Multi-system Autoimmune Disease Flashcards
… are forms of arthritis that usually strike the bones in your spine and nearby joints.
Spondyloarthropathies are forms of arthritis that usually strike the bones in your spine and nearby joints.
Spondyloarthropathies types
- … spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- … Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
-
Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS

Spondyloarthropathies types
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- … Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is …
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS

Spondyloarthropathies types
- … spondylitis
- … Arthropathy
- … Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark … involvement is UVEITIS
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic Arthropathy
- Reactive Arthropathy
- Intestinal Arthropathy
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Hallmark ocular involvement is UVEITIS
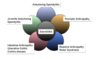
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly … limb, asymmetric
- E..
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant … aggregation
- Association with HLA-…
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, asymmetric
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with HLA-B27
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, …
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic …
- Absence of … factor / anti …
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior …)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with …-B27
- Pattern of peripheral arthritis: predominantly lower limb, asymmetric
- Enthesitis
- Tendency to radiographic sacroiliitis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor / anti CCP
- Extra-articular features characteristic of the group (such as anterior uveitis)
- Significant familial aggregation
- Association with HLA-B27
… is inflammation of the …, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone
Enthesitis is inflammation of the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments insert into the bone
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than … years
- … onset
- Improvement with …
- No improvement with …
- … pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- … onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- E…
- … history
- Uveitis
- … arthritis
- Response to …
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
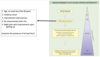
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least … of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- E…
- family history
- U…
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to …
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Disease Probability
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than … years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with …
- No improvement with …
- Night pain with … upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs
- Chronic back pain - ‘inflammatory’ (requires the presence of at least four of the following)
- Age at onset less than 40 years
- Insidious onset
- Improvement with exercise
- No improvement with rest
- Night pain with improvement upon getting up
- Enthesitis
- family history
- Uveitis
- Asymmetic arthritis
- Response to NSAIDs

Imaging for Ankylosing Spondylitis diagnosis
Sacroiliac joint X-ray, if normal or equivocal, then CT or MRI, or HLA-B27 test
In patients with over … months back pain, with/without peripheral manifestations and age at onset 1 SpA feature or HLA-… + plus >2 other SpA features
In patients with over 3 months back pain, with/without peripheral manifestations and age at onset <45 years - Sacroiliitis on imaging plus >1 SpA feature or HLA-B27 + plus >2 other SpA features

Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects … adults
- Peak onset between …-… yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*

Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately ..-..*
- Greek ‘ankylos‘- bent/crooked (fused) - ‘spondylos‘-a spinal vertebra
- Characteristically affects young adults
- Peak onset between 20-30 yrs
- Male:female - approximately 3:1*

Examining tenderness over sacroiliac joint

… test is classically used to determine if there is a decrease in lumbar spine range of motion (flexion), most commonly as a result of ankylosing spondylitis.
Schober’s test is classically used to determine if there is a decrease in lumbar spine range of motion (flexion), most commonly as a result of ankylosing spondylitis.
For both versions of the test, an increase of less than 5cm is a positive test and may indicate ankylosing spondylitis (AS).

Positive Schober’s Test
Less than 5cm increase in length with forward flexion: Decreased lumbar spine range of motion, ankylosing spondylitis

The … to Wall Distance is a routine clinical test for thoracic kyphosis that has been in use for many years
The Occiput to Wall Distance is a routine clinical test for thoracic kyphosis that has been in use for many years

Ankylosis of spine
on right

Ankylosed sacroiliac joints

Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ …%).
- … pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal …
- Hip and Shoulder pain- … arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- … … pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior …
- Limited spinal mobility
- … and … pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited … mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- E…
- Constitutional features- … and …. Disturbed …, caused by back or joint pain at …, may contribute to …
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Ankylosing Spondylitis - Clinical features
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ ….%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the … …
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral … -Acute … or … Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
- Low back pain - Often the first symptom (in ~ 75%).
- Buttock pain - indicative of SI involvement. Often poorly localised and may be referred to the posterior thigh.
- Limited spinal mobility
- Hip and Shoulder pain- girdle arthritis
- Peripheral arthritis -Acute monoarthritis or oligoarthritis Mostly non-erosive and non-destructive.
- Enthesitis.
- Constitutional features- fatigue and malaise. Disturbed sleep, caused by back or joint pain at night, may contribute to fatigue
Other organ involvement - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Anterior … (iritis) – 40%
- … tendonitis (enthesitis)
- Aortic … (4%)
- Apical lung … (1.5%)
- A-V conduction defects (rare)
- Amyloidosis (rare)
- Anterior uveitis (iritis) – 40%
- Achillies tendonitis (enthesitis)
- Aortic regurgitation (4%)
- Apical lung fibrosis (1.5%)
- A-V conduction defects (rare)
- Amyloidosis (rare)
Other organ involvement - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- … uveitis (iritis) – 40%
- Achillies … (enthesitis)
- … regurgitation (4%)
- Apical lung fibrosis (1.5%)
- A-V … defects (rare)
- …dosis (rare)
- Anterior uveitis (iritis) – 40%
- Achillies tendonitis (enthesitis)
- Aortic regurgitation (4%)
- Apical lung fibrosis (1.5%)
- A-V conduction defects (rare)
- Amyloidosis (rare)
Association of HLA-B27 and Spondyloarthropathies
general healthy can be positive for HLA-B27 - note

