Defining the Pelvic Region Flashcards
(28 cards)
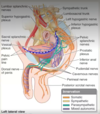
The bony pelvis
_The four bones that together* make the pelvis (os coxa):_
- Two … bones: ilium, ischium and pubis
- …, formed by the fusion of the … sacral vertebrae
- …, formed by the fusion of the …. coccygeal vertebrae
*inc the ligaments
- Two innominate bones: ilium, ischium and pubis
- Sacrum, formed by the fusion of the 5 sacral vertebrae
- Coccyx, formed by the fusion of the 4 coccygeal vertebrae
*inc the ligaments
The articulated pelvis
- The primary joints of the pelvis are the …-… joints and the pubic …
- Weight is transferred from the … skeleton to the … via ligaments to the … during standing and the ischial … during sitting.
- The pubic … is a … disc
- The … joint is a secondary … joint.

- The primary joints of the pelvis are the sacro-iliac joints and the pubic symphysis.
- Weight is transferred from the axial skeleton to the ilia via ligaments to the femurs during standing and the ischial tuberosities during sitting.
- The pubic symphysis is a fibrocartilaginous disc
- The sacroiliac joint is a secondary cartilaginous joint.
What bones are shown? (not specific bones - just the group name)
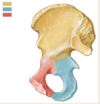
Innominate bones
What bones are shown? (specific - yellow, red blue)
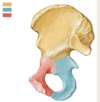
Innominate bones
- Yellow = Ilium
- Red - Pubis
- Blue = Ischium

The pelvic brim
Formed by the:
- Pro… and A.. (wing) of sacrum (White/black line)
- Right + Left li**nea terminalis:
- … line (blue line)
- … line (green line)

Formed by the:
- Promontory and ala (wing) of sacrum (White/black line)
- Right + Left linea terminalis:
- Arcuate line (blue line)
- Pectineal line (green line)

Ligaments of the pelvis
- … : between the sacrum and the ilium, has an anterior and posterior components
- … : between the sacrum to the coccyx
- … : between the ischial spine and the sacrum/coccyx
- … : posterior to the sacrospinous; between the lateral aspect of sacrum + coccyx onto medial margin of ischial tuberosity
- Sacroiliac : between the sacrum and the ilium, has an anterior and posterior components
- Sacrococcygeal : between the sacrum to the coccyx
- Sacrospinous : between the ischial spine and the sacrum/coccyx
- Sacrotuberous : posterior to the sacrospinous; between the lateral aspect of sacrum + coccyx onto medial margin of ischial tuberosity

The perineum
- Refers to the space located at the pelvic … and … to the pelvic diaphragm (ie muscles of the pelvic floor)
- It can be said to describe the narrow region between the …
- Diamond-shaped surface extending from the mons … (in females) to the medial surface of the thighs and posteriorly to the … folds
- A transverse line joining the two ischial tuberosities splits the perineum into two triangles:
- These are …
- The mid point of this line defines the … body
- The … body sees the … of several sphincter and perineal pouch muscles
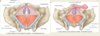
- Refers to the space located at the pelvic outlet and inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (ie muscles of the pelvic floor)
- It can be said to describe the narrow region between the thighs
- Diamond-shaped surface extending from the mons pubis (in females) to the medial surface of the thighs and posteriorly to the gluteal folds
- A transverse line joining the two ischial tuberosities splits the perineum into two triangles:
- Urogenital and anal triangles
- The mid point of this line defines the perineal body
- The perineal body sees the convergence of several sphincter and perineal pouch muscles

The perineal spaces
- The arrangement of the … layers in the pelvis * create two potential spaces- the … and … perineal spaces.
- But- they are not empty spaces the each contain certain structures. *details of which you do not need to know for 203.

- The arrangement of the fascial layers in the pelvis * create two potential spaces- the superficial and deep perineal spaces.
- But- they are not empty spaces the each contain certain structures. *details of which you do not need to know for 203.

Superficial Perineal pouch
- Superficial perineal pouch is a space between the perineal … and the perineal ….
- It contains:*
- Males: … (bulb and crura) of the penis and ischocavernosus and bulbospongiosus
- Females: … and ischocavernosus and bulb of vestibule (bulbospongiosus), greater … gland
- The … in both sexes
- Superficial … perineal muscle
- … Vessels
- Superficial perineal pouch is a space between the perineal fascia and the perineal membrane.
- It contains:*
- Males: Root (bulb and crura) of the penis and ischocavernosus and bulbospongiosus
- Females: Clitoris and ischocavernosus and bulb of vestibule (bulbospongiosus), greater vestibular gland
- Urethra
- Superficial Transverse perineal muscle
- Pudendal Vessels
Deep perineal pouch
- Deep perineal pouch is deep to the perineal membrane.
- It contains:*
- Males: … glands, dorsal neurovasculature of the …
- Females: Dorsal neurovasculature of the …
- Both sexes: Urethra and external urethra …
- Ischioanal … pads
- Deep Transverse perineal muscle- maybe more of a … mass in females- associated with the … body.

