Anatomy of the Leg and Foot Flashcards
Function of the Foot
- 3 functions - what are they?
- Stability/standing (support body weight)
- Locomotion/propulsion (acts as lever)
- Shock absorption
Function of the Foot
- Stability/standing (support … …)
- …/propulsion (acts as …)
- … absorption
- Stability/standing (support body weight)
- Locomotion/propulsion (acts as lever)
- Shock absorption
Bones of the leg


Bones of the leg


Bones of the leg


Bones of the foot


Bones of the foot


Bones of the foot
- Label the tarsal bones of the foot.
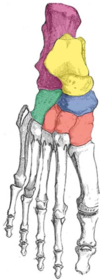

Supination of foot vs Pronation of foot
- Supination (feet … – …/… of front of foot)
- Pronation (feet … – …/… of front of foot)
- When standing on irregular surfaces
- Supination (feet together – inversion/adduction of front of foot)
- Pronation (feet apart – eversion/abduction of front of foot)
- When standing on irregular surfaces

If you stand with your feet parallel and face forward, and rotate your body and look over your left shoulder - your … foot would be supinated and your … foot would be pronated
If you stand with your feet parallel and face forward, and rotate your body and look over your left shoulder - your left foot would be supinated and your right foot would be pronated
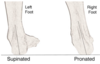
Joints of the foot


Joints of the foot


Joints of the foot
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. … - inversion/eversion and … tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and Transverse tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
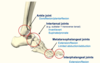
Joints of the foot
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and transverse tarsal - … and …)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited …/…)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)
- Ankle joint (dorsiflexion and plantarflexion)
- Intertarsal joints (e.g. Subtalar - inversion/eversion and Transverse tarsal - supination and pronation)
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (extension/flexion and limited abduction/adduction)
- Interphalangeal joints (extension/flexion)

Ankle Joint is the articulation between the … and …/…
Ankle Joint is the articulation between the talus and tibia/fibula

The ankle joint is what type of joint?
synovial hinge joint

The ankle joint allows what movements?
dorsiflexion (extension of foot - lift up) and plantarflexion (flexion of foot - downwards)

Label the diagram


The ankle joint is stabilised by what ligaments?
-
Collateral ligaments
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (3 parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (3 parts total)

Ankle joint - collateral ligaments
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (… parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (… parts total)
- Lateral ligament - lateral malleolus to talus/calcaneus (3 parts total)
- Medial/deltoid ligament - medial malleolus to talus/calcaneus/navicular (3 parts total)

Ankle joint ligaments
- There are two main sets of ligaments, which originate from each malleolus.
- Medial Ligament
- The medial ligament (or deltoid ligament) is attached to the medial malleolus - 3 parts (to talus/calcaneus)
- Lateral Ligament
- The lateral ligament originates from the lateral malleolus - 3 parts (to talus/calcaneus/navicular)
- Medial Ligament

Clinical: Injury to ,,, ligament due to excessive inversion of foot (usually anterior talofibular ligament)
Clinical: Injury to lateral ligament due to excessive inversion of foot (usually anterior talofibular ligament) - red line on RHS

Subtalar joint
- Between … and calcaneus
- Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion
- Between talus and calcaneus
- Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion

The subtalar joint is responsible for what movements of the foot?
Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion

Subtalar joint
- Between talus and …
- Allows inversion/eversion during …
- Between talus and calcaneus
- Allows inversion/eversion during locomotion

Transverse tarsal joint
- Allows eversion/inversion and pronation/supination
- Important for standing on … …
- Articulation between talus and navicular and also the calcaneus and cuboid (line traverses foot - separates foot into … and …)
- Allows eversion/inversion and pronation/supination
- Important for standing on uneven ground
- Articulation between talus and navicular and also the calcaneus and cuboid (line traverses foot - separates into hindfoot and forefoot)
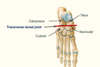
Transverse tarsal joint
- Allows eversion/inversion and …/…
- Important for standing on uneven ground
- Articulation between … and navicular and also the … and cuboid (line traverses foot - separates into hindfoot and forefoot)
- Allows eversion/inversion and pronation/supination
- Important for standing on uneven ground
- Articulation between talus and navicular and also the calcaneus and cuboid (line traverses foot - separates into hindfoot and forefoot)
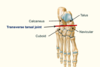
The transverse tarsal joint allows what movements of the foot?
eversion/inversion and pronation/supination