How is it diagnosed? - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- History
- Clinical examination
- Blood test (not diagnostic): ESR, …, Anaemia, HLA …
- Radiological:
- …- pelvis (SI joints and hips) and spine
- …- more sensitive and picks up changes early
- GOALS OF THERAPY:
- Symptomatic relief -Eliminate/reduce pain and stiffness.
- Restore/preserve function
- Prevent … damage
- Prevent … … - to maintain spinal mobility, and prevent development of spinal deformities
- Minimise extra-spinal and extra-articular manifestation
- History
- Clinical examination
- Blood test (not diagnostic): ESR, CRP, Anaemia, HLA B27
- Radiological:
- X-rays- pelvis (SI joints and hips) and spine
- MRI- more sensitive and picks up changes early
- GOALS OF THERAPY:
- Symptomatic relief -Eliminate/reduce pain and stiffness.
- Restore/preserve function
- Prevent joint damage
- Prevent spinal fusion - to maintain spinal mobility, and prevent development of spinal deformities
- Minimise extra-spinal and extra-articular manifestation
How is it diagnosed? - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- …
- Clinical …
- Blood test (not diagnostic): …, CRP, …, HLA B27
- Radiological:
- X-rays- pelvis (SI joints and hips) and spine
- MRI- more sensitive and picks up changes early
- GOALS OF THERAPY:
- Symptomatic relief -Eliminate/reduce pain and …
- Restore/preserve …
- Prevent joint damage
- Prevent spinal fusion - to maintain spinal …, and prevent development of spinal …
- Minimise extra-spinal and extra-articular manifestation
- History
- Clinical examination
- Blood test (not diagnostic): ESR, CRP, Anaemia, HLA B27
- Radiological:
- X-rays- pelvis (SI joints and hips) and spine
- MRI- more sensitive and picks up changes early
- GOALS OF THERAPY:
- Symptomatic relief -Eliminate/reduce pain and stiffness.
- Restore/preserve function
- Prevent joint damage
- Prevent spinal fusion - to maintain spinal mobility, and prevent development of spinal deformities
- Minimise extra-spinal and extra-articular manifestation
Treatment - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- … & …
- Pain relief: simple analgesics & Anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs)
- … (if peripheral joints affected)
- Steroids-oral/intra-muscular/intra-venous
- Anti-… agents
- Surgery e.g. hip replacement
- …-Osteoporosis prophylaxis
- Osteopathy, Chiropractic (any form of spinal manipulation) is not recommended.
- Physiotherapy & exercise
- Pain relief: simple analgesics & Anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs)
- DMARDs (if peripheral joints affected)
- Steroids-oral/intra-muscular/intra-venous
- Anti-TNF agents
- Surgery e.g. hip replacement
- DEXA-Osteoporosis prophylaxis
- Osteopathy, Chiropractic (any form of spinal manipulation) is not recommended.
Treatment - Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Physiotherapy & exercise
- Pain relief: simple analgesics & Anti-inflammatory (…)
- DMARDs (if peripheral joints affected)
- …-oral/intra-muscular/intra-venous
- Anti-TNF agents
- Surgery e.g. … replacement
- DEXA-Osteoporosis …
- Osteopathy, Chiropractic (any form of spinal manipulation) is not recommended.
- Physiotherapy & exercise
- Pain relief: simple analgesics & Anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs)
- DMARDs (if peripheral joints affected)
- Steroids-oral/intra-muscular/intra-venous
- Anti-TNF agents
- Surgery e.g. hip replacement
- DEXA-Osteoporosis prophylaxis
- Osteopathy, Chiropractic (any form of spinal manipulation) is not recommended.
NICE Guidance on use of Anti-TNF alpha agents in AS
- The patient’s disease satisfies the modified New York criteria for diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- A score of ≥… units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- and
- ≥… cm on the 0 to 10 cm spinal pain visual analogue scale (VAS).
- A score of ≥… units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- Conventional treatment with two or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs taken sequentially at maximum tolerated or recommended dosage for 4 weeks has failed to control symptoms.
- The patient’s disease satisfies the modified New York criteria for diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.•
- A score of ≥4 units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- and
- ≥4 cm on the 0 to 10 cm spinal pain visual analogue scale (VAS).
- A score of ≥4 units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- Conventional treatment with two or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs taken sequentially at maximum tolerated or recommended dosage for 4 weeks has failed to control symptoms.
NICE Guidance on use of Anti-TNF alpha agents in AS
- The patient’s disease satisfies the modified New York criteria for diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.•
- A score of ≥4 units on the … Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- and
- ≥4 cm on the 0 to 10 cm spinal pain … … scale (VAS).
- A score of ≥4 units on the … Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- Conventional treatment with … or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs taken sequentially at maximum tolerated or recommended dosage for … weeks has failed to control symptoms.
- The patient’s disease satisfies the modified New York criteria for diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.•
- A score of ≥4 units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- and
- ≥4 cm on the 0 to 10 cm spinal pain visual analogue scale (VAS).
- A score of ≥4 units on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)
- Conventional treatment with two or more non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs taken sequentially at maximum tolerated or recommended dosage for 4 weeks has failed to control symptoms.
Reactive Arthritis Triad
- Common organisms:
- Chlamydia / Gonorrhoea, Shigella / Salmonella / Yersinia / Campylobacter / C.Difficile, Flu
- Cant see, cant pee, cant climb a tree…
- Common organisms:
- Chlamydia / Gonorrhoea, Shigella / Salmonella / Yersinia / Campylobacter / C.Difficile, Flu
- Conjunctivitis: discharge, erythema, burning, photophobia
- Urethritis: dysuria, urgency, frequency, discharge
- Arthritis: Knees, ankles, feet
Reactive Arthritis Triad
- Common organisms:
- … / Gonorrhoea, Shigella / Salmonella / Yersinia / Campylobacter / C.Difficile, Flu
- …: discharge, erythema, burning, photophobia
- …: dysuria, urgency, frequency, discharge
- …: Knees, ankles, feet
- Common organisms:
- Chlamydia / Gonorrhoea, Shigella / Salmonella / Yersinia / Campylobacter / C.Difficile, Flu
- Conjunctivitis: discharge, erythema, burning, photophobia
- Urethritis: dysuria, urgency, frequency, discharge
- Arthritis: Knees, ankles, feetul

