Physiology of Puberty COPY Flashcards
1
Q
Define Puberty
A
- The stage of physical maturation in which an individual becomes physiologically capable of pro-creation (sexual reproduction)
2
Q
Physical Changes in Puberty
- … spurt
- … … characteristics
- M…/s…
A
- Growth spurt
- Secondary sex characteristics
- Menarche/spermatogenesis
3
Q
Physical Changes in Girls
- … …
- 8 - 14 yrs
- 6 - 10 cm / yr peak
- 2.5 yrs duration
- … … (…)
- 8 - 13 yrs ( 11 yrs )
- Usually the first sign
- … … (…)
- 9 - 13 yrs
- 1st Pubertal Sign in …%
- … … (…)
- 9.5 - 15 yrs
- May follow Menarche
- … (…)
- 10 - 16 yrs ( 13 yrs )
A
-
GROWTH SPURT
- 8 - 14 yrs
- 6 - 10 cm / yr peak
- 2.5 yrs duration
-
BREAST GROWTH (Thelarche)
- 8 - 13 yrs ( 11 yrs )
- Usually the first sign
-
PUBIC HAIR (Pubarche)
- 9 - 13 yrs
- 1st Pubertal Sign in 25%
-
AXILLARY HAIR (Adrenarche)
- 9.5 - 15 yrs
- May fllow Menarche
-
MENSTRUATION (Menarche)
- 10 - 16 yrs ( 13 yrs )
4
Q
Endocrine Changes in Puberty
- …-…-… synchrony – established in … life
- Until … – neural mechanisms suppress … release
- At …-… yrs – pulsatile nocturnal … release

A
- H-P-G synchrony – established in fetal life
- Until puberty – neural mechanisms suppress GnRH release
- At 6-9 yrs – pulsatile nocturnal GnRH release
5
Q
Endocrine Changes in Puberty
- Pulsatile … release (nocturnal) every … - … min - 6 to 9 years
- increased … leads to increased … and increased …
- …/… become sensitized to the effects of these
- Final phase: development of …/… feedback mechanism
- … stimulates the adrenals – … & … hair
A
- Pulsatile GnRH release (nocturnal) every 90-120 min - 6 to 9 y
- increased GnRH leads to increased FSH and increased LH
- Ovaries/testes become sensitized to the effects of FSH and LH
- Final phase: development of positive/negative feedback mechanism
- ACTH stimulates the adrenals – Pubic & Axillary hair
6
Q
Testes
- Production of … (…)
- … cells under FSH control
- Production of … (Testosterone)
- … cells under LH control
- …% from testes, …% from adrenals
- Testosterone in blood – converted to … in the target organs
A
- Production of gametes (sperms)
- Sertoli cells under FSH control
- Production of androgens (Testosterone)
- Leydig cells under LH control
- 95% from testes, 5% from adrenals
- Testosterone in blood – converted to DHT in the target organs
7
Q
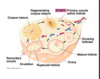
The Ovarian Cycle
- … phase
- Initially E rises (…) with LH surge in …
- … occurs
- … phase
- … feedback after ovulation
- No further … in the same cycle
A
- Follicular phase
- Initially E rises (FSH) with LH surge in mid cycle
- Ovulation occurs
- Luteal phase
- Negative feedback after ovulation
- No further ovulation in the same cycle

8
Q
What is this showing?

A
Endometrial cycle
9
Q
Age of Menarche
- Related to general health, genetic and nutritional factors
- Mean age is … at a rate of … months per decade
- Mean age in 1840 = … y; 1990 = … y
- One in … girls now reaches menarche while at primary school
- Body … and % … is also important
- Mean weight at menarche is …kg
- …-…% fat
- …, patients with … – late onset
A
- Related to general health, genetic and nutritional factors
- Mean age is falling at a rate of 4 months per decade
- Mean age in 1840 = 16.5 y; 1990 = 12.8 y
- One in 8 girls now reaches menarche while at primary school
-
Body weight and % fat is also important
- Mean weight at menarche is 47.8kg
- 16-24% fat
- Athletes, patients with anorexia – late onset
10
Q
Adrenarche
- … … – responsible for axillary and pubic hair
- … stimulates zona … of adrenal cortex
- DHEAS & Androstenedione
- Girls – starts by …, adequate levels by …
- Boys – starts by …, adequate levels by …
A
- Adrenal androgens – responsible for axillary and pubic hair
- ACTH stimulates zona reticularis of adrenal cortex
- DHEAS & Androstenedione
- Girls – starts by 6, adequate levels by 8
- Boys – starts by 8, adequate levels by 10
11
Q
Define Adrenarche
- Adrenarche refers to the time during puberty when the adrenal glands increase their production and secretion of adrenal …
- Plasma concentrations of dehydroepiandrosterone (…) and DHEA-sulfate(s), the most important adrenal androgens, begin to increase in children by approximately … to …years.
- However, the signs of adrenarche, such as … and … … development, a…, and body …, do not typically occur until … to ….
A
- Adrenarche refers to the time during puberty when the adrenal glands increase their production and secretion of adrenal androgens. Plasma concentrations of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA-sulfate(s), the most important adrenal androgens, begin to increase in children by approximately 6 to 8 years. However, the signs of adrenarche, such as pubic and axillary hair development, acne, and body odor, do not typically occur until early to midpuberty.
12
Q
Chronological Order of Puberty - Girls
- … ….
- … development
- … hair
- … hair
- …
A
- Growth spurt
- Breast development
- Pubic hair
- Axillary hair
- Menarche
13
Q
Chronological Order of Puberty - Boys
- … volume
- … length
- … hair
- … …
- … / … hair
- … voice
A
- Testicular volume
- Penile length
- Pubic hair
- Growth spurt
- Axillary / Facial hair
- Deep voice
14
Q
For each row, what is the subtitle?