What joint is important for standing on uneven ground?
Transverse tarsal joint (allows pronation and supination)

Arches of the foot
- The foot has three arches: two … (medial and lateral) arches and one anterior … arch
- Function:
- Shock absorbers during …
- Act as springboards (…)
- Distribution of weight (to calcaneus + ball of foot)
- During standing – Arches flatten
- The foot has three arches: two longitudinal (medial and lateral) arches and one anterior transverse arch
- Function:
- Shock absorbers during locomotion
- Act as springboards (propulsion)
- Distribution of weight (to calcaneus + ball of foot)
- During standing – Arches flatten
Arches of the foot
- The foot has three arches: two longitudinal (… and …) arches and one anterior transverse arch
- Function:
- … absorbers during locomotion
- Act as springboards (propulsion)
- Distribution of weight (to … + … of foot)
- During standing – Arches …
- The foot has three arches: two longitudinal (medial and lateral) arches and one anterior transverse arch
- Function:
- Shock absorbers during locomotion
- Act as springboards (propulsion)
- Distribution of weight (to calcaneus + ball of foot)
- During standing – Arches flatten
Longitudinal arches


Which longitudinal arch of the foot is less defined?
lateral longitudinal arch

The longitudinal arches of the foot are supported by long tendons, intrinsic … muscles, intrinsic ligaments and plantar …
The longitudinal arches of the foot are supported by long tendons, intrinsic plantar muscles, intrinsic ligaments and plantar aponeurosis

The … arches of the foot are supported by long tendons, intrinsic plantar muscles, intrinsic ligaments and plantar aponeurosis
The longitudinal arches of the foot are supported by long tendons, intrinsic plantar muscles, intrinsic ligaments and plantar aponeurosis

- Clinical: Fallen … … arch can lead to pes planus (flat feet)
- Due to degeneration of ligaments or injury to tibialis posterior; also seen in children
- Clinical: Fallen medial longitudinal arch can lead to pes planus (flat feet)
- Due to degeneration of ligaments or injury to tibialis posterior; also seen in children

Clinical: Fallen medial longitudinal arch can lead to what?
pes planus (flat feet) - Due to degeneration of ligaments or injury to tibialis posterior; also seen in children
Transverse arch
- Supported by long tendons (such … longus and … posterior)
- Supported by long tendons (such fibularis longus and tibialis posterior)

What is the red curve showing?

transverse arch of foot
Plantar aponeurosis is the … of … fascia
Plantar aponeurosis is the thickening of deep fascia
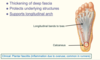
Plantar aponeurosis
- Thickening of deep …
- … underlying structures
- Supports … arch
- Thickening of deep fascia
- Protects underlying structures
- Supports longitudinal arch

The plantar aponeurosis supports the … arch
The plantar aponeurosis supports the longitudinal arch

Clinical: Plantar … (inflammation of plantar aponeurosis due to overuse; common in …)
Clinical: Plantar fasciitis (inflammation of plantar aponeurosis due to overuse; common in runners)
Muscle compartments of the leg
- 3 compartments - these are:
- Anterior - extend/invert foot - supplied by … … nerve
- Posterior - flex/invert foot - supplied by … nerve
- Lateral - evert foot - supplied by superficial fibular nerve
- 3 compartments - these are:
- Anterior - extend/invert foot - supplied by deep fibular nerve
- Posterior - flex/invert foot - supplied by tibial nerve
- Lateral - evert foot - supplied by superficial fibular nerve

Muscle compartments of the leg
- 3 compartments - these are:
- Anterior - …/… foot - supplied by deep fibular nerve
- Posterior - …/… foot - supplied by tibial nerve
- Lateral - … foot - supplied by superficial fibular nerve
- 3 compartments - these are:
- Anterior - extend/invert foot - supplied by deep fibular nerve
- Posterior - flex/invert foot - supplied by tibial nerve
- Lateral - evert foot - supplied by superficial fibular nerve

