaustion (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- … post-activation by activation-induced cell death
- Apoptosis post-activation by activation-induced cell death
Regulatory T cells (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- CD25+FoxP3 positive T cells and other types of regulatory T cells actively suppress immune responses by cytokine and … signalling
- CD25+FoxP3 positive T cells and other types of regulatory T cells actively suppress immune responses by cytokine and juxtacrine signalling
Peripheral anergy (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- Weak signalling between APC/ CD4 T cell without co-stimulation causes T cells to become …-…
- Weak signalling between APC/ CD4 T cell without co-stimulation causes T cells to become non-responsive
Classification of AID (autoimmune disease) with a few examples
- Organ-specific
- E.g. T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, … thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia
- Multi-system
- E.g. Systemic lupus …, … arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome
- Organ-specific
- E.g. T1 Diabetes, Pemphigus/pemphigoid, Graves disease, Hashimotos thryoiditis, Autoimmune cytopenias;anaemia, thrombocytopenia
- Multi-system
- E.g. Systemic lupus erythematosis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome

Peripheral tolerance mechanisms
- Failure of peripheral tolerance mechanisms may allow … of potentially auto-reactive T cells, leading to the development of … …
- Failure of peripheral tolerance mechanisms may allow activation of potentially auto-reactive T cells, leading to the development of autoimmune disease

Multiple pathogenic immune mechanisms underlie autoimmune diseases
- ‘It is a vast oversimplification to consider most autoimmune diseases to be mediated solely by one part of the immune system. It is more useful instead to consider that autoimmune responses, like responses to pathogens, engage the integrated immune system and therefore typically require T cells, B cell and APC’
- Charles Janeway
- This is particularly true of the chronic, multi-system autoimmune disorders such as … arthritis (see symposium) and S.. , where multiple immune mechanisms become involved
- ‘It is a vast oversimplification to consider most autoimmune diseases to be mediated solely by one part of the immune system. It is more useful instead to consider that autoimmune responses, like responses to pathogens, engage the integrated immune system and therefore typically require T cells, B cell and APC’
- Charles Janeway
- This is particularly true of the chronic, multi-system autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis (see symposium) and SLE, where multiple immune mechanisms become involved
What are the main manifestations of coeliac disease?
Main manifestations are malabsorption (loose stool, weight loss, vitamin deficiency, anaemia, poor growth in children) but myriad others now recognised
Monogenic disorders and autoimmunity: IPEX (immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-Linked)
- What are the key features? (3)
- Key features:
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Dermatitis
- Organ-specific autoimmunity
Monogenic disorders and autoimmunity: APACED
(autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, candidiasis and ectodermal dystrophy)
- AIRE gene regulates ectopic expression of tissue-specific antigens in thymus
- AIRE mutations result in failure of … selection
- Strongly associated with organ-specific auutoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, alopecia, autoimmune adrenal disease etc)
- … also a key feature of the disease
- Results from antibodies to IL-17 – this cytokine seems to be important in host defence against fungi at mucosal surfaces
- AIRE gene regulates ectopic expression of tissue-specific antigens in thymus
- AIRE mutations result in failure of negative selection
- Strongly associated with organ-specific auutoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, alopecia, autoimmune adrenal disease etc)
- Candidiasis also a key feature of the disease
- Results from antibodies to IL-17 – this cytokine seems to be important in host defence against fungi at mucosal surfaces

Autoimmunity represents a failure of …
Autoimmunity represents a failure of tolerance
Pathogenic mechanisms in AID: T cells
- Type … hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-dependent mechanisms
- T cells activate macrophages and other elements of innate immunity
- CD.. T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate autoreactive T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are sensitised, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an adjuvant
- Type IV hypersensitivity according to Gell and Coombes
- Tissue damage is directly mediated by T cell-dependent mechanisms
- T cells activate macrophages and other elements of innate immunity
- CD8 T cells damage tissue directly
- Much more difficult to demonstrate autoreactive T cells in vitro than it is to demonstrate antibody
- Experimental models rely on genetically susceptible animals that are sensitised, often by exposure to a self-antigen with an adjuvant
Coeliac pathogenesis
- The damage is mediated by … cells; note that antibodies are produced, but do not contribute to tissue damage
- Inflammation resolves with strict gluten …
- 30-50% of Europeans express HLA-DQ2 and/ or HLA-DQ8 – not clear which additional genetic/ environmental factors are important in coeliac
- The damage is mediated by T cells; note that antibodies are produced, but do not contribute to tissue damage
- Inflammation resolves with strict gluten avoidance
- 30-50% of Europeans express HLA-DQ2 and/ or HLA-DQ8 – not clear which additional genetic/ environmental factors are important in coeliac

The HLA system
- APCs present processed peptide to T cells in combination with highly polymorphic … (HLA) molecules
- Encoded by the HLA system on chromosome 6
- Class I: A, B, C
- Class II: DR, DP and DQ
- Complex nomenclature used to describe ‘tissue type’ in an individual
- Eg HLA B27=expresses serotype 27 at B locus of HLA class I
- EG HLA DR2=expresses serotype 2 at locus 2 of HLA class II
- Strong association between the expression of HLA molecules and some … diseases
- APCs present processed peptide to T cells in combination with highly polymorphic MHC (HLA) molecules
- Encoded by the HLA system on chromosome 6
- Class I: A, B, C
- Class II: DR, DP and DQ
- Complex nomenclature used to describe ‘tissue type’ in an individual
- Eg HLA B27=expresses serotype 27 at B locus of HLA class I
- EG HLA DR2=expresses serotype 2 at locus 2 of HLA class II
- Strong association between the expression of HLA molecules and some autoimmune diseases

