Gynae and the law/women's rights - Female Genital Mutilation & Termination of Pregnancy Flashcards
(33 cards)
What is Female Genital Mutilation? (FGM)
FGM is a destructive operation, during which the female genitals are partly or entirely removed or injured
Female Genital Mutilation is also called…
‘female genital cutting’, ‘cutting’, ‘female circumcision’, ‘purification’ or ‘ritual cleanliness’, ‘Gash’, ‘excision’, ‘female genital distortion’, ‘female sexual mutilation’
The term ‘Female Genital Mutilation’ was adoped in … by UN agencies
2008
- “The term is non-judgmental as it is a medical term describing what is done to female genitalia. Mutilation is the removal of healthy tissue” (Declaration: on the Terminology FGM: 6th IAC General Assembly, 2005, Mali)
- This Term has a negative connotation and emphasises the gravity of the harm caused by the practice
WHO definition of Female Genital Mutilation
‘All procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons’
Numerous factors contribute to the prevalence of the practice of FGM, yet in every society in which it occurs, FGM is a manifestation of entrenched … …
gender inequality
Reasons for Female Genital Mutilation
- Raising Girls: Preparation for …, marriage and to prove …
- Femininity: FGM is associated with cultural ideas of femininity and modesty, which include the notion that girls are ‘clean; and ‘beautiful’ after removal of body parts that are considered ‘male’ or ‘unclean’
- Reduce …: Narrowing of the vaginal opening is thought to discourage extra-marital sex because of the fear of re-opening
- Social Convention: …
- …: FGM can be considered a … tradition, which is often used as an argument for it’s continuation
- …: FGM practitioners often believe in a … justification, actually expressed very rarely by … leaders.
- Raising Girls: Preparation for adulthood, marriage and to prove virginity
- Femininity: FGM is associated with cultural ideas of femininity and modesty, which include the notion that girls are ‘clean; and ‘beautiful’ after removal of body parts that are considered ‘male’ or ‘unclean’
- Reduce Libido: Narrowing of the vaginal opening is thought to discourage extra-marital sex because of the fear of re-opening
- Social Convention: Conforming
- Culture: FGM can be considered a cultural tradition, which is often used as an argument for it’s continuation
- Religion: FGM practitioners often believe in a religious justification, actually expressed very rarely by religious leaders.
Epidemiology - FGM
- How many million affected worldwide?
- How many million affected in Europe?
- How many million affected worldwide? - 200 million
- How many million affected in Europe? - 1 million

FGM in the UK/Europe
- Why is FGM happening in Europe? Why a problem? Is it our problem?
- Increasingly identified in families who originate from FGM-practicing-countries- victims are …, who continued this practice when they …
- Up to … million girls and women living in the EU are affected by FGM
- … live in the UK,… in France, … in Germany, Austria and Switzerland.
- Why is FGM happening in Europe? Why a problem? Is it our problem?
- Increasingly identified in families who originate from FGM-practicing-countries- victims are migrants, who continued this practice when they migrated
- Up to 1 million girls and women living in the EU are affected by FGM
- 140,000 of them live in the UK, 100,000 in France, 50,000 in Germany, Austria and Switzerland.
FGM in the UK/Europe - Ignorance
- Victims are usually approached in the health sector and by authorities in an inadequate way, ignorance prevails
- Make a change:
- … around communication and language
- Seek out … … and learn from … …
- Understand who is at …
- Ignorance:
- Victims are usually approached in the health sector and by authorities in an inadequate way, ignorance prevails
- Make a change:
- Training around communication and language
- Seek out online resources and learn from real life stories of survivors
- Understand who is at risk
FGM in the UK/Europe - Medical Qualification
- Few European country examine or explore FGM as part of the regular curriculum or vocational training of doctors, midwives and social workers.
- Make a change:
- Increased …
- … empowerment to ‘always ask’
- … - formal guidance available to HCW and patient information leaflets
- Few European country examine or explore FGM as part of the regular curriculum or vocational training of doctors, midwives and social workers.
- Make a change:
- Increased Education
- Midwifery empowerment to ‘always ask’
- RCOG - formal guidance available to HCW and patient information leaflets
Who does FGM?
- FGM is usually performed by ‘… …’ - women who …
- It is also performed by traditional … and occasionally by …, nurses or doctors trained in Western medicine.
- The procedure is usually performed without … and under dreadful and unhygienic circumstances.
- The procedure may be done using …, …, … or …
- Often takes place in a specific dedicated place where girls and women are left alone until they are ‘better’ to return to their community - tents/ huts/ secluded areas.
- FGM is usually performed by ‘professional circumcisers’ - women who have a high reputation within their societies
- It is also performed by traditional midwives and occasionally by healers, nurses or doctors trained in Western medicine.
- The procedure is usually performed without anaesthetic and under dreadful and unhygienic circumstances.
- The procedure may be done using razor blades, scissors, knives, shards of glass
- Often takes place in a specific dedicated place where girls and women are left alone until they are ‘better’ to return to their community - tents/ huts/ secluded areas.
Classification of FGM
- How many Types?
- Type… and Type … form the majority of procedures (80%)
- Which type is the most severe?
- 4 Types
- Clitoroidectomy
- Excision
- Infibulation
- All other procedures
- Type 1 and Type 2 are the most common - 80% of all FGM
- Type 3 is the most extreme
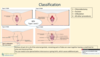
What is Type 3 FGM?
- Type 3 = Infibulation
- Excision of part of or all of the external genitals, remaining parts of labia are sewn together leaving a small hole for urine and menstrual flow
- After FGM, the scar must be opened before intercourse or giving bith - which causes additional pain