Anterior compartment of leg
- Extend (dorsiflex) and invert foot
- Supplied by Deep fibular nerve
- 3 muscles - origin from either the … or …
- Tibialis anterior (extends/inverts foot)
- Extensor digitorum longus (extends lateral 4 toes)
- Extensor hallucis longus (extends great toe)
- Tendons of these muscles all pass under the Extensor retinaculum
- Extend (dorsiflex) and invert foot
- Supplied by Deep fibular nerve
- 3 muscles - origin from either the tibia or fibula
- Tibialis anterior (extends/inverts foot)
- Extensor digitorum longus (extends lateral 4 toes)
- Extensor hallucis longus (extends great toe)
- Tendons of these muscles all pass under the Extensor retinaculum
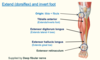
Anterior compartment of leg
- Extend (dorsiflex) and invert foot
- Supplied by Deep fibular nerve
- 3 muscles - origin from either the tibia or fibula
- … anterior (extends/inverts foot)
- Extensor … longus (extends lateral 4 toes)
- Extensor … longus (extends great toe)
- Tendons of these muscles all pass under the Extensor …
- Extend (dorsiflex) and invert foot
- Supplied by Deep fibular nerve
- 3 muscles - origin from either the tibia or fibula
- Tibialis anterior (extends/inverts foot)
- Extensor digitorum longus (extends lateral 4 toes)
- Extensor hallucis longus (extends great toe)
- Tendons of these muscles all pass under the Extensor retinaculum

Anterior compartment of leg
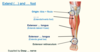

Extensor hallucis longus extends what?
great toe
Extensor digitorum longus extends what?
lateral 4 toes

Anterior compartment of leg - passing into foot


Extensor digitorum longus inserts into the … and … phalanges
Extensor digitorum longus inserts into the middle and distal phalanges

Tibialis anterior inserts into medial … + 1st …
Tibialis anterior inserts into medial cuneiform + 1st metatarsal

Extensor hallucis longus inserts into what?
distal phalanx of great toe

Posterior compartment of leg - Superficial group
- … (…) foot and leg

- Flex (plantarflex) foot and leg

Posterior compartment of leg - Superficial group
- … (…) foot and leg

- Flex (plantarflex) foot and leg

- The posterior compartment of the leg contains seven muscles, organised into two layers – … and … The two layers are separated by a band of fascia.
- The posterior leg is the largest of the three compartments. Collectively, the muscles in this area … and … the foot. They are innervated by the … nerve, a terminal branch of the sciatic nerve.
- The posterior compartment of the leg contains seven muscles, organised into two layers – superficial and deep. The two layers are separated by a band of fascia.
- The posterior leg is the largest of the three compartments. Collectively, the muscles in this area plantarflex and invert the foot. They are innervated by the tibial nerve, a terminal branch of the sciatic nerve.
Gastrocnemius muscle
- Origin: … of femur
- … leg and foot
- Half way down - gives rise to … (Achilles tendon)
- Inserts into calcaneal tuberosity
- Origin: Condyles of femur
- Flexes leg and foot
- Half way down - gives rise to tendocalcaenus (Achilles tendon)
- Inserts into calcaneal tuberosity
Soleus muscle
- Origin - … and …
- … foot
- Passes underneath the gastrocnemius but tendon fuses with tendocalcaneus
- Insertion - Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by tibial nerve
- Origin - fibula and tibia
- Flexes foot
- Passes underneath the gastrocnemius but tendon fuses with tendocalcaneus
- Insertion - Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by tibial nerve

Gastrocnemius muscle
- Origin: Condyles of femur
- Flexes leg and foot
- Half way down - gives rise to tendocalcaenus (… tendon)
- Inserts into … …
- Origin: Condyles of femur
- Flexes leg and foot
- Half way down - gives rise to tendocalcaenus (Achilles tendon)
- Inserts into calcaneal tuberosity