Antibody-mediated autoimmune disease: myasthenia gravis
- Production of … antibody against the acetylcholine receptor
- Reduces normal transmission at neuromuscular junction - fatigability and …
- Production of pathogenic antibody against the acetylcholine receptor
- reduces normal transmission at neuromuscular junction - fatigability and weakness

Monogenic disorders and autoimmunity: IPEX (immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-Linked)
- Exceedingly rare X Linked mutation affecting Forkhead p3 (FoxP3) gene
- Abrogates production of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells
- Key features:
- –… … disease
- –Dermatitis
- –Organ-specific …
- Exceedingly rare X Linked mutation affecting Forkhead p3 (FoxP3) gene
- Abrogates production of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells
- Key features:
- –Inflammatory bowel disease
- –Dermatitis
- –Organ-specific autoimmunity
A note about antibodies and autoimmune disease
- In these examples, the auto-antibody is said to be ‘…’ as it is directly leading to disease
- Auto-antibodies are also found in myriad other autoimmune diseases
- These antibodies seem to be produced as a by-product of the inflammatory process. They don’t fulfil the criteria to be …
- They are useful for diagnosis – see next lecture, eg
- Tissue transglutaminase antibody (…), islet cell antibody (…), gastric parietal cell antibody (pernicious anaemia) etc etc
- In these examples, the auto-antibody is said to be ‘pathogenic’ as it is directly leading to disease
- Auto-antibodies are also found in myriad other autoimmune diseases
- These antibodies seem to be produced as a by-product of the inflammatory process. They don’t fulfil the criteria to be pathogenic
- They are useful for diagnosis – see next lecture, eg
- Tissue transglutaminase antibody (coeliac), islet cell antibody (diabetes), gastric parietal cell antibody (pernicious anaemia) etc etc
Autoimmunity (or auto-reactivity) = immune responses to …-…
Autoimmunity (or auto-reactivity) = immune responses to self-antigens
Spontaneous urticaria
- IgG FcεR1 antibody cross-links mast cell receptor causing …
- Manifests with … and swelling
- IgG FcεR1 antibody cross-links mast cell receptor causing degranulation. Manifests with hives and swelling

The HLA system
- APCs present processed peptide to T cells in combination with highly polymorphic MHC (HLA) molecules
- Encoded by the HLA system on chromosome …
- Class …: A, B, C
- Class …: DR, DP and DQ
- Complex nomenclature used to describe ‘tissue type’ in an individual
- Eg HLA B27=expresses serotype 27 at B locus of HLA class I
- EG HLA DR2=expresses serotype 2 at locus 2 of HLA class II
- Strong association between the expression of HLA molecules and some … diseases
- APCs present processed peptide to T cells in combination with highly polymorphic MHC (HLA) molecules
- Encoded by the HLA system on chromosome 6
- Class I: A, B, C
- Class II: DR, DP and DQ
- Complex nomenclature used to describe ‘tissue type’ in an individual
- Eg HLA B27=expresses serotype 27 at B locus of HLA class I
- EG HLA DR2=expresses serotype 2 at locus 2 of HLA class II
- Strong association between the expression of HLA molecules and some autoimmune diseases

T cell-mediated autoimmunity: autoimmune hypothyroidism (Hashimotos thyroiditis)
- Commonest cause of hypothyroidism in industrialised countries
- Particularly … over 30
- Autoimmune destruction of thyroid: organ infiltrated by … and … T cells
- Commonest cause of hypothyroidism in industrialised countries
- Particularly women over 30
- Autoimmune destruction of thyroid: organ infiltrated by CD4 and CD8 T cells

What is the commonest cause of hypothyroidism in industrialised countries?
Hashimotos thyroiditis
Coeliac disease - Appearance
- Normal vs Coeliac disease

…=a state of immunological non-reactivity to an antigen
Tolerance=a state of immunological non-reactivity to an antigen
Antigen segregation (Tolerance) - Mechanism
- … barriers to sequestered antigen (‘immunological privilege’)
- Physical barriers to sequestered antigen (‘immunological privilege’)
Coeliac pathogenesis
- The damage is mediated by T cells; note that antibodies are produced, but do not contribute to tissue damage
- … resolves with strict gluten avoidance
- ..-..% of Europeans express HLA-DQ2 and/ or HLA-DQ8 – not clear which additional genetic/ environmental factors are important in coeliac
- The damage is mediated by T cells; note that antibodies are produced, but do not contribute to tissue damage
- Inflammation resolves with strict gluten avoidance
- 30-50% of Europeans express HLA-DQ2 and/ or HLA-DQ8 – not clear which additional genetic/ environmental factors are important in coeliac

Coeliac disease has characteristics of an … disease, but unusually triggered by an exogenous antigen (…) in pre-disposed individuals
Coeliac disease has characteristics of an autoimmune disease, but unusually triggered by an exogenous antigen (gluten) in pre-disposed individuals


