Drug Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Flashcards
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs
- Exenatide for example
- Administered s.c. injection …-… mins before last meal of day
- Facilitates glucose control by:
- Augmenting … response
- Suppresses pancreatic release of … helping stop the liver overproducing glucose
- Slows down gastric …
- Reduces … and promote … via hypothalamic receptors
- Reduces liver … content
- Exenatide for example
- Administered s.c. injection 30-60 mins before last meal of day
- Facilitates glucose control by:
- Augmenting pancreas response
- Suppresses pancreatic release of glucagon helping stop the liver overproducing glucose
- Slows down gastric emptying
- Reduces appetite and promote satiety via hypothalamic receptors
- Reduces liver fat content
Insulin - Net Effect is what? (in what 3 types of cell/tissue?)
Net effect is to cause hypoglycemia and increase fuel storage in muscle, fat tissue and liver
Thiazolidinediones - Glitazones
- … now only remaining approved
- It activates … proliferator-activated receptor-y (PPAR-y)
- PPARs involved in … of insulin-responsive genes and in regulation of adipocyte … metabolism
- Pioglitazone now only remaining approved
- It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-y (PPAR-y)
- PPARs involved in transcription of insulin-responsive genes and in regulation of adipocyte lipid metabolism
- Pioglitazone subject to interactions - why?
- May lower … … level containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
- Due to liver metabolism
- May lower oral contraceptive levels containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone
Insulin Action
- Insulin affects all major … pathways
- carbohydrate, fat, protein
- Major target tissues are: (3)
- Insulin affects all major metabolic pathways
- carbohydrate, fat, protein
- Major target tissues are:
- Liver, adipose, and skeletal muscle
Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors
- Inhibition of renal tubular Na+-glucose cotransporter -> reversal of hyperglycaemia -> reversal of “gluco…”
- Increased Insulin … in muscle, increase GLUT… translocation, increased insulin signalling
- Increased sensitivity in liver - decreased glucose-…-…
- Decreased gluco… - decreased Cori cycle - decreased PEP carboykinase
- Improved …cell function
- Inhibition of renal tubular Na+-glucose cotransporter -> reversal of hyperglycaemia -> reversal of “glucotoxicity”
- Increased Insulin sensitivity in muscle, increase GLUT4 translocation, increased insulin signalling
- Increased sensitivity in liver - decreased glucose-6-phosphatase
- Decreased gluconeogenesis - decreased Cori cycle - decreased PEP carboykinase
- Improved beta cell function
How does glucose cause insulin release?
- Glucose in bloodstream - picked up by beta cell using GLUT-… transporter - glucose into beta cell - metabolised by … - increase ATP levels inside cell - inhibits ATP sensitive … channels - close them - potassium ions cannot leave cell - stuck inside - change voltage of cell - open voltage dependent calcium channels - calcium ions outside cell enter - contribute … charge to depolarise cell - also involved in … process - calcium ions cause insulin granules to move to plasma membrane - release insulin into bloodstream
Glucose in bloodstream - picked up by beta cell using GLUT-2 transporter - glucose into beta cell - metabolised by glycolysis - increase ATP levels inside cell - inhibits ATP sensitive potassium channels - close them - potassium ions cannot leave cell - stuck inside - change voltage of cell - open voltage dependent calcium channels - calcium ions outside cell enter - contribute positive charge to depolarise cell - also involved in exocytosis process - calcium ions cause insulin granules to move to plasma membrane - release insulin into bloodstream
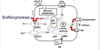
Sulphonylureas - T2 diabetes
- Examples include:
- Gliclazide, glipizide, glimepride
- All are … active
- Are they bound to anything?
- Examples include:
- Gliclazide, glipizide, glimepride
- All are orally active
- All bound to plasma protein (90-99%)

Type 2 diabetes: treatment options
- Tackle …dysfunction:
- Sulphonylureas, GLP-1 analogues, DDP-4 inhibitors (these … insulin release)
- … resistance reduction:
- … and TZD’s
- … glucose absorption:
- SGLT-2 inhibitors
- Loss of … mass:
- Insulin replacement
- Lifestyle changes such as … and …, also treat underlying conditions such as … and … associated with T2 diabetes
- Tackle B-cell dysfunction:
- Sulphonylureas, GLP-1 analogues, DDP-4 inhibitors (increase insulin release)
-
Insulin resistance reduction:
- Metformin and TZD’s
-
Renal glucose absorption:
- SGLT-2 inhibitors
- Loss of B-cell mass:
- Insulin replacement
- Lifestyle changes such as exercise and diet, also treat underlying conditions such as obesity and dyslipidaemia associated with T2 diabetes

