Pharmacological Aspects of Immunology 2 : Biological Therapies Flashcards
Therapies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide … …
- …-… anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- … anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
Therapies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-… anti-… drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic … of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
Therapies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: …, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- … synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- … agents (…): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: Methatrexate, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
Therapies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (…)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (…)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of …
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): …-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - only provide symptom relief
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids)
- Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) - Slow the clinical and radiographic progression of RA
- Synthetic DMARDs: MTX, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs: JAK inhibitors- tofacitinib, baricitinib
- Biologic agents (biologicals): TNF-blockers, Drugs targeting IL-1, IL-6 , B-cells and T-cells
Synthetic DMARDs – Methotrexate (MTX)
- … choice DMARD, the … standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat …
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell …
- Increases … level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces … of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- “Anchor drug” in … therapies
- Reduces inflammation quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of folic acid reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.

- First choice DMARD, the gold standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat cancer
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- “Anchor drug” in combination therapies
- Reduces inflammation quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of folic acid reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.
Synthetic DMARDs – Methotrexate (MTX)
- First choice DMARD, the gold standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat cancer
- Anti… (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- “… drug” in combination therapies
- Reduces … quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from … disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of folic acid reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.

- First choice DMARD, the gold standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat cancer
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- “Anchor drug” in combination therapies
- Reduces inflammation quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of folic acid reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.
Synthetic DMARDs – Methotrexate (MTX)
- First choice DMARD, the gold standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat cancer
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- … adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- v“Anchor drug” in combination therapies
- Reduces inflammation quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of … acid reduces side-effects caused by … acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg … per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.

- First choice DMARD, the gold standard - Introduced in 1947, used in high doses to treat cancer
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- v“Anchor drug” in combination therapies
- Reduces inflammation quickly and keeps it under tight control
- Reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease in people with RA
- Taking supplements of folic acid reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.
What is the first choice DMARD (the gold standard)?
Methotrexate
Methotrexate is used in high doses to treat what?
cancer
Methotrexate:…
- … (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases … level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging …
- Induces … of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
- Antimetabolite (folate analogue), inhibits cell proliferation
- Increases adenosine level (anti-inflammatory)
- Reduces the production of damaging polyamines
- Induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells
Methotrexate is an “… drug” in combination therapies
Methotrexate is an “Anchor drug” in combination therapies
Taking supplements of folic acid whilst taking … reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
Taking supplements of folic acid whilst taking methotrexate reduces side-effects caused by folic acid depletion
What is the dose for methotrexate? (range)
- Administered between 7.5 and 25mg weekly per os or s.c. – at this dose no significant anti-cancer or immunosuppressive effect.
Adverse effects of synthetic DMARDs
- …-… weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – …% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, allergic reactions
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Risk of infections (pneumonia)
- Hepatotoxicity (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, allergic reactions
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Risk of infections (pneumonia)
- Hepatotoxicity (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
Adverse effects of synthetic DMARDs
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of …
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, … reactions
- Headache
- … loss
- Risk of … (e.g…)
- … (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, allergic reactions
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Risk of infections (pneumonia)
- Hepatotoxicity (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
Adverse effects of synthetic DMARDs
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- What are the 9 side effects?
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, allergic reactions
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Risk of infections (pneumonia)
- Hepatotoxicity (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
Adverse effects of synthetic DMARDs
- How many weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms?
- 8-12 weeks treatment required to achieve improvement of symptoms
- MTX – 30% of patients experience adverse effects
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhoea
- Rash, allergic reactions
- Headache
- Hair loss
- Risk of infections (pneumonia)
- Hepatotoxicity (metabolism)
- Kidney toxicity (route of elimination)
Additional side effects of specific synthetic DMARDS:
- … – accumulation of the drug in the eye
- Leflunomide – hypertension
- Hydroxychloroquine – accumulation of the drug in the eye
- Leflunomide – hypertension

Additional side effects of specific synthetic DMARDS:
- Hydroxychloroquine – accumulation of the drug in the …
- Leflunomide – …
- Hydroxychloroquine – accumulation of the drug in the eye
- Leflunomide – hypertension