Most common organism causing reactive arthritis
Chlamydia (but can be Gonorrhoea, Shigella / Salmonella / Yersinia / Campylobacter / C.Difficile, Flu)
triad for…

- reactive arthritis:
- Conjunctivitis: discharge, erythema, burning, photophobia
- Urethritis: dysuria, urgency, frequency, discharge
- Arthritis: Knees, ankles, feet
Reactive arthritis images

Investigations for Reactive Arthritis
- ESR, …-… protein, FBC, Liver and Renal function, RF
- … analysis, … of affected joints
- … examination if … symptoms present
- Joint fluid Aspiration-Cell count, crystals, Gram stain & culture
- Bacterial culture of:
- Feces, Urine or urethral swab, Cervical sample, Throat
- … culture (not always necessary)
- Treatment
- Rest
- … if infection is still present
- NSAIDs
- Intra-articular/Systemic corticosteroids
- Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in some cases
- ESR, C-Reactive protein, FBC, Liver and Renal function, RF
- Urine analysis, Radiograph of affected joints
- Ophthalmologic examination if eye symptoms present
- Joint fluid Aspiration-Cell count, crystals, Gram stain & culture
- Bacterial culture of:
- Feces, Urine or urethral swab, Cervical sample, Throat
- Blood culture (not always necessary)
- Treatment
- Rest
- Antibiotics if infection is still present
- NSAIDs
- Intra-articular/Systemic corticosteroids
- Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in some cases
Investigations for Reactive Arthritis
- …, C-Reactive protein, FBC, Liver and Renal function, RF
- Urine analysis, Radiograph of affected joints
- Ophthalmologic examination if eye symptoms present
- Joint fluid …-Cell count, crystals, Gram stain & culture
- Bacterial culture of:
- …, Urine or … swab, Cervical sample, Throat
- Blood culture (not always necessary)
- Treatment
- R…
- Antibiotics if infection is still present
- N..
- Intra-articular/Systemic …
- Disease modifying .. … drugs in some cases
- ESR, C-Reactive protein, FBC, Liver and Renal function, RF
- Urine analysis, Radiograph of affected joints
- Ophthalmologic examination if eye symptoms present
- Joint fluid Aspiration-Cell count, crystals, Gram stain & culture
- Bacterial culture of:
- Feces, Urine or urethral swab, Cervical sample, Throat
- Blood culture (not always necessary)
-
Treatment
- Rest
- Antibiotics if infection is still present
- NSAIDs
- Intra-articular/Systemic corticosteroids
- Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in some cases
Psoriatic Arthritis
- Arthritis may precede the onset of psoriasis / can also be … degree relative with …
- Prevalence 0.04%-0.1%
- … … is equal
- … changes have the strongest association with arthritis
- Spondyloarthropathy seen in about 5%
- Sacroiliac joint involvement can be symmetric or asymmetric
- Arthritis may precede the onset of psoriasis / can also be first degree relative with psoriasis
- Prevalence 0.04%-0.1%
- Sex distribution is equal
- Nail changes have the strongest association with arthritis
- Spondyloarthropathy seen in about 5%
- Sacroiliac joint involvement can be symmetric or asymmetric
Psoriatic Arthritis
- Arthritis may … the onset of psoriasis / can also be first degree relative with psoriasis
- Prevalence …%
- Sex distribution is equal
- Nail changes have the strongest association with arthritis
- Spondyloarthropathy seen in about …%
- … joint involvement can be symmetric or asymmetric
- Arthritis may precede the onset of psoriasis / can also be first degree relative with psoriasis
- Prevalence 0.04%-0.1%
- Sex distribution is equal
- Nail changes have the strongest association with arthritis
- Spondyloarthropathy seen in about 5%
- Sacroiliac joint involvement can be symmetric or asymmetric
THE MOLL AND WRIGHT CLASSIFICATION OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
- Arthritis with … joint involvement predominant
- Arthritis M…
- Symmetric polyarthritis – indistinguishable from RA
- Asymmetric oligoarticular arthritis
- … spondylitis
- Arthritis with DIP joint involvement predominant
- Arthritis mutilans
- Symmetric polyarthritis – indistinguishable from RA
- Asymmetric oligoarticular arthritis
- Predominant spondylitis

THE MOLL AND WRIGHT CLASSIFICATION OF PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
- Arthritis with DIP joint involvement predominant
- Arthritis mutilans
- … polyarthritis – indistinguishable from RA
- … oligoarticular arthritis
- Predominant spondylitis
- Arthritis with DIP joint involvement predominant
- Arthritis mutilans
- Symmetric polyarthritis – indistinguishable from RA
- Asymmetric oligoarticular arthritis
- Predominant spondylitis
Symmetric polyarthritis – indistinguishable from …
Symmetric polyarthritis – indistinguishable from RA
X-ray shows what?

Classic ‘pencil in cup’ erosive changes - Psoriatic Arthritis

Anti-TNF in Psoriatic Arthritis
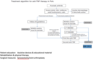
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy Summary

Which joints are diseased?

PIPs / DIPs
Name the radiological appearance seen on the x-ray

Pencil in cup - psoriatic arthritis
Name the pathology

Dactylitis
What is vasculitis?
Vasculitis means inflammation of the blood vessels.