A
- Beginning of puberty
- Growth Spurt
- Years of Puberty
- Menarche/Voice Deepening

15
Q
Disorders of Puberty - Early or Precocious
- Girls – under … yrs
- Boys – under … yrs
A
- Girls – under 8 yrs
- Boys – under 9 yrs
16
Q
Disorders of Puberty - Delayed
- Girls – over … yrs
- Boys – over … yrs
A
- Girls – over 14 yrs
- Boys – over 14 yrs
17
Q
Precocious Puberty
- … or … puberty
- Presence of true pubertal features at an … & … age
- Central or True precocious puberty
- … dependent
- Peripheral or Pseudo-precocious puberty
- … independent
- Central or True precocious puberty
- Normal variants
- … T…
- … A…
A
- Early or Premature puberty
- Presence of true pubertal features at an young & inappropriate age
- Central or True precocious puberty
- Gonadotrophin dependent
- Peripheral or Pseudo-precocious puberty
- Gonadotrophin independent
- Central or True precocious puberty
- Normal variants
- Premature Thelarche
- Premature Adrenarche
18
Q
Concerns raised by early onset puberty
- Possible underlying sinister cause
- … – up to …%
- … & …-… upheaval at an inappropriately young age
- Early cessation of … leading to decreased final … …
A
- Possible underlying sinister cause
- Boys – upto 80%
- Emotional & pyscho-social upheaval at an inappropriately young age
- Early cessation of growth leading to decreased final adult height
19
Q
What is the Diagnosis?
-
Emileigh, 14 months
- Blood clots in nappy
- Bilat breast buds
- Ht & Wt >97th centile
- LH 2.2, FSH 3.2,
- 17β estradiol 432
- Uterus – enlarged
- Bone age – 2.8 yrs
- MRI scan shown

A
- Hypothalamic Hamartoma - premature true puberty - LH and FSH should be undetectable, uterus enlarged, blood clots in nappy, bones advanced (oestrogen), Breast buds

20
Q
Precocious Puberty - Central (testing / treatment)
- Long acting … analog therapy
- Sustained supra-physiological … levels
- Paradoxical cessation of … release
- Stops further … …
- Pubertal progression resumes when treatment stopped (at …-… yrs)
A
- Long acting LHRH analog therapy
- Sustained supra-physiological LHRH levels
- Paradoxical cessation of gonadotrophin release
- Stops further pubertal progression
- Pubertal progression resumes when treatment stopped (at 10-12 yrs)
21
Q
Normal Variants - Precocious Puberty
- Premature …
- Isolated … development
- Usually seen in children
- Premature …
- Isolated … … development
- Caution: first sign of … in some
A
- Premature thelarche
- Isolated breast development
- Usually seen in children <2-3 yrs of age
- Premature adrenarche
- Isolated pubic hair development
- Caution: first sign of puberty in some
22
Q
Pseudo-precocious puberty - Females / Males
-
Females:
- Iso-sexual or feminising
- Causes - MAS - stands for… , O…/A…
- Hetero-sexual or masculinising
- C.., O../A…
- Iso-sexual or feminising
-
Males:
- Iso-sexual or masculinising
- Causes - C…, A…l/L… cell …
- Hetero-sexual or feminising
- A…
- Iso-sexual or masculinising
A
- Females:
- Iso-sexual or feminising
- Causes - MAS - stands for McCune-Albright syndrome , Ovarian/Adrenal
- Hetero-sexual or masculinising
- CAH, Ovarian/Adrenal
- Hetero-sexual or masculinising
- CAH, Ovarian/Adrenal
- Iso-sexual or feminising
- Males:
- Iso-sexual or masculinising
- Causes - CAH, Adrenal/Leydig cell tumour
- Hetero-sexual or feminising
- Adrenal
- Iso-sexual or masculinising
23
Q
What is the diagnosis?
- Mairna, 6 yrs
- Obese
- Pubic hair stage 2
- No breast bud
- LH <1, FSH 1.4,
- 17β estradiol 32
- Steroid profile
A
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
24
Q
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal … disorders characterized by impaired … synthesis.
- It results from the deficiency of one of the … enzymes required for the synthesis of … in the adrenal ….
A
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis.
- It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex.