Targeted synthetic DMARDs
- When are they given instead of synthetic DMARDs?
- In moderate-to-severe active RA in patients who have had an inadequate response to, or are intolerant to one or more DMARDs (as monotherapy or in combination with MTX)
Targeted synthetic DMARDs
- Used in what condition?
- What are the two main ones? (and what do they selectively inhibit?)
- Used in Rheumatoid Arthritis
-
Tofacitinib
- selectively inhibits the JAK1 and JAK3
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis and ulcerative colitis.
- Dosage: 5 mg twice daily per os
-
Baricitinib
- selectively and reversibly inhibits JAK1 and JAK2
- Dosage: 4 mg once daily per os

What does Tofacitinib selectively inhibit?
selectively inhibits the JAK1 and JAK3

What does Baricitinib selectively and reversibly inhibit?
selectively and reversibly inhibits JAK1 and JAK2

Oral … 5 mg twice daily is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis
Oral tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis
Tofacitinib is used for RA, but what else? (2)
psoriatic arthritis and ulcerative colitis
What is the dosage of Tofacitinib?
5 mg twice daily per os
What is the dosage of Baricitinib?
4 mg once daily per os
Adverse effects of Targeted Synthetic DMARDs
- Anaemia, cough, diarrhoea, fatigue, fever, gastrointestinal discomfort, increased risk of infection (which DMARD?)
- Dyslipidaemia, herpes zoster, increased risk of infection, nausea, oropharyngeal pain, thrombocytosis (which DMARD?)
- Anaemia, cough, diarrhoea, fatigue, fever, gastrointestinal discomfort, increased risk of infection (tofacitinib)
- Dyslipidaemia, herpes zoster, increased risk of infection, nausea, oropharyngeal pain, thrombocytosis (baricitinib)
Adverse effects of tofacitinib include … (7)
- Anaemia, cough, diarrhoea, fatigue, fever, gastrointestinal discomfort, increased risk of infection
Adverse effects of baricitinib include… (6)
- Dyslipidaemia, herpes zoster, increased risk of infection, nausea, oropharyngeal pain, thrombocytosis
New era in the treatment of RA – The biologics

- In RA - IL-1 production decreased
- In osteoarthritis, IL-1 production was not changed
- Shows blocking TNF-alpha could reduce the level of IL-1

Central role of TNF in the inflammatory cascade of RA


The anti-TNF-a therapy
- In 1992, Ravinder Maini and his colleagues tested a TNF-a blocker on 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis that was not responding to existing treatments. What were the results?
- In 1992, Ravinder Maini and his colleagues tested a TNF-a blocker on 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis that was not responding to existing treatments. The results were remarkable – nearly every patient had a rapid reduction of pain and fatigue and improved mobility, and the swelling in their joints went down.
- Between 1993 and 1994 researchers from the Kennedy Institute carried out a larger study comparing a TNF-a blocker with a placebo. Almost 80 percent of patients receiving a high dose of the TNF-a blocker responded to treatment, compared to just 8 percent on placebo.
- Further research at the Kennedy Institute in the late 1990s showed that combining TNF-a blockers with MTX made the treatment even more effective.
- TNF blockade, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for RA, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis.
- Anti-TNF drugs have been the biggest pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
The anti-TNF-a therapy
- In 1992, Ravinder Maini and his colleagues tested a TNF-a blocker on 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis that was not responding to existing treatments. The results were remarkable – nearly every patient had a rapid reduction of pain and fatigue and improved mobility, and the swelling in their joints went down.
- Between 1993 and 1994 researchers from the Kennedy Institute carried out a larger study comparing a TNF-a blocker with a placebo. Almost … percent of patients receiving a high dose of the TNF-a blocker responded to treatment, compared to just … percent on placebo.
- Further research at the Kennedy Institute in the late 1990s showed that combining TNF-a blockers with MTX made the treatment even more effective.
- In 1992, Ravinder Maini and his colleagues tested a TNF-a blocker on 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis that was not responding to existing treatments. The results were remarkable – nearly every patient had a rapid reduction of pain and fatigue and improved mobility, and the swelling in their joints went down.
- Between 1993 and 1994 researchers from the Kennedy Institute carried out a larger study comparing a TNF-a blocker with a placebo. Almost 80 percent of patients receiving a high dose of the TNF-a blocker responded to treatment, compared to just 8 percent on placebo.
- Further research at the Kennedy Institute in the late 1990s showed that combining TNF-a blockers with MTX made the treatment even more effective.
- TNF blockade, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for RA, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis.
- Anti-TNF drugs have been the biggest pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
The anti-TNF-a therapy
- TNF …, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for RA, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis.
- …-… drugs have been the … pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
- TNF blockade, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for RA, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis.
- Anti-TNF drugs have been the biggest pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
TNF blockade, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for …, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and …
TNF blockade, both effective and relatively safe, has dramatically changed therapy for RA, Crohn’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis.
…drugs have been the biggest pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
Anti-TNF drugs have been the biggest pharmaceutical drug class with sales exceeding $25 billion per annum.
Canada Gairdner International Award 2014 - what was it for?