Plantaris muscle
- Origin: femur
- … leg and foot
- Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus (via … …)
- Supplied by tibial nerve
- Origin: femur
- Flexes leg and foot
- Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by tibial nerve

Plantaris muscle
- Origin: …
- Flexes leg and foot
- Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by … nerve
- Origin: femur
- Flexes leg and foot
- Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by tibial nerve

Soleus muscle
- Origin - fibula and tibia
- Flexes foot
- Passes underneath the gastrocnemius but tendon fuses with …
- Insertion - Posterior surface of calcaneus (via … tendon)
- Supplied by … nerve
- Origin - fibula and tibia
- Flexes foot
- Passes underneath the gastrocnemius but tendon fuses with tendocalcaneus
- Insertion - Posterior surface of calcaneus (via calcaneal tendon)
- Supplied by tibial nerve

What nerve innervates the superficial group of the posterior compartment of the leg ?
tibial nerve

Posterior compartment of leg - Deep Group
- There are four muscles in the deep compartment of the posterior leg. One muscle, the …, acts only on the knee joint.
- The remaining three muscles (… posterior, flexor … longus and flexor … longus) act on the ankle and foot.
- There are four muscles in the deep compartment of the posterior leg. One muscle, the popliteus, acts only on the knee joint.
- The remaining three muscles (tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus) act on the ankle and foot.

Posterior compartment of leg - Deep group
- Flex (plantar flex) and … foot
- Origin: … + …
- 3 muscles
- Flexor digitorum longus - flexes lateral 4 toes
- Tibialis posterior - inverts foot
- Flexor hallucis longus - flexes great toe
- Flex (plantar flex) and invert foot
- Origin: tibia + fibula
- 3 muscles
- Flexor digitorum longus - flexes lateral 4 toes
- Tibialis posterior - inverts foot
- Flexor hallucis longus - flexes great toe
- Tendon passes under flexor retinaculum

Posterior compartment of leg - Deep group
- Flex (plantar flex) and invert foot
- Origin: tibia + fibula
- 3 muscles
- Flexor … longus - flexes lateral 4 toes
- … posterior - inverts foot
- Flexor … longus - flexes great toe
- Tendon passes under flexor retinaculum
- Flex (plantar flex) and invert foot
- Origin: tibia + fibula
- 3 muscles
- Flexor digitorum longus - flexes lateral 4 toes
- Tibialis posterior - inverts foot
- Flexor hallucis longus - flexes great toe
- Tendon passes under flexor retinaculum

What nerve innervates the deep compartment of the posterior compartment of the leg?
tibial nerve - same as superficial muscle compartment
Label the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg

Posterior compartment of leg - deep muscles into foot
- Flexor hallucis longus inserts into … .. of … toe
- Tibialis posterior inserts into medial … + …
- Flexor digitorum longus inserts into distal … - crosses flexor hallucis longus
- Flexor hallucis longus inserts into distal phalanx of great toe
- Tibialis posterior inserts into medial cuneiform + navicular
- Flexor digitorum longus inserts into distal phalanges - crosses flexor hallucis longus

Posterior compartment of leg - deep muscles into foot
- Flexor hallucis longus inserts into distal phalanx of great toe
- Tibialis posterior inserts into medial cuneiform + navicular
- Flexor digitorum longus inserts into distal phalanges - crosses flexor hallucis longus
- Flexor hallucis longus inserts into distal phalanx of great toe
- Tibialis posterior inserts into medial cuneiform + navicular
- Flexor digitorum longus inserts into distal phalanges - crosses flexor hallucis longus

Lateral compartment of leg
- There are two muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg; the … … and … …
- The common function of the muscles is eversion – turning the sole of the foot … They are both innervated by the superficial fibular nerve.
- There are two muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg; the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis (also known as peroneal longus and brevis)
- The common function of the muscles is eversion – turning the sole of the foot outwards. They are both innervated by the superficial fibular nerve.