Complications of FGM - Immediate/Short Term
- Haemorrhage
- Pain
- Injury to adjacent tissues
- Fractures
- Urinary Retention
- Wound Infection (herbs, ash)
- Tetanus
- Gangrene
- HIV/Hep (non-sterile instruments)
- Sepsis
- Death
Complications of FGM - Long Term
- Recurrent …
- Painful …
- … Scarring and cysts
- … Difficulties
- I… (Ascending infections, smears, penetration)
- Complications in …
- P…
- Recurrent UTI
- Painful menstruation
- Keloid Scarring and cysts
- Sexual Difficulties
- Infertility (Ascending infections, smears, penetration)
- Complications in pregnancy
- Psychological
Complications of FGM - Pregnancy/ Delivery
- Difficulty with:
- Carrying out … examinations
- … of labour - IOL with prostaglandins
- Evacuation of uterus in …/RPOC
- Intervention sin labour - FSE/FBS, identifying cord …
- … labour
- Increase risk of severe … and h…
- Increased risk of … section - particularly if not dislosed prior to birth, no plan for management
- Difficulty with:
- Carrying out vaginal examinations
- Induction of labour - IOL with prostaglandins
- Evacuation of uterus in miscarriage/RPOC
- Intervention sin labour - FSE/FBS, identifying cord prolapse
- Prolonged labour
- Increase risk of severe tears and haemorrhage
- Increased risk of caesarean section - particularly if not dislosed prior to birth, no plan for management
Management of FGM - Child Under 18
- What is done?
- Ring police (101) - mandatory reporting since Oct 2015
- Contact designated child protection / safeguarding lead
- Referral Social Services
Management of FGM in adults - Non-pregnant
- Assessment:
- Identify … and whether ..-… is indicated, associated … etc
- Referral:
- Women: FGM service (psychosexual, urogynae, infertility)
- Offer … services
- Testing …, Hep B+C, … Health Screen
- Consider any … at risk
- Assessment:
- Identify type of FGM and whether de-infibulation is indicated, associated cysts etc
- Referral:
- Women: FGM service (psychosexual, urogynae, infertility)
- Offer psychological services
- Testing HIV, Hep B+C, Sexual Health Screen
- Consider any children at risk
De-infibulation
- Treatment for FGM (deinfibulation). Surgery can be performed to open up the vagina, if necessary. This is called deinfibulation.

FGM - Management in Pregnancy
- Antenatal
- Ask all women about FGM at booking irrespective of ….
- Offer referral for … assessment
- All trusts to have named lead obstetrician and midwife (for s…)
- Examine: Document the …? Whether de-infibulation indicated and when
- Antenate/1st stage labour/delivery/post CS
- Involve safeguarding / social services - think about risk to any …
- Intrapartum
- …-… if indicated and discussed, manage labial tears as standard practice
- Post-natal
- Debrief/Education/Safeguarding/Social Services
- Antenatal
- Ask all women about FGM at booking irrespective of country of origin
- Offer referral for psychological assessment
- All trusts to have named lead obstetrician and midwife (safeguarding)
- Examine: Document the Type? Whether de-infibulation indicated and when
- Antenate/1st stage labour/delivery/post CS
- Involve safeguarding / social services - think about risk to any female newborn
- Intrapartum
- De-infibulation if indicated and discussed, manage labial tears as standard practice
- Post-natal
- Debrief/Education/Safeguarding/Social Services
Is Re-infundibulation legal?
No - illegal

FGM and UK Law Quiz
- T or F

- T
- T
- T
- T
- T
- F
- T
- T
The Female Genital Mutilation Act 2003 - Can Parents can face prosecution?
- Yes they can
- Home Office aims to ‘strengthen the law’ only one person in the UK has ever been convicted

FGM - Prosecution - the first (and only) in 2019
- What happened?
- In the successful prosecution of February 2019, the defendant stated that the injuries to her daughter were caused by her daughter falling on sharp metal object after reaching for cookies
- The injuries required emergency surgery
- Doctor determined it to be FGM T2
- Most prosecutions are not successful