The targets of biologic agents in RA
- What are the 4 targets?
- Targets include IL-1, IL-6, T cell and B cell

The biological therapies are administered how?
Protein drugs administered parenterally
The biological therapies
- Biological therapy is recommended if:
- Patient has failed to respond to treatment with at least two standard (synthetic) DMARDs, one of which must be … (unless patient cannot take … for medical reason)
- Patient’s RA disease activity score (DAS 28) is measured as 5.1 or over, on two occasions, one month apart
- Biological therapy is recommended if:
- Patient has failed to respond to treatment with at least two standard (synthetic) DMARDs, one of which must be methotrexate (unless patient cannot take methotrexate for medical reason)
- Patient’s RA disease activity score (DAS 28) is measured as 5.1 or over, on two occasions, one month apart
The biological therapies
- Biological therapy is recommended if:
- Patient has failed to respond to treatment with at least … standard (synthetic) DMARDs, one of which must be MTX (unless patient cannot take MTX for medical reason)
- Patient’s RA disease activity score (DAS 28) is measured as … or over, on two occasions, one month apart
- Biological therapy is recommended if:
- Patient has failed to respond to treatment with at least two standard (synthetic) DMARDs, one of which must be MTX (unless patient cannot take MTX for medical reason)
- Patient’s RA disease activity score (DAS 28) is measured as 5.1 or over, on two occasions, one month apart
Currently licensed biologics for the treatment of RA in the UK
- …-…: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab,
- certolizumab pegol
- Monoclonal antibody against … cells: rituximab
- … cell co-stimulation inhibitor: abatacept
- Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R: tocilizumab, sarilumab
- → Licenced in the US: IL-1R antagonist anakinra
- TNF-blockers: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab,
- certolizumab pegol
- Monoclonal antibody against B cells: rituximab
- T cell co-stimulation inhibitor: abatacept
- Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R: tocilizumab, sarilumab
- → Licenced in the US: IL-1R antagonist anakinra
Currently licensed biologics for the treatment of RA in the UK
- TNF-blockers: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab,
- certolizumab pegol
- Monoclonal antibody against B cells: rituximab
- T cell co-stimulation inhibitor: abatacept
- … antibodies against IL-…R: tocilizumab, sarilumab
- → Licenced in the US: IL-…R antagonist anakinra
- TNF-blockers: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab,
- certolizumab pegol
- Monoclonal antibody against B cells: rituximab
- T cell co-stimulation inhibitor: abatacept
- Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R: tocilizumab, sarilumab
- → Licenced in the US: IL-1R antagonist anakinra
What are the 5 TNF-blockers licensed in the UK?
- infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol
Currently licensed biologics for the treatment of RA in the UK (what 4 types?)
TNF-blockers, Monoclonal antibody against B cells, T cell co-stimulation inhibitor, Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R
TNF-blockers, Monoclonal antibody against B cells, T cell co-stimulation inhibitor, Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R are all currently licensed … for treatment of … in the UK
TNF-blockers, Monoclonal antibody against B cells, T cell co-stimulation inhibitor, Monoclonal antibodies against IL-6R are all currently licensed biologics for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in the UK
Rituximab is a drug known as a … antibody.
Rituximab is a drug known as a monoclonal antibody.
abatacept is a …-cell co-stimulation inhibitor
abatacept is a T-cell co-stimulation inhibitor
The TNF-blockers
- … – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- Etanercept – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Adalimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- … – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Certolizumab pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
- Infliximab – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- Etanercept – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Adalimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Golimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Certolizumab pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
The TNF-blockers
- Infliximab – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- … – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Adalimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Golimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- … pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
- Infliximab – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- Etanercept – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Adalimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Golimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Certolizumab pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
The TNF-blockers
- … – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- Etanercept – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- … – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Golimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Certolizumab pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
- Infliximab – partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-hTNF-a antibody
- Etanercept – soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Adalimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Golimumab – human IgG1 monoclonal anti-TNF-a antibody
- Certolizumab pegol – PEGylated anti-TNF-a monoclonal antibody fragment
When TNF-blockers are combined with MTX, they give excellent …. protection
When TNF-blockers are combined with MTX, they give excellent joint protection
When TNF-blockers are combined with …, they give excellent joint protection
When TNF-blockers are combined with methotrexate, they give excellent joint protection
When …-blockers are combined with MTX, they give excellent joint protection
When TNF-blockers are combined with MTX, they give excellent joint protection
Infliximab – The chimeric antibody
- Partially humanized … monoclonal anti-human TNF-… antibody – first anti-TNF biologic
- Neutralizes free, membrane and receptor-bound TNF-… → antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Also used for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis
- NICE only approves infliximab, if combined with …
- Administered as … infusion 3mg per kg of body weight, repeated 2 weeks and 6 weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.
- Partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-human TNF-a antibody – first anti-TNF biologic
- Neutralizes free, membrane and receptor-bound TNF-a → antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Also used for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis
- NICE only approves infliximab, if combined with MTX
- Administered as intravenous infusion 3mg per kg of body weight, repeated 2 weeks and 6 weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.