Lateral compartment of leg
- There are two muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg; the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis (also known as peroneal longus and brevis)
- The common function of the muscles is … – turning the sole of the foot outwards. They are both innervated by the … … nerve.
- There are two muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg; the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis (also known as peroneal longus and brevis)
- The common function of the muscles is eversion – turning the sole of the foot outwards. They are both innervated by the superficial fibular nerve.

Label the lateral compartment of the leg (2 muscles)
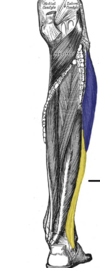

Fibularis longus
- The fibularis longus is the … and more … muscle within the compartment
- Evert foot and … foot
- The fibularis longus is the larger and more superficial muscle within the compartment
- Evert foot and plantarflex foot

Fibularis brevis
- The fibularis brevis muscles is … and … than the fibularis longus.
- … of the foot.
- The fibularis brevis muscles is deeper and shorter than the fibularis longus.
- Eversion of the foot.

Lateral compartment of leg


Lateral compartment of leg


Fibularis longus maintains the … arch
Fibularis longus maintains the transverse arch
Long tendons of the foot

Long tendons of the foot


Long tendons of the foot

Intrinsic muscles of the foot
- Similar to the …
- BE AWARE OF THESE MUSCLES ONLY - dont need to remember names or attachments
- Similar to the hand
- BE AWARE OF THESE MUSCLES ONLY - dont need to remember names or attachments

Blood supply to leg and foot (1)
- … artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under sartorius muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped … fossa - within this, the artery becomes the … artery
- Descends with vein through … fossa and enters the leg - splits into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- Anterior tibial artery pierces interosseous membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- Posterior tibial artery continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - fibular artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the posterior tibial artery continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through tarsal tunnel)
- Femoral artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under sartorius muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped popliteal fossa - within this, the artery becomes the popliteal artery
- Descends with vein through popliteal fossa and enters the leg - splits into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- Anterior tibial artery pierces interosseous membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- Posterior tibial artery continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - fibular artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the posterior tibial artery continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through tarsal tunnel)

Blood supply to leg and foot (1)
- Femoral artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under sartorius muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped popliteal fossa - within this, the artery becomes the popliteal artery
- Descends with vein through popliteal fossa and enters the leg - splits into … and … … arteries
- … … … pierces interosseous membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- … … … continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - fibular artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the … … … continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through tarsal tunnel)
- Femoral artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under sartorius muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped popliteal fossa - within this, the artery becomes the popliteal artery
- Descends with vein through popliteal fossa and enters the leg - splits into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- Anterior tibial artery pierces interosseous membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- Posterior tibial artery continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - fibular artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the posterior tibial artery continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through tarsal tunnel)

Blood supply to leg and foot (1)
- Femoral artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under … muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped popliteal fossa - within this, the artery becomes the popliteal artery
- Descends with vein through popliteal … and enters the leg - splits into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- Anterior tibial artery pierces … membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- Posterior tibial artery continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - … artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the posterior tibial artery continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through … …)
- Femoral artery passes through anterior compartment of thigh under sartorius muscle - heading towards medial side
- Passes through adductor hiatus to enter the diamond shaped popliteal fossa - within this, the artery becomes the popliteal artery
- Descends with vein through popliteal fossa and enters the leg - splits into anterior and posterior tibial arteries
- Anterior tibial artery pierces interosseous membrane to reach anterior compartment of the leg
- Posterior tibial artery continues down - forms a neurovascular bundle with tibial nerve - part way down gives off a branch - fibular artery, which heads towards lateral side of our leg - the posterior tibial artery continues down between the deep flexor muscles and passes under the flexor retinaculum with our tibial nerve (passes through tarsal tunnel)

Tarsal tunnel
- It is converted into a tunnel by the flexor retinaculum, which spans obliquely between the medial … and the … to form the roof.
- Underneath, contents reside: (anterior to posterior)
- … … tendon
- Flexor … … tendon
- Posterior tibial artery/vein
- Tibial nerve
- Flexor hallucis longus
- It is converted into a tunnel by the flexor retinaculum, which spans obliquely between the medial malleolus and the calcaneus to form the roof.
- Underneath, contents reside: (anterior to posterior)
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- Posterior tibial artery/vein
- Tibial nerve
- Flexor hallucis longus