Vasculitis Presentations

Vasculitis Classification


Vasculitis - Classification tree

Vasculitis Case 1:
- A 64 year old man complains of general malaise and has lost 6kg in weight over six months
- Haemoptysis 9 days ago
- Purpuric rash on his legs
- BP is 165/90.
- Dipstick urinalysis showed +++blood and ++protein.
- Creatinine is 320, Hb 95 and platelets 210.
- Serology: ANCA, Anti GBM abs, Anti phospholipid screen, ANA/ENA, dsDNA / Complement, Anti streptococcal abs, RF / Anti CCP
- If the ANCA is +, what could he have?

- A 64 year old man complains of general malaise and has lost 6kg in weight over six months
- Haemoptysis 9 days ago
- Purpuric rash on his legs
- BP is 165/90.
- Dipstick urinalysis showed +++blood and ++protein.
- Creatinine is 320, Hb 95 and platelets 210.
- Serology: ANCA, Anti GBM abs, Anti phospholipid screen, ANA/ENA, dsDNA / Complement, Anti streptococcal abs, RF / Anti CCP
- If the ANCA is +, what could he have?
- Most likely to be GPA
BUT screen for -
- Infections: Hep B/C, N. Meningitidis
- Drug: Cocaine, Amphetamines
- Medications: NSAIDs, Abx, Thiazide Diuretics, Warfarin
- Malignancy: Lymphomas, Myeloma
- Inflammatory: RA / SLE

Vasculitis is classified into 3 groups, which are…
Small, medium and large

Types of Vasculitis (by size of arteries affected)
- The vasculitic diseases are usually classified according to the predominant size of vessel involved.
- Vasculitis mainly affecting … arteries:
- Giant Cell Arteritis/Temporal Arteritis (GCA)
- Takayasu Arteritis (TA)
- Vasculitis mainly affecting … … arteries:
- Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)
- Kawasaki Disease (KD
- Diseases affecting the … blood vessels - These are divided into … associated vasculitis and non-… vasculitis.
- … associated vasculitis
- Eosinophillic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
- Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA)
- Drug induced
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (WG)
- Non-… vasculitis
- Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
- Behcet’s
- CTD related vasculitis
- Cyroglobulinemic vasculitis
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
- … associated vasculitis
- The vasculitic diseases are usually classified according to the predominant size of vessel involved.
- Vasculitis mainly affecting large arteries:
- Giant Cell Arteritis/Temporal Arteritis (GCA)
- Takayasu Arteritis (TA)
- Vasculitis mainly affecting middle sized arteries:
- Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN)
- Kawasaki Disease (KD
- Diseases affecting the small blood vessels - These are divided into ANCA associated vasculitis and non-ANCA vasculitis.
- ANCA associated vasculitis
- Eosinophillic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
- Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA)
- Drug induced
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis (WG)
- Non-ANCA vasculitis
- Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
- Behcet’s
- CTD related vasculitis
- Cyroglobulinemic vasculitis
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
- ANCA associated vasculitis
Examination Features - GCA
- Abnormal … Temporal Artery
- Tender
- Thickened
- Reduced/ Absent …
- … Tenderness
- Cranial Nerve …
- Vascular …
- … Pulses
-
Abnormal Superficial Temporal Artery
- Tender
- Thickened
- Reduced/ Absent Pulsation
- Scalp Tenderness
- Cranial Nerve Palsies
- Vascular Bruits
- Asymmetric Pulses

Vasculitis Mimickers:
- Infections: Hep B/C, N. Meningitidis
- Drug: …, …
- Medications: NSAIDs, Abx, Thiazide Diuretics, Warfarin
- Malignancy: Lymphomas, …
- Inflammatory: … / SLE
- Infections: Hep B/C, N. Meningitidis
- Drug: Cocaine, Amphetamines
- Medications: NSAIDs, Abx, Thiazide Diuretics, Warfarin
- Malignancy: Lymphomas, Myeloma
- Inflammatory: RA / SLE
Vasculitis Mimickers:
- Infections: Hep B/C, N. …
- Drug: Cocaine, Amphetamines
- Medications: …, Abx, … Diuretics, …
- Malignancy: …, Myeloma
- Inflammatory: RA / …
- Infections: Hep B/C, N. Meningitidis
- Drug: Cocaine, Amphetamines
- Medications: NSAIDs, Abx, Thiazide Diuretics, Warfarin
- Malignancy: Lymphomas, Myeloma
- Inflammatory: RA / SLE
ANCA positive Vasculitis Treatment