Drugs that lower blood glucose levels in T2 diabetes are usually trying to mimic or enhance …
insulin
Side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors
- Rapid weight … (Due to glycosuria (up to 70g/day))
- Tiredness
- Osmotic diuretic so …
- Can worsen … infections and …
- Rapid weight loss (Due to glycosuria (up to 70g/day))
- Tiredness
- Osmotic diuretic so dehydration
- Can worsen UTI and thrush
Glitazones (Thiazolidinediones) can be used in …, but more commonly used with other anti diabetic medications
Glitazones (Thiazolidinediones) can be used in monotherapy, but more commonly used with other anti diabetic medications
Give 2 examples of SGLT2 inhibitors
Dapagliflozin and Canagliflozin
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors
- Oral … agents
- Mechanism of action is via increased levels of Incretins …-1 and G…
- Increased Incretins
- Inhibit … release
- Increase glucose-induced … secretion
- Decrease gastric …
- Reduce … glucose production
- Improved … glucose utilisation
- Oral hypoglycemic agents
- Mechanism of action is via increased levels of Incretics GLP-1 and GIP
- Increased Incretins
- Inhibit glucagon release
- Increase glucose-induced insulin secretion
- Decrease gastric emptying
- Reduce hepatic glucose production
- Improved peripheral glucose utilisation
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs are an adjuvant therapy for type II diabetic on …, a …, …. or a combination of these drugs
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs are an adjuvant therapy for type II diabetic on metformin, a sulfonylurea, thiazolidinediones or a combination of these drugs
SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Dapagliflozin
- IC50 for SGLT2 is 1/… of the IC50 for SGLT1
- Canagliflozin
- IC50 for SGLT2 is less than 1/… of the 1C50 for SGLT1
- Why is this important?
- Dapagliflozin
- IC50 for SGLT2 is 1/1200 of the IC50 for SGLT1
- Canagliflozin
- IC50 for SGLT2 is less than 1/160 of the 1C50 for SGLT1
- Important because it is specific for SGLT2 and will have very little effect on SGLT1
Exenatide
- … plasma concentration
- Strong effects on …
- … only (So far)
- New … formulation in clinical trials - neutralizes the acid in local area protecting against breakdown while also enhancing absorption
- High plasma concentration
- Strong effects on receptors
- Injectables only (So far)
- New oral formulation in clinical trials - neutralizes the acid in local area protecting against breakdown while also enhancing absorption
Gliclazide, glipizide, glimepride are examples of what class of drug?
Sulphonylureas

Glitazone pharmacokinetics
- Pioglitazone: what is the daily dosage?
- Plasma levels peak about … hr
- Plasma half-life is …-… hr; active metabolites (t1/2 = …-… hr)
- Liver metabolism and excreted in faeces (…/3) and urine (…/3)
- Pioglitazone: taken once or twice a day orally
- Plasma levels peak about 3 hr
- Plasma half-life is 3-7 hr; active metabolites (t1/2 = 16-24 hr)
- Liver metabolism and excreted in faeces (2/3) and urine (1/3)
Pioglitazone is the only remaining approved …
Glitazones (thiazolidinediones)
Metformin - mechanism of action
- The exact mechanism is unknown but does involve primarily suppression of hepatic glucose production through …
- Inhibition of mitochondrial complex …
- … ATP synthesis (… is an energy intensive process)
- … AMP:ATP ratio inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Activating …-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
- AMPK increases expression of the nuclear transcription factor SHP which in turn … the expression of hepatic gluconeogenic genes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase
- Inhibition of mitochondrial complex …
- The exact mechanism is unknown but does involve primarily suppression of hepatic glucose production through gluconeogenesis
- Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I
- Decrease ATP synthesis (gluconeogenesis is an energy intensive process)
- Increase AMP:ATP ratio inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
- Activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
- AMPK increases expression of the nuclear transcription factor SHP which in turn inhibits the expression of hepatic gluconeogenic genes phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase
- Inhibition of mitochondrial complex I
Type 2 diabetes - A moving target
- As you get impaired glucose … which is increasing, for example in …, basal … glucose levels increase and also ones after your meal increase (known as …) - until a diagnosis of T2 diabetes
As you get impaired glucose tolerance which is increasing, for example in obesity, basal plasma glucose levels increase and also ones after your meal increase (known as postprandial) - until a diagnosis of T2 diabetes

Insulin Effects - Muscle cells
- increases GLUT-… translocation to the membrane and hence increase … uptake, … oxidation, … synthesis, amino acid uptake, protein synthesis
- decreases …, amino acid …
- increases GLUT-4 translocation to the membrane and hence increase glucose uptake, glucose oxidation, glycogen synthesis, amino acid uptake, protein synthesis
- decreases glycogenolysis, amino acid release
Insulin Effects - Hepatic cells
• decreases gluco… ,glyco…, keto…, (increases … synthesis)
Hepatic cells
• decreases gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, ketogenesis, (increases glycogen synthesis)