Tarsal tunnel


Tarsal tunnel
- It is converted into a tunnel by the flexor retinaculum, which spans obliquely between the … malleolus and the calcaneus to form the roof.
- Underneath, contents reside: (anterior to posterior)
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- … … artery/vein
- … nerve
- Flexor … longus
- It is converted into a tunnel by the flexor retinaculum, which spans obliquely between the medial malleolus and the calcaneus to form the roof.
- Underneath, contents reside: (anterior to posterior)
- Tibialis posterior tendon
- Flexor digitorum longus tendon
- Posterior tibial artery/vein
- Tibial nerve
- Flexor hallucis longus

Where can we take the pulse of the posterior tibial artery?
within the tarsal tunnel

Medial/lateral plantar arteries
- … … artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- Medial plantar artery on medial side of foot towards great toe
- Lateral plantar artery heads laterally and swings round to form … … arch (passes under adductor hallucis muscle)
- This arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes … and … and anastamose with dorsalis pedis artery
-
Posterior tibial artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- Medial plantar artery on medial side of foot towards great toe
- Lateral plantar artery heads laterally and swings round to form deep plantar arch (passes under adductor hallucis muscle)
- Deep plantar arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes 1 and 2 and anastamose with dorsalis pedis artery

Medial/lateral plantar arteries
- Posterior tibial artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- Medial plantar artery on medial side of foot towards … …
- Lateral plantar artery heads laterally and swings round to form deep plantar arch (passes under … hallucis muscle)
- Deep plantar arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes 1 and 2 and anastamose with … pedis artery
- Posterior tibial artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- Medial plantar artery on medial side of foot towards great toe
- Lateral plantar artery heads laterally and swings round to form deep plantar arch (passes under adductor hallucis muscle)
- Deep plantar arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes 1 and 2 and anastamose with dorsalis pedis artery

Medial/lateral plantar arteries
- Posterior tibial artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- … plantar artery on … side of foot towards great toe
- … plantar artery heads … and swings round to form deep plantar arch (passes under adductor hallucis muscle)
- Deep plantar arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes 1 and 2 and anastamose with dorsalis pedis artery
- Posterior tibial artery enters the foot, divides into plantar arteries:
- Medial plantar artery on medial side of foot towards great toe
- Lateral plantar artery heads laterally and swings round to form deep plantar arch (passes under adductor hallucis muscle)
- Deep plantar arch pierces through into reach the dorsum of the foot between toes 1 and 2 and anastamose with dorsalis pedis artery

Label the diagram


Dorsalis pedis artery
- … … artery descends with the deep fibular nerve, passing towards extensor retinaculum
- Changes name to dorsalis pedis (dorsal artery of the foot)
- Sits … to the large tendon of extensor hallucis longus
- Dorsalis pedis passes through towards plantar side of foot to anastomose with deep plantar arch
- Anterior tibial artery descends with the deep fibular nerve, passing towards extensor retinaculum
- Changes name to dorsalis pedis (dorsal artery of the foot)
- Sits laterally to the large tendon of extensor hallucis longus
- Dorsalis pedis passes through towards plantar side of foot to anastomose with deep plantar arch

Dorsalis pedis artery
- Anterior tibial artery descends with the deep … nerve, passing towards … retinaculum
- Changes name to dorsalis pedis (dorsal artery of the foot)
- Sits laterally to the large tendon of extensor hallucis longus
- Dorsalis pedis passes through towards plantar side of foot to anastomose with … … arch
- Anterior tibial artery descends with the deep fibular nerve, passing towards extensor retinaculum
- Changes name to dorsalis pedis (dorsal artery of the foot)
- Sits laterally to the large tendon of extensor hallucis longus
- Dorsalis pedis passes through towards plantar side of foot to anastomose with deep plantar arch