Vasculitis Systems Review
- Systemic symptoms
- Cutaneous (… / ulcers)
- Mucus membranes (ulcers / eyes)
- ENT (nasal … / … loss / …)
- Bowels (PR bleeding / abdo pain / perforation)
- Respiratory (wheeze / haemoptysis / fibrosis)
- Cardiovascular (pulses / percarditis / CP)
- Renal (… BP / renal … / …uria)
- Neuro (… / seizures / …)
- Systemic symptoms
- Cutaneous (purpura / ulcers)
- Mucus membranes (ulcers / eyes)
- ENT (nasal crusting / hearing loss / sinusitis)
- Bowels (PR bleeding / abdo pain / perforation)
- Respiratory (wheeze / haemoptysis / fibrosis)
- Cardiovascular (pulses / percarditis / CP)
- Renal (High BP / renal failure / proteinuria)
- Neuro (stroke / seizures / neuropathy)
Vasculitis Systems Review
- Systemic symptoms
- Cutaneous (purpura / …)
- Mucus membranes (… / eyes)
- ENT (nasal crusting / hearing loss / sinusitis)
- Bowels (… bleeding / … pain / perforation)
- Respiratory (… / haemoptysis / …)
- Cardiovascular (pulses / … / CP)
- Renal (High BP / renal failure / proteinuria)
- Neuro (stroke / … / neuropathy)
- Systemic symptoms
- Cutaneous (purpura / ulcers)
- Mucus membranes (ulcers / eyes)
- ENT (nasal crusting / hearing loss / sinusitis)
- Bowels (PR bleeding / abdo pain / perforation)
- Respiratory (wheeze / haemoptysis / fibrosis)
- Cardiovascular (pulses / percarditis / CP)
- Renal (High BP / renal failure / proteinuria)
- Neuro (stroke / seizures / neuropathy)
In general, flares of systemic vasculitides require escalation of immunosuppressive treatment:
- …. (3 days IV Methylpred 1g)
- Cyclophosphamide / R…
- Azathioprine / M…
- Corticosteroids (3 days IV Methylpred 1g)
- Cyclophosphamide / Rituximab
- Azathioprine / Methotrexate
In general, flares of systemic vasculitides require escalation of immunosuppressive treatment:
- Corticosteroids (… days IV Methylpred 1g)
- C… / Rituximab
- A… / Methotrexate
- Corticosteroids (3 days IV Methylpred 1g)
- Cyclophosphamide / Rituximab
- Azathioprine / Methotrexate
Case 2 - Vasculitis
- 55 year old lady
- Proximal myalgia
- Complaining of pain and difficulty turning over in bed and combing her hair
- ESR 60
- CRP 45
- Diagnosis?
- What other diagnosis is associated with this?
- … cell …
- 55 year old lady
- Proximal myalgia
- Complaining of pain and difficulty turning over in bed and combing her hair
- ESR 60
- CRP 45
- What other diagnosis is associated with Polymyalgia Rheumatica?
- Giant cell arteritis

Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) & Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA)
- Age > …
- Scalp tenderness and headache (temporal and unilateral)
- Jaw or limb …
- Blindness or …
- Weight loss, anorexia, fever, night sweats, malaise
- Raised … and …
- Biopsy or …
- … muscle pain and stiffness
- Age > 50
- Scalp tenderness and headache (temporal and unilateral)
- Jaw or limb claudication
- Blindness or diplopia
- Weight loss, anorexia, fever, night sweats, malaise
- Raised ESR and CRP
- Biopsy or USS
- Proximal muscle pain and stiffness
Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) & Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA)
- Age > 50
- … tenderness and … (temporal and unilateral)
- Jaw or limb claudication
- … or diplopia
- Weight …, …, fever, … sweats, …
- Raised ESR and CRP
- … or USS
- Proximal … pain and …
- Age > 50
- Scalp tenderness and headache (temporal and unilateral)
- Jaw or limb claudication
- Blindness or diplopia
- Weight loss, anorexia, fever, night sweats, malaise
- Raised ESR and CRP
- Biopsy or USS
- Proximal muscle pain and stiffness
Examination Features - GCA
- Abnormal Superficial Temporal Artery
- …
- …
- …/ … Pulsation
- Scalp …
- … Nerve Palsies
- … Bruits
- Asymmetric …
-
Abnormal Superficial Temporal Artery
- Tender
- Thickened
- Reduced/ Absent Pulsation
- Scalp Tenderness
- Cranial Nerve Palsies
- Vascular Bruits
- Asymmetric Pulses

Visual Loss - GCA
- … Defect
- Afferent … Defect
- Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuritis
- Central Retinal Artery …
- …
- Early … Review
- Field Defect
- Afferent Pupillary Defect
- Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuritis
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
-
Diplopia
- Early Opthalmology Review

Giant cell arteritis - May cause abnormal findings on fundoscopy:
- Central retinal artery occlusion may cause a …-spot
- Anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy may cause a … disc … (caused by inflammatory occlusion of posterior ciliary arteries and subsequent ischaemia of optic nerve)
- Central retinal artery occlusion may cause a cherry-spot
- Anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy may cause a Pallid disc oedema (caused by inflammatory occlusion of posterior ciliary arteries and subsequent ischaemia of optic nerve)

Giant cell arteritis - May cause abnormal findings on fundoscopy:
- …. … artery occlusion may cause a cherry-spot
- … … optic neuropathy may cause a Pallid disc oedema (caused by inflammatory occlusion of posterior ciliary arteries and subsequent ischaemia of optic nerve)
- Central retinal artery occlusion may cause a cherry-spot
- Anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy may cause a Pallid disc oedema (caused by inflammatory occlusion of posterior ciliary arteries and subsequent ischaemia of optic nerve)

GCA Investigations…
- FBC, U&Es, LFTs, CRP, ESR.
- CXR
- Urinalysis
- Temporal Artery biopsy
- USS Temporal Arteries
GCA Investigations…
- …, U&Es, LFTs, CRP, ESR.
- CXR
- U..
- Temporal Artery B…
- … of Temporal Arteries
- FBC, U&Es, LFTs, CRP, ESR.
- CXR
- Urinalysis
- Temporal Artery biopsy
- USS Temporal Arteries
Biopsy and USS - GCA
- … … biopsy (TAB) should be considered whenever a diagnosis of GCA is suspected.
- This should not delay … therapy
- TAB may be … in some patients (Skip lesions)
- Imaging techniques show promise for the diagnosis and monitoring of GCA. … sensitivity.
- These do not replace TAB for cranial GCA.
- … limited as it requires a high level of experience and training.
- PET and MRI currently reserved for investigation of suspected …-vessel GCA.
- Temporal artery biopsy (TAB) should be considered whenever a diagnosis of GCA is suspected.
- This should not delay glucocorticosteroid therapy
- TAB may be negative in some patients (Skip lesions)
- Imaging techniques show promise for the diagnosis and monitoring of GCA. High sensitivity.
- These do not replace TAB for cranial GCA.
- USS limited as it requires a high level of experience and training.
- PET and MRI currently reserved for investigation of suspected large-vessel GCA.
Biopsy and USS - GCA
- Temporal artery biopsy (TAB) should be considered whenever a diagnosis of GCA is suspected.
- This should not delay glucocorticosteroid therapy
- TAB may be negative in some patients (… lesions)
- … techniques show promise for the diagnosis and monitoring of GCA. High sensitivity.
- These do not replace TAB for cranial GCA.
- USS limited as it requires a … level of experience and training.
- PET and … currently reserved for investigation of suspected large-vessel GCA.
- Temporal artery biopsy (TAB) should be considered whenever a diagnosis of GCA is suspected.
- This should not delay glucocorticosteroid therapy
- TAB may be negative in some patients (Skip lesions)
- Imaging techniques show promise for the diagnosis and monitoring of GCA. High sensitivity.
- These do not replace TAB for cranial GCA.
- USS limited as it requires a high level of experience and training.
- PET and MRI currently reserved for investigation of suspected large-vessel GCA.
This is a Temporal Biopsy sample showing ….