Infliximab – The chimeric antibody
- Partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-human TNF-a antibody – first anti-TNF biologic
- Neutralizes free, membrane and receptor-bound TNF-a → antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Also used for the treatment of … disease, … colitis, plaque …, ankylosing …
- … only approves infliximab, if combined with MTX
- Administered as intravenous infusion …mg per kg of body weight, repeated 2 weeks and 6 weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.
- Partially humanized mouse monoclonal anti-human TNF-a antibody – first anti-TNF biologic
- Neutralizes free, membrane and receptor-bound TNF-a → antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
- Also used for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis
- NICE only approves infliximab, if combined with MTX
- Administered as intravenous infusion 3mg per kg of body weight, repeated 2 weeks and 6 weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.

Infliximab dosage - Administered as intravenous infusion 3mg per kg of body weight, repeated … weeks and … weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.
Infliximab dosage - Administered as intravenous infusion 3mg per kg of body weight, repeated 2 weeks and 6 weeks after the first infusion, then every 8 weeks.
Etanercept – The soluble TNF receptor dimer
- … domain of the hu p75 TNFR fused with the Fc domain of hu Ig…
- Binds free and membrane-bound TNF, reducing the accessible TNF in … → ADCC
- Also used for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- 25mg twice a week, or 50mg weekly by subcutaneous injection
- Extracellular domain of the hu p75 TNFR fused with the Fc domain of hu IgG1
- Binds free and membrane-bound TNF, reducing the accessible TNF in RA → ADCC
- Also used for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- 25mg twice a week, or 50mg weekly by subcutaneous injection

Etanercept – The soluble TNF receptor dimer
- Extracellular domain of the hu p75 TNFR fused with the Fc domain of hu IgG1
- Binds free and membrane-bound TNF, reducing the accessible TNF in RA → ADCC
- Also used for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- …mg twice a week, or …mg weekly by subcutaneous injection
- Binds both TNF… and TNF…
- Extracellular domain of the hu p75 TNFR fused with the Fc domain of hu IgG1
- Binds free and membrane-bound TNF, reducing the accessible TNF in RA → ADCC
- Also used for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- 25mg twice a week, or 50mg weekly by subcutaneous injection
- Binds both TNF-alpha and TNF-beta