Nerve supply to the leg
- Supplied by the terminal branches of the … nerve (apart from the skin on medial side of leg and foot - saphenous nerve - terminal branch of femoral nerve)
- … nerve approaches popliteal fossa - 2 branches:
- … nerve towards posterior compartment
- … … nerve (further divides into deep fibular - anterior compartment, superficial fibular - lateral compartment)
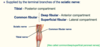
- Supplied by the terminal branches of the sciatic nerve (apart from the skin on medial side of leg and foot - saphenous nerve - terminal branch of femoral nerve)
- Sciatic nerve approaches popliteal fossa - 2 branches:
- Tibial nerve towards posterior compartment
- Common fibular nerve (further divides into deep fibular - anterior compartment, superficial fibular - lateral compartment)
Nerve supply to the leg
- Supplied by the terminal branches of the sciatic nerve (apart from the skin on medial side of leg and foot - saphenous nerve - terminal branch of … nerve)
- Sciatic nerve approaches popliteal fossa - 2 branches:
- Tibial nerve towards posterior compartment
- Common fibular nerve (further divides into … fibular - anterior compartment, … fibular - lateral compartment)
- Supplied by the terminal branches of the sciatic nerve (apart from the skin on medial side of leg and foot - saphenous nerve - terminal branch of femoral nerve)
- Sciatic nerve approaches popliteal fossa - 2 branches:
- Tibial nerve towards posterior compartment
- Common fibular nerve (further divides into deep fibular - anterior compartment, superficial fibular - lateral compartment)

Nerve supply to the leg - Label


Tibial nerve


- The tibial nerve passes through the … tunnel to enter the foot - divides into medial and lateral … nerves
- Supplies the … … muscles and … surface of foot (skin)
- The tibial nerve passes through the tarsal tunnel to enter the foot - divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves
- Supplies the plantar intrinsic muscles and plantar surface of foot (skin)
Tibial nerve - Motor vs sensory function
- Motor: … compartment of leg + plantar … muscles
- Sensory: … surface of foot
- Motor: Posterior compartment of leg + plantar Intrinsic muscles
- Sensory: Plantar surface of foot
Clinical: … tunnel syndrome (compression of tibial nerve)
Clinical: tarsal tunnel syndrome (compression of tibial nerve)
Clinical: … tunnel syndrome (compression of … nerve)
Clinical: … tunnel syndrome (compression of tibial nerve)
Common fibular nerve
- Common fibular nerve divides into … fibular nerve and … fibular nerve
- … fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - anterior compartment of leg and dorsal intrinsic muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes 1 and 2
- … fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - lateral compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on dorsum of foot + anterior leg
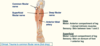
- Common fibular nerve divides into superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve
-
Deep fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - anterior compartment of leg and dorsal intrinsic muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes 1 and 2
-
Superficial fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - lateral compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on dorsum of foot + anterior leg

Common fibular nerve
- Common fibular nerve divides into superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve
- Deep fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - … compartment of leg and dorsal intrinsic muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes … and …
- Superficial fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - … compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on … of foot + anterior leg
- Common fibular nerve divides into superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve
- Deep fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - anterior compartment of leg and dorsal intrinsic muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes 1 and 2
- Superficial fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - lateral compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on dorsum of foot + anterior leg
Common fibular nerve
- Common fibular nerve divides into superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve
- Deep fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - anterior compartment of leg and dorsal … muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes 1 and 2
- Superficial fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - lateral compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on dorsum of foot + … leg
- Common fibular nerve divides into superficial fibular nerve and deep fibular nerve
- Deep fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - anterior compartment of leg and dorsal intrinsic muscles
- Sensory - skin between toes 1 and 2
- Superficial fibular nerve:
- Motor supply - lateral compartment of leg
- Sensory - skin on dorsum of foot + anterior leg

Clinical: Trauma to … … nerve (foot drop)
Clinical: Trauma to common fibular nerve (foot drop)

Clinical: Trauma to common fibular nerve (foot …)
Clinical: Trauma to common fibular nerve (foot drop)
Cutaneous innervation - leg and foot


Cutaneous innervation - leg and foot


Cutaneous innervation - leg and foot