Immune cell infiltration
Treatment - GCA
- … – immediately (tapering regimen)
- Uncomplicated GCA (no jaw claudication or visual disturbance)
- 40mg … daily.
- Evolving visual loss or amaurosis fugax (complicated GCA):
- 500 mg to 1 g of i.v. … for 3 days before oral ….
- Established visual loss
- 60 mg … daily to protect the contralateral eye.
- Also additional management
-
Steroids – immediately (tapering regimen)
- Uncomplicated GCA (no jaw claudication or visual disturbance)
- 40mg prednisolone daily.
-
Evolving visual loss or amaurosis fugax (complicated GCA):
- 500 mg to 1 g of i.v. methylprednisolone for 3 days before oral glucocorticosteroids.
-
Established visual loss
- 60 mg prednisolone daily to protect the contralateral eye.
Treatment - GCA
- Steroids – immediately (tapering regimen)
- Uncomplicated GCA (no jaw … or … disturbance)
- …mg prednisolone daily.
- Evolving visual loss or amaurosis fugax (complicated GCA):
- 500 mg to 1 g of i.v. methylprednisolone for 3 days before oral glucocorticosteroids.
- Established visual loss
- …. mg prednisolone daily to protect the … eye.
- Also additional management
-
Steroids – immediately (tapering regimen)
- Uncomplicated GCA (no jaw claudication or visual disturbance)
- 40mg prednisolone daily.
-
Evolving visual loss or amaurosis fugax (complicated GCA):
- 500 mg to 1 g of i.v. methylprednisolone for 3 days before oral glucocorticosteroids.
-
Established visual loss
- 60 mg prednisolone daily to protect the contralateral eye.
Additional Management - GCA
- … Protection
- … … Inhibitor (PPI)
- Regular … Review
- Relapse Management: steroids or steroid-sparing agent
- Bone Protection
- Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI)
- Regular Specialist Review
- Relapse Management: steroids or steroid-sparing agent
Additional Management - GCA
- Bone …
- Proton Pump …
- Regular … Review
- Relapse Management: … or …-sparing agent
- Bone Protection
- Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI)
- Regular Specialist Review
- Relapse Management: steroids or steroid-sparing agent
PMR diagnostic criteria (Polymyalgia rheumatica)
Also - PMR is associated with …: 1/50 with … get PMR but 1/10 PMR get ….
- PMR is associated with GCA: 1/50 with GCA get PMR but 1/10 PMR get GCA.

PMR diagnostic criteria (Polymyalgia rheumatica)

Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Chronic, …, … disease
- Broad spectrum of clinical features involving almost all organs and tissues
- Prevalence in the UK: … per 100,000
- …:… = 10-20:1 (GENDER)
- Peak onset between 15- 40 years
- More common and severe in those of Afro-Caribbean, India, Hispanic and Chinese origin living in USA and Europe> …
- Chronic, relapsing, remitting disease
- Broad spectrum of clinical features involving almost all organs and tissues
- Prevalence in the UK: 97 per 100,000
- F:M= 10-20:1
- Peak onset between 15- 40 years
- More common and severe in those of Afro-Caribbean, India, Hispanic and Chinese origin living in USA and Europe> Caucasians
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- …, relapsing, remitting disease
- Broad spectrum of clinical features involving almost all organs and tissues
- Prevalence in the UK: 97 per 100,000
- F:M= 10-20:1
- Peak onset between …-… years
- … common and … in those of Afro-Caribbean, India, Hispanic and Chinese origin living in USA and Europe> Caucasians
- Chronic, relapsing, remitting disease
- Broad spectrum of clinical features involving almost all organs and tissues
- Prevalence in the UK: 97 per 100,000
- F:M= 10-20:1
- Peak onset between 15- 40 years
- More common and severe in those of Afro-Caribbean, India, Hispanic and Chinese origin living in USA and Europe> Caucasians

SLE Signs/Symptoms
- … rash
- Discoid rash
- Serositis – Pleuritis / Pericarditis
- … ulcers
- Arthritis – non-erosive
- Photosensitivity
- … disorders
- … disorders
- ANA + anti Smith / dsDNA / antiphospholipid abs
- … symptoms
- Malar rash
- Discoid rash
- Serositis – Pleuritis / Pericarditis
- Oral ulcers
- Arthritis – non-erosive
- Photosensitivity
- Blood disorders
- Renal disorders
- ANA + anti Smith / dsDNA / antiphospholipid abs
- Neurologic symptoms
SLE Signs/Symptoms
- Malar rash
- … rash
- Serositis – P… / P…
- Oral ulcers
- A… – non-erosive
- …sensitivity
- Blood disorders
- Renal disorders
- ANA + anti Smith / dsDNA / antiphospholipid abs
- Neurologic symptoms
- Malar rash
- Discoid rash
- Serositis – Pleuritis / Pericarditis
- Oral ulcers
- Arthritis – non-erosive
- Photosensitivity
- Blood disorders
- Renal disorders
- ANA + anti Smith / dsDNA / antiphospholipid abs
- Neurologic symptoms
SLE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY

SLE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY

SLE – 2019 classification criteria
- …. positive ≥1:80
- … clinical and ≥10 points (count highest in each criterion)
- ANA positive ≥1:80
- One clinical and ≥10 points (count highest in each criterion)

SLE – 2019 classification criteria
- ANA positive ≥…
- One clinical and ≥… points (count highest in each criterion)
- ANA positive ≥1:80
- One clinical and ≥10 points (count highest in each criterion)

SLE

SLE Investigations
- … – … protein: … ratio
- Full blood count
- … and electrolytes
- ESR
- …
- … function test
- Antibodies: ANA; ENA; Anti –dsDNA; Lupus anticoagulant; ANTI C1q;
- C3, C…
- Urinalysis – urinary protein: creatinine ratio
- Full blood count
- Urea and electrolytes
- ESR
- CRP
- Liver function test
- Antibodies: ANA; ENA; Anti –dsDNA; Lupus anticoagulant; ANTI C1q;
- C3, C4
SLE Investigations
- Urinalysis – urinary protein: creatinine ratio
- … blood count
- Urea and …
- …
- CRP
- Liver function test
- Antibodies: ANA; ENA; Anti –dsDNA; Lupus anticoagulant; ANTI C1q;
- C…, C…
- Urinalysis – urinary protein: creatinine ratio
- Full blood count
- Urea and electrolytes
- ESR
- CRP
- Liver function test
- Antibodies: ANA; ENA; Anti –dsDNA; Lupus anticoagulant; ANTI C1q;
- C3, C4 - if complement is low, disease is more active
In SLE, if complement is low, disease is … active
In SLE, if complement is low, disease is more active (C3 and C4 - measure)
SLE Principals of management
- Nonpharmacological management (… protection; … cessation; … risk modification; … prevention)
- Nonpharmacological management (sun protection; smoking cessation; CVD risk modification; osteoporosis prevention)

Sjogren’s syndrome
- Lymphocytic infiltration of … glands
- S…: Dry eyes (lacrimal gland involvement) and xerostomia (salivary gland involvement)
- Extra-glandular disease: joint pain, skin disease and pulmonary disease
- F…, myalgia
- Complications:
- Non-… Lymphoma
- Chronic dry eyes -> … and … damage
- Chronic dry mouth -> … caries
- … heart block
- Lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine glands
- Sicca: Dry eyes (lacrimal gland involvement) and xerostomia (salivary gland involvement)
- Extra-glandular disease: joint pain, skin disease and pulmonary disease
- Fatigue, myalgia
-
Complications:
- Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
- Chronic dry eyes -> corneal and conjunctival damage
- Chronic dry mouth -> dental caries
- Congenital heart block
Sjogren’s syndrome
- … infiltration of exocrine glands
- Sicca: Dry … (lacrimal gland involvement) and xerostomia (… … involvement)
- Extra-glandular disease: joint pain, skin disease and pulmonary disease
- Fatigue, myalgia
- Complications:
- Non-Hodgkins …
- Chronic … … -> corneal and conjunctival damage
- Chronic … … -> dental caries
- Congenital heart block
- Lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine glands
- Sicca: Dry eyes (lacrimal gland involvement) and xerostomia (salivary gland involvement)
- Extra-glandular disease: joint pain, skin disease and pulmonary disease
- Fatigue, myalgia
-
Complications:
- Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma
- Chronic dry eyes -> corneal and conjunctival damage
- Chronic dry mouth -> dental caries
- Congenital heart block
Sjogren’s Syndrome Diagnosis
- Need …/6 criteria including one of the red criterion
- Need 4/6 criteria including one of the red criterion