Adalimumab, golimumab – The fully human anti-TNF-a mAbs
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease
- … mg by subcutaneous injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with MTX
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Longer half-life
- … mg monthly by subcutaneous injection
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease
- 40 mg by subcutaneous injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with MTX
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Longer half-life
- 50 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection
Adalimumab, golimumab – The fully human anti-TNF-a mAbs
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, … disease
- 40 mg by subcutaneous injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with …
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- … half-life
- 50 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease
- 40 mg by subcutaneous injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with MTX
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Longer half-life
- 50 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection
Adalimumab, golimumab – The fully human anti-TNF-a mAbs
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, … arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease
- 40 mg by … injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with MTX
- Also used in … arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Longer half-life
- 50 mg monthly by … injection
- Adalimumab
- Also used in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease
- 40 mg by subcutaneous injection every other week
- Golimumab
- In combination with MTX
- Also used in psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
- Longer half-life
- 50 mg monthly by subcutaneous injection
What are the names of the fully human anti-TNF-a mAbs? (monoclonal antibodies)

What is the name of the soluble TNF receptor dimer?
Etanercept

What is the name for the chimeric antibody? (TNF-blocker licensed for use)
infliximab

Certolizumab pegol – The Fab’ fragment
- … Fab’ fragment of humanized anti-TNF-a mAb – no … portion
- Also used for the treatment of Chron’s disease
- 400 mg by subcutaneous injection at weeks 0, 2 and 4 (given as two injections of 200 mg), and then 200 mg every other week thereafter
- PEGylated Fab’ fragment of humanized anti-TNF-a mAb – no Fc portion
- Also used for the treatment of Chron’s disease
- 400 mg by subcutaneous injection at weeks 0, 2 and 4 (given as two injections of 200 mg), and then 200 mg every other week thereafter

Certolizumab pegol – The Fab’ fragment
- PEGylated Fab’ fragment of humanized anti-TNF-a mAb – no Fc portion
- Also used for the treatment of … disease
- … mg by subcutaneous injection at weeks 0, 2 and 4 (given as two injections of 200 mg), and then 200 mg every other week thereafter
- PEGylated Fab’ fragment of humanized anti-TNF-a mAb – no Fc portion
- Also used for the treatment of Chron’s disease
- 400 mg by subcutaneous injection at weeks 0, 2 and 4 (given as two injections of 200 mg), and then 200 mg every other week thereafter

Clinical and functional efficacy following 26 weeks of adalimumab treatment in combination with different doses of MTX
- Figure shows combination of Adalimuma with MTX
- Higher dose of MTX combined with Adalimumab = … efficacy for RA
- Figure shows combination of Adalimuma with MTX
- Higher dose of MTX combined with Adalimumab = higher efficacy for RA

Anti-TNF therapy: Considerations, side effects
- Patients screened before starting treatment to exclude an increased risk of side effects, in particular for a past history of … , multiple …, recurrent infection, leg ulcers and a past history of …
- … X-ray to be taken to exclude signs of previous … and to exclude signs of heart failure
- Increased risk of infections, reactivation of …
- Live vaccines, against e.g. yellow fever or polio, should be avoided
- Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as 10 years.
- Patients can stay on the drug for as long as they continue to respond well to it.
- Patients screened before starting treatment to exclude an increased risk of side effects, in particular for a past history of tuberculosis (TB), multiple sclerosis, recurrent infection, leg ulcers and a past history of cancer
- Chest X-ray to be taken to exclude signs of previous TB and to exclude signs of heart failure
- Increased risk of infections, reactivation of TB
- Live vaccines, against e.g. yellow fever or polio, should be avoided
- Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as 10 years.
- Patients can stay on the drug for as long as they continue to respond well to it.
Anti-TNF therapy: Considerations, side effects
- Patients screened before starting treatment to exclude an increased risk of side effects, in particular for a past history of tuberculosis (TB), multiple sclerosis, recurrent infection, leg ulcers and a past history of cancer
- Chest X-ray to be taken to exclude signs of previous TB and to exclude signs of heart failure
- Increased risk of …, … of TB
- … vaccines, against e.g. yellow fever or polio, should be avoided
- Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as … years.
- Patients can stay on the drug for as long as they continue to respond well to it.
- Patients screened before starting treatment to exclude an increased risk of side effects, in particular for a past history of tuberculosis (TB), multiple sclerosis, recurrent infection, leg ulcers and a past history of cancer
- Chest X-ray to be taken to exclude signs of previous TB and to exclude signs of heart failure
- Increased risk of infections, reactivation of TB
- Live vaccines, against e.g. yellow fever or polio, should be avoided
- Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as 10 years.
- Patients can stay on the drug for as long as they continue to respond well to it.
Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as … years.
- Anti-TNF therapy can be administered for as long as 10 years.
- Patients can stay on the drug for as long as they continue to respond well to it.
Failure of anti-TNF treatment – use of other biologics
- Some patients may have
- an … clinical response
- lose their … over time
- experience … side effects
- have … issues
- precluding the use of anti-TNF medication.
- It is estimated that 30% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus MTX.
- Some patients may have
- an inadequate clinical response
- lose their responsiveness over time
- experience unacceptable side effects
- have medical issues
- precluding the use of anti-TNF medication.
- It is estimated that 30% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus MTX.
Failure of anti-TNF treatment – use of other biologics
- Some patients may have
- an inadequate clinical response
- lose their responsiveness over time
- experience unacceptable side effects
- have medical issues
- precluding the use of anti-TNF medication.
- It is estimated that …% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus MTX.
- Some patients may have
- an inadequate clinical response
- lose their responsiveness over time
- experience unacceptable side effects
- have medical issues
- precluding the use of anti-TNF medication.
- It is estimated that 30% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus MTX.
It is estimated that 30% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus …
It is estimated that 30% of RA patients fail to respond adequately to a combination of a TNF inhibitor plus MTX.
Rituximab – The B-cell depleting agent
- Partially … anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab … B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)… mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).

- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).
Rituximab – The B-cell depleting agent
- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) …
- Also used for the treatment of …
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).

- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).
Rituximab – The B-cell depleting agent
- Partially humanized anti-… mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated … (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An … infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).

- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).
Rituximab – The B-cell depleting agent
- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) …-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions … weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for … weeks).

- Partially humanized anti-CD20 mAb
- Rituximab opsonized B-cells are attacked and killed by three mechanisms:
- 1)Complement mediated cytotoxicity
- 2-3) Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) – FcgR or CR mediated opsonic phagocytosis
- 4) Apoptosis
- Also used for the treatment of SLE
- An intravenous infusion (1 g) on two occasions two weeks apart (although some centres give smaller weekly injections for four weeks).
Abatacept – The T-cell co-stimulation inhibitor
- CTLA-4/ hu IgG1 soluble receptor fusion protein
- Competitive inhibitor of CD…
- Increases … for T-cell activation
- Suppresses the … of synovial recirculating T cells
- Reduces the level of inflammatory mediators
- Intravenous infusion of 500 mg, 750 mg or 1000 mg (depending on patient’s weight) over 30 to 60 minutes. After the first dose, it is given two weeks later, then two weeks after that, then monthly thereafter.
- CTLA-4/ hu IgG1 soluble receptor fusion protein
- Competitive inhibitor of CD28
- Increases threshold for T-cell activation
- Suppresses the proliferation of synovial recirculating T cells
- Reduces the level of inflammatory mediators
- Intravenous infusion of 500 mg, 750 mg or 1000 mg (depending on patient’s weight) over 30 to 60 minutes. After the first dose, it is given two weeks later, then two weeks after that, then monthly thereafter.

Abatacept – The T-cell co-stimulation inhibitor
- …-4/ hu Ig… soluble receptor fusion protein
- … inhibitor of CD28
- Increases threshold for T-cell activation
- Suppresses the proliferation of synovial recirculating T cells
- … the level of inflammatory mediators
- Intravenous infusion of 500 mg, 750 mg or 1000 mg (depending on patient’s weight) over 30 to 60 minutes. After the first dose, it is given two weeks later, then two weeks after that, then monthly thereafter.
- CTLA-4/ hu IgG1 soluble receptor fusion protein
- Competitive inhibitor of CD28
- Increases threshold for T-cell activation
- Suppresses the proliferation of synovial recirculating T cells
- Reduces the level of inflammatory mediators
- Intravenous infusion of 500 mg, 750 mg or 1000 mg (depending on patient’s weight) over 30 to 60 minutes. After the first dose, it is given two weeks later, then two weeks after that, then monthly thereafter.