25
This is showing ... biosynthesis

**Steroid biosynthesis**
26
27
_Delayed Puberty_
* Absence of ... pubertal onset at an ... age
* Not necessarily lack of ... in a ...
* ...-files – very important
* Normal ...
* Constitutional ... & ... delay
* Absence of **true** pubertal onset at an **appropriate** age
* Not necessarily lack of **periods** in a **girl**
* **X**-files – very important
* Normal **variant**
* Constitutional **growth & pubertal** delay
28
_Concerns raised by delay in Puberty_
* Possible sinister underlying cause
* ... that puberty will never occur
* Emotional and psychosocial upset of ..., specially when associated with ... stature
* Long term sequelae: Reduced ... ...
* Possible sinister underlying cause
* **Fear** that puberty will never occur
* Emotional and psychosocial upset of **immaturity**, specially when associated with **short** stature
* Long term sequelae: Reduced **bone mineralization**
29
_What is the diagnosis?_
* Steven, 16 yrs
* No pubertal progress
* Learning difficulties
* Tall, 98th centile
* PH-2, G-2, TV-6ml
* LH 12, FSH 16, T 40
* Bone age – 14.5 yrs
**Klinefelter Syndrome**

30
_Klinefelter Syndrome_
* 1 in ... ... infants
* 47 ... / Multiple ...
* ... problems
* ... deficiency
* ...spermia / ...
* (Micro ... -\> Sex change)
* Lifelong ... replacement therapy
* 1 in **1000 male** infants
* 47 **XXY** / Multiple **X**
* **Behavioural** problems
* **Androgen** deficiency
* **Azoospermia / Infertility**
* (Micro **genitalia** -\> Sex change)
* Lifelong **testosterone** replacement therapy
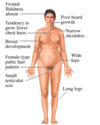
31
_What is the diagnosis?_
* Rosie, 12 yrs
* Short Stature
* No pubertal onset
* Recurrent ear infections
* Increased carrying angle
* Widely spaced nipples
* LH 56, FSH 95,
* 17β estradiol 45
* Karyotype
**Turner Syndrome**

32
_Turner Syndrome_
* 1 in ... live ... births
* Triad - ... stature, ... gonads, primary ...
* ... features – Webbing of neck, cubitus valgus
* ... of aorta, horse shoe ...
* Early clue - L...
* Surprisingly ... !!!
* Turner ...

* 1 in **2000** live **female** births
* Triad - **Short** stature, **streak** gonads, primary **amenorrhoea**
* **Dysmorphic** features – Webbing of neck, cubitus valgus
* **Coarctation** of aorta, horse shoe **kidneys**
* Early clue - **Lymphedema**
* Surprisingly **normal**!!!
* Turner **Mosaic**
33
_Turner Syndrome_
* Exclude co-existing ... anomalies
* ... Hormone therapy
* Pubertal induction + ongoing ...
* Active monitoring to detect ...
* Assisted ...
* Exclude co-existing **congenital** anomalies
* **Growth** Hormone therapy
* Pubertal induction + ongoing **HRT**
* Active monitoring to detect **co-morbidities**
* Assisted **conception**
34
_What is the diagnosis?_
* James, 15 yrs
* Absent smell sensation
* PH-1, G-1, AxH-1, TV-2ml each
* LH \<1, FSH 1.2, T 0.8
* LHRH stimulation test – peak LH remained \<1
* HCG stimulation test – min. increase in T
* MRI scan – Normal
* Kallman gene analysis – Negative
* Lifelong Testosterone replacement therapy
**Gonadotrophin deficiency**
35
_Normal Variant - Delayed puberty_
* Constitutional delayed growth & puberty
* More common in ...
* ... & ... in school days
* ... onset of puberty
* ... age delayed slightly
* ... history – often present
* Normal ... ...
* Pubertal ... – sometimes necessary
* Constitutional delayed growth & puberty
* More common in **boys**
* **Small & Short** in school days
* Late onset of **puberty**
* **Bone age** delayed slightly
* **Family** history – often present
* **Normal adult height**
* Pubertal **induction** – sometimes necessary