Sjogren’s Syndrome Diagnosis
- Need 4/6 criteria including one of the BOLD criterion
- Dry eyes >… months / using … … TDS:
- Dry mouth >… months / need … to swallow dry foods / recurrent …. salivary glands
- Shirmer’s test <5mm/5 mins / positive vital dye staining
- Abnormal parotid sialography or salivary scintigraphy or unstimulated whole salivary flow (<1.5ml/15mins)
- Focal lymphocytic sialoadenditis on lip biopsy
- Anti-… / Anti … positive
- Need 4/6 criteria including one of the BOLD criterion
- Dry eyes >3 months / using artificial tears TDS:
- Dry mouth >3 months / need liquids to swallow dry foods / recurrent swollen salivary glands
- Shirmer’s test <5mm/5 mins / positive vital dye staining
- Abnormal parotid sialography or salivary scintigraphy or unstimulated whole salivary flow (<1.5ml/15mins)
- Focal lymphocytic sialoadenditis on lip biopsy
- Anti-Ro / Anti La positive
Sjogren’s Syndrome Diagnosis
- Need …/6 criteria including one of the BOLD criterion
- Dry … >3 months / using artificial tears TDS:
- Dry … >3 months / need liquids to swallow dry foods / recurrent swollen salivary glands
- … test <5mm/5 mins / positive vital dye staining
- Abnormal parotid sialography or salivary scintigraphy or unstimulated whole salivary … (<1.5ml/15mins)
- Focal lymphocytic sialoadenditis on lip biopsy
- Anti-Ro / Anti La positive
-
Need 4/6 criteria including one of the BOLD/italic criterion
- Dry eyes >3 months / using artificial tears TDS:
- Dry mouth >3 months / need liquids to swallow dry foods / recurrent swollen salivary glands
- Shirmer’s test <5mm/5 mins / positive vital dye staining
- Abnormal parotid sialography or salivary scintigraphy or unstimulated whole salivary flow (<1.5ml/15mins)
- Focal lymphocytic sialoadenditis on lip biopsy
- Anti-Ro / Anti La positive
Sjogren’s Syndrome Treatment
- Conservative:
- Stop … / … hygiene /
- Artificial … and …
- Medications:
- Cholinergic agents: pilocarpine / cevimeline
- … / Steroids
- … eg. hydroxychloroquine / methotrexate / rituximab
-
Conservative:
- Stop smoking / oral hygiene /
- Artificial tears and saliva
- Medications:
- Cholinergic agents: pilocarpine / cevimeline
- NSAIDs / Steroids
- Immunosuppressants eg. hydroxychloroquine / methotrexate / rituximab
Sjogren’s Syndrome Treatment
- Conservative:
- Stop smoking / oral hygiene /
- … tears and saliva
- Medications:
- … agents: pilocarpine / cevimeline
- NSAIDs / …
- Immunosuppressants eg. hydroxychloroquine / … / …
- Conservative:
- Stop smoking / oral hygiene /
- Artificial tears and saliva
- Medications:
- Cholinergic agents: pilocarpine / cevimeline
- NSAIDs / Steroids
- Immunosuppressants eg. hydroxychloroquine / methotrexate / rituximab
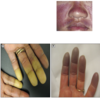
Spot Diagnosis
- … syndrome:
- Reynaud’s (WHITE BLUE RED)
- Telangeictasia of lips
- Tight shiny skin on finger - scelrodactyly
- Calcinosis
- Oesophageal dismotility - reflux

-
Crest syndrome:
- Reynaud’s (WHITE BLUE RED)
- Telangeictasia of lips
- Tight shiny skin on finger - scelrodactyly
- Calcinosis
- Oesophageal dismotility - reflux
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
- … activation, vascular damage and excessive deposition of collagen
- More frequent in ages ..-..
- 5:1 …(gender)
- Antibodies:
- anti topoisomerase (anti-Scl-70)
- Anti … (ACA)
- anti-RNA polymerase III
- ANA
- Immune activation, vascular damage and excessive deposition of collagen
- More frequent in ages 30-50
- 5:1 female
- Antibodies:
- anti topoisomerase (anti-Scl-70)
- Anti centromere (ACA)
- anti-RNA polymerase III
- ANA
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
- Immune activation, vascular damage and excessive deposition of …
- More frequent in ages 30-50
- 5:1 …
- Antibodies:
- anti … (anti-Scl-70)
- Anti centromere (ACA)
- anti-… polymerase III
- ANA
- Immune activation, vascular damage and excessive deposition of collagen
- More frequent in ages 30-50
- 5:1 female
- Antibodies:
- anti topoisomerase (anti-Scl-70)
- Anti centromere (ACA)
- anti-RNA polymerase III
- ANA
Systemic Sclerosis Clinical Features
- Sclerodactyly
- … phenomenon
- Heartburn
- Abnormal nailfold …
- …iectasia
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- … lung disease
- Lower bowel: distension / diarrhea / constipation
- Renal failure / proteinuria
- … dysfunction
- Sclerodactyly
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Heartburn
- Abnormal nailfold capillaries
- Telangiectasia
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Interstitial lung disease
- Lower bowel: distension / diarrhea / constipation
- Renal failure / proteinuria
- Erectile dysfunction

Systemic Sclerosis Clinical Features
- Sclerodactyly
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- …
- Abnormal … capillaries
- Telangiectasia
- Pulmonary arterial …
- Interstitial lung disease
- … bowel: distension / diarrhea / constipation
- … failure / proteinuria
- Erectile dysfunction
- Sclerodactyly
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Heartburn
- Abnormal nailfold capillaries
- Telangiectasia
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Interstitial lung disease
- Lower bowel: distension / diarrhea / constipation
- Renal failure / proteinuria
- Erectile dysfunction

Systemic Sclerosis Types
- Limited = …. (calcinosis, Raynaud’s, Esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasias)
- …= scleroderma proximal to elbows
- Overlap syndromes with SLE / …
- Sine …
- Limited = CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud’s, Esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasias)
- Diffuse= scleroderma proximal to elbows
- Overlap syndromes with SLE / Sjogren’s
- Sine scleroderma
Systemic Sclerosis Treatment
- Conservative
- Stop …
- Controlled …
- Wear …
- Warm … baths
- Medications
- Raynaud’s – amlodipine / losartan / fluoxetine / sildenafil
- Reflux - …
- …- mycophenolate, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, steroids, rituximab, IV immunoglobulins
- Conservative
- Stop smoking
- Controlled exercise
- Wear gloves
- Warm wax baths
- Medications
- Raynaud’s – amlodipine / losartan / fluoxetine / sildenafil
- Reflux - omeprazole
- Immunosuppressants- mycophenolate, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, steroids, rituximab, IV immunoglobulins
Systemic Sclerosis Treatment
- Conservative
- Stop smoking
- Controlled exercise
- Wear gloves
- … … baths
- Medications
- …. – amlodipine / losartan / fluoxetine / sildenafil
- … - omeprazole
- Immunosuppressants- mycophenolate, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, steroids, rituximab, IV immunoglobulins
-
Conservative
- Stop smoking
- Controlled exercise
- Wear gloves
- Warm wax baths
-
Medications
- Raynaud’s – amlodipine / losartan / fluoxetine / sildenafil
- Reflux - omeprazole
- Immunosuppressants- mycophenolate, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, steroids, rituximab, IV immunoglobulins