Abatacept is a competitive inhibitor of CD…
Abatacept is a competitive inhibitor of CD28
Abatacept is a …-cell co-… inhibitor
Abatacept is a T-cell co-stimulation inhibitor (CTLA-4/ hu IgG1 soluble receptor fusion protein)
CTLA4-Ig fusion protein (IgG1) (a…)
CTLA4-Ig fusion protein (IgG1) (abatacept)
Tocilizumab and sarilumab – The IL-6R inhibitors
- Tocilizumab: … anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody
- Also used in systemic juvenile idiopathic …
- Intravenous infusion 8 mg/kg of body weight
- Sarilumab: fully … monoclonal antibody against IL-6Ra
- 200 mg once every two weeks, administered as a subcutaneous injection
- Tocilizumab: humanized anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody
- Also used in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Intravenous infusion 8 mg/kg of body weight
- Sarilumab: fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Ra
- 200 mg once every two weeks, administered as a subcutaneous injection

Tocilizumab and sarilumab – The IL-6R inhibitors
- Tocilizumab: humanized anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody
- Also used in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Intravenous infusion … mg/kg of body weight
- Sarilumab: fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Ra
- … mg once every two weeks, administered as a subcutaneous injection
- Tocilizumab: humanized anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody
- Also used in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Intravenous infusion 8 mg/kg of body weight
- Sarilumab: fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Ra
- 200 mg once every two weeks, administered as a subcutaneous injection

Tocilizumab and sarilumab are the IL-… inhibitors
Tocilizumab and sarilumab are the IL-6R inhibitors
Tocilizumab and … have been authorized for UK patients with critical COVID-19 infection.
Tocilizumab and sarilumab have been authorized for UK patients with critical COVID-19 infection.
Anakinra – The IL-1R antagonist
- … IL-1ra
- Differs from native human IL-1ra: it has the addition of a single … residue at its amino terminus
- In RA:
- Reduces bone …
- Decreases osteoclast production
- Blocks IL-1-induced MMP release from synovial cells
- Not used in the UK to treat RA, but licensed in the US
-
Recombinant IL-1ra
- Differs from native human IL-1ra: it has the addition of a single methionine residue at its amino terminus
- In RA:
- Reduces bone erosion
- Decreases osteoclast production
- Blocks IL-1-induced MMP release from synovial cells
- Not used in the UK to treat RA, but licensed in the US

Anakinra – The IL-1R antagonist
- Recombinant IL-1ra
- Differs from native human IL-1ra: it has the addition of a single methionine residue at its amino terminus
- In RA:
- Reduces bone erosion
- … osteoclast production
- … IL-1-induced MMP release from synovial cells
- Not used in the … to treat RA, but licensed in the …
- Recombinant IL-1ra
- Differs from native human IL-1ra: it has the addition of a single methionine residue at its amino terminus
- In RA:
- Reduces bone erosion
- Decreases osteoclast production
- Blocks IL-1-induced MMP release from synovial cells
- Not used in the UK to treat RA, but licensed in the US

Adverse effects of biological therapies
- Increased risk of infections:
- … respiratory tract infections (nasopharyngitis)
- …
- Urinary tract infections
- It is recommended to receive influenza and pneumococcal vaccines before embarking on biological therapy
- Avoid … vaccines
- Nausea
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Allergic reactions
- Contraindicated in … and while … … (rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, abatacept, anakinra)
- Increased risk of infections:
- Upper respiratory tract infections (nasopharyngitis)
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections
- It is recommended to receive influenza and pneumococcal vaccines before embarking on biological therapy
- Avoid live vaccines
- Nausea
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Allergic reactions
- Contraindicated in pregnancy and while breast feeding (rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, abatacept, anakinra)
Adverse effects of biological therapies
- Increased risk of …
- N…
- H..
- …tension
- … reactions
- Contraindicated in pregnancy and while breast feeding (rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, abatacept, anakinra)
- Increased risk of infections:
- Upper respiratory tract infections (nasopharyngitis)
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections
- It is recommended to receive influenza and pneumococcal vaccines before embarking on biological therapy
- Avoid live vaccines
- Upper respiratory tract infections (nasopharyngitis)
- Nausea
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Allergic reactions
- Contraindicated in pregnancy and while breast feeding (rituximab, tocilizumab, sarilumab, abatacept, anakinra)
Summary of the biologics in RA

Summary of the biologics in RA

Summary of the biologics in RA
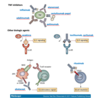
Summary of the biologics in RA

Summary of the biologics in RA
- Fill in the blanks