- Deep perineal pouch is deep to the perineal membrane.
- It contains:*
- Males: Bulbourethral glands, dorsal neurovasculature of the penis
- Females: Dorsal neurovasculature of the clitoris
- Urethra and external urethra sphincter
- Ischioanal fat pads
- Deep Transverse perineal muscle- maybe more of a smooth mass in females- associated with the perineal body.
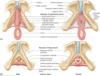
The pelvic cavity (True)
- Borders:
- … - sacrum/coccyx
- … - pubic symphysis
- … - pelvic floor
- … - pelvic brim
- … - obturator internus m
- Contents:
- … organs/tracts
- …
- …

- Borders:
- Posterior - sacrum/coccyx
- Anterior - pubic symphysis
- Inferior - pelvic floor
- Superior - pelvic brim
- Lateral - obturator internus m
- Contents:
- Reproductive organs/tracts
- Bladder
- Rectum
The pelvic musculature
Composed of muscles that:
- Line the wall:
- P…
- O… i…
- Line the floor:
- C…
- Levator ani (…, … and …)
- Line the wall:
- Piriformis
- Obturator internus
- Line the floor:
- Coccygeus
- Levator ani (iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus and puborectalis)

The fibers which form a sling for the rectum are named the …
The fibers which form a sling for the rectum are named the Puborectalis

The … muscle or PC muscle is a hammock-like muscle, found in both sexes, that stretches from the … bone to the … forming the floor of the pelvic cavity and supporting the pelvic organs.
The pubococcygeus muscle or PC muscle is a hammock-like muscle, found in both sexes, that stretches from the pubic bone to the coccyx (tail bone) forming the floor of the pelvic cavity and supporting the pelvic organs.

The levator ani consists of two parts, the inner … muscle and the outer … muscle, both attached to the sacrum at the back but starting from the pubic bones and the ilial bones, respectively, in front.
The levator ani consists of two parts, the inner pubococcygeus muscle and the outer iliococcygeus muscle, both attached to the sacrum at the back but starting from the pubic bones and the ilial bones, respectively, in front.

The … or … is a muscle of the pelvic floor, located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament.
The Coccygeus or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor, located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament.

Blood Supply and Drainage - Pelvic region
-
Arteries
- … division of internal iliac, providing several branches (Superior, vesical, inferior vesical, uterine, vaginal, obturator, internal pudendal, middle rectal, inferior gluteal)
- … division of internal iliac, (Iliolumbar, lateral sacral, superior gluteal)
- …, from abdominal aorta, supplying the gonads
-
Veins
- … iliac , to common iliac veins
- …, to IVC or L renal vein
-
Arteries
- Anterior division of internal iliac, providing several branches (Superior, vesical, inferior vesical, uterine, vaginal, obturator, internal pudendal, middle rectal, inferior gluteal)
- Posterior division of internal iliac, (Iliolumbar, lateral sacral, superior gluteal)
- Gonadal, from abdominal aorta, supplying the gonads
-
Veins
- Internal iliac, to common iliac veins
- Gonadal, to IVC or L renal vein

Nerves in the pelvis
- … plexuses (L4-Co), subdivided into
- … (L4-S4 <=Note: joined by lumbar L4/5)
- … (S4-Co)
- Function as … or …
- e.g. sciatic nerve, sup/inf gluteal, pudendal nerve
- Somatic plexuses (L4-Co), subdivided into
- Lumbosacral (L4-S4 <=Note: joined by lumbar L4/5)
- Coccygeal (S4-Co)
- Function as motor or sensory
- e.g. sciatic nerve, sup/inf gluteal, pudendal nerve
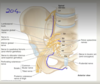
Anterior division of internal iliac:
- … vesical (supplies bladder), ob… (into foramen), … vesical, uterine, vaginal, … rectal (not everyone has one), inferior … (out of pelvis), internal … (out of pelvis - underneath pelvic floor muscles - long course)
- Male = do not have which arteries?
- Superior vesical (supplies bladder), obturator (into foramen), inferior vesical, uterine, vaginal, middle rectal (not everyone has one), inferior gluteal (out of pelvis), internal pedendal (out of pelvis - underneath pelvic floor muscles - long course)
- Male = Do not have Vaginal and uterine

Inferior pedendal artery
- It arises from the … division of … iliac artery
- It runs on the lateral … wall
- It exits the pelvic cavity through the … sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the … region.
- Pathway is very …
- It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery
- It runs on the lateral pelvic wall
- It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region.
- Pathway is very long

Visceral nerves
-
Parasympathetic flow:
- Pelvic … nerves (S2-4)
-
Sympathetic flow:
- … sympathetic trunk
- Superior and Inferior … plexuses
-
Parasympathetic flow:
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-4)
-
Sympathetic flow:
- Sacral sympathetic trunk
- Superior and Inferior hypogastric plexuses

Pudendal nerve
- The pudendal nerve traverses through the … and … foramen to enter the pudendal ….
- It gives rise to the inferior …, … branches, posterior s…/l… branches and … nerve to the penis/clitoris.
- The pudendal nerve traverses through the greater and lesser foramen to enter the pudendal canal.
- It gives rise to the inferior rectal, perineal branches, posterior scrotal/labia branches and dorsal nerve to the penis/clitoris.

… nerves shown

Pudendal