C11 - The hindgut of carnivores and horses, blood supply and innervation Flashcards
1
Q
Define hindgut
A
- The caudal portion the the embryonic gut which develops into the colon and the rectum
- Begins at the cecum
- Ends at the anus
2
Q
Give the portions of the hindgut
A
- Cecum (Right side of the abdominal cavity, except from in pig)
- Colon
- Rectum (Partly inside, partly outside the abdomen)
3
Q
Colon
Dog
A
-
Colon ascendens
- Shortest of the three segments
- Lateral: duodenum descendens and right lobe of pancreas
- Medial: root of the mesentery
- Flexura coli dextra
-
Colon transversum
- Right → left, passes between stomach and a. mesenterica cranialis
- Th12 level
- Flexura coli sinistra
-
Colon descendens
- Extends to the pelvic inlet, continued by the rectum
- Longest of the three segments
- Lies dorsally in the left half of the abdominal cavity
- Related medially to duodenum ascendens: plica duodenocolica
- Location: dosal in the abdomen

4
Q
Colon
Horse
A
-
Colon ascendens [Colon crassum] (Loop fromed by the colon ventrale and colon dorsale, which bends aronud to the left side)
- Colon ventrale dextrum (Cecum → flexura sternalis, 4 tenia and haustra)
- Flexura sternalis [=flexura diaphragmatica ventralis]
- Colon ventrale sinistrum (Flexura sternalis → flexura pelvina, 4 tenia and haustra)
- Flexura pelvina
- Colon dorsale sinistrum (Flexura pelvina → flexura diaphragmatica
- Flexura diaphragmatica [=flexura dorsalis]
- Colon dorsale dextrum (Terminal part of colon crassum, joins colon transversum, 3 tenia)
- Ampulla coli (Dilatation of colon dorsale dextrum)
- Colon transversum
- Colon descendens [Colon tenue] (Flexura coli sinistra → rectum)
- Teniae coli
- Haustra coli
- Everything is attached to the right side
- Only tenia and haustra on the ventral portion
- Can hold 120 liter

5
Q
Colon
Horse: distribution of haustra & tenia
A
-
Colon ascendens:
-
Colon ventrale dextrum: 4 tenia
- Tenia libera medialis
- Tenia libera lateralis
- Tenia mesocolica medialis
- Tenia mesocolica lateralis
-
Colon ventrale sinistrum: 4 tenia
- Tenia libera medialis
- Tenia libera lateralis
- Tenia mesocolica medialis
- Tenia mesocolica lateralis
-
Colon dorsale sinistrum: 1 tenia
- Tenia mesocolica
-
Colon dorsale dextrum: 3 tenia
- Tenia libera medialis
- Tenia libera lateralis
- Tenia mesocolica
- Ampulla coli: 3 tenia
-
Colon ventrale dextrum: 4 tenia
-
Colon descendens:
- 2 tenia
- Tenia libera
- Tenia mesocolica
- 2 tenia
Total: 17????? riktig?
6
Q
Caecum
Dog and horse
A
- Basis caeci (Dorsal dilation of cecum, eq)
- Corpus caeci
- Apex caeci
- Curvatura caeci major
- Curvatura caeci minor
-
Teniae caeci (eq, su) (Bands of cecum)
- Tenia dorsalis (Ø su)
- Tenia ventralis
- Tenia medialis
- Tenia lateralis
- Haustra caeci (eq, su) (Sacculations of the cecum between the teniae and between the plica semilunares)
- Ostium caecocolicum (Opening between cecum → colon)
- Valva caecocolica (eq)
- M. sphincter caeci (ca, bo, su)
- Plica iliocolica (Attaches to tenia dorsalis)
- Plica caecocolica (C**olon ventrale dextrum → tenia lateralis of the caecum)
-
Dog:
- No haustra, no tenia
- Right side, L2-L4
- Caudal directed
- Attached to ileum and colon ascendens by peritoneal folds
- Communicate with colon ascendens at the ostium ileocaecolicaum
-
Horse:
- Location in horse:
- Right dorsal part of the abdominal cavity
- Most dorsal part: basis caeci
- Basis caeci extends from pelvic inlet to rib 14/15
- Dorsally: attaches to fascies ventralis of right kidney and right lobe of the pancreas
- Left surface of basis caci is attached to the root of the mesentery
- Haustra/tenia: 4
- Can hold 30-50 liter
- Location in horse:

7
Q
Caecum
Give the interspecies differences
A
-
Tenia caeci (eq, sus)
- Tenia dorsalis (ø sus)
- Tenia ventralis
- Tenia medialis
- Tenia lateralis
- Haustra caeci (eq, sus)
- Valva caecolica (eq)
- M. sphincter caeci (ø eq)
- Ca: ø haustra & tenia
- Ru: ø haustra & tenia
- Eq: 4 haustra & tenia
- Su: 3 huastra & tenia
8
Q
Rectum
Dog and horse
A
- Ampulla recti (enlargement of terminal part)
- Follows colon into the pelvic cavity, terminates at canalis analis
- Pelvic part of large intestines
- Most is covered with peritoneum
Dog:
- Short
- L7 level
- enters the pelvic cavity ventral to sacrum
- In the retroperitoneal part of the pelvic cavity: ampulla recti
- Outer muscle layer of rectum: m. retrococcygeus
Horse:
- Peritoneal cover is last → retroperitoneal tissue
- No more sacculation
- Amulla coli = canalis analis
- M. retrococcygeus deep from long muscle layer of the rectum
9
Q
Bloodsuply of the large intestines
Dog
A
- Caecum: a. ileocolica → a. caecalis
- Colon ascendens:
- a. ileocolica → r. colicus
- a. mesenterica cranialis → a. colica dextra
- Colon transversus: a. mesenterica cranialis → a. colica media
- Colon descendens:
- a. mesenterica caudalis → a. colica sinistra
- a. colica media
- Rectum: a. mesenterica caudalis → a. rectalis cranialis
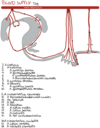
10
Q
Blood supply of the large intestines
Horse
A
- Cecum:
- A. ileocolica → a. caecalis medialis et lateralis
- Colon ascendens:
- Colon ventrale: a. ileocolica → r. colicus
- Colon dorsale: a. mesenterica cranialis → a. colica dextra
- Colon transversus:
- A. mesenterica cranialis → a. colica media
- Colon descendens:
- A. mesenterica caudalis → a. colica sinistra
- Rectum:
- A. mesenterica caudalis → a. rectalis cranialis
11
Q
Innervation
A
- Sympathetic:
- Decreased activity
- Ggl. & plexus mesentericus cranialis
- Ggl. & plexus mesentericus caudalis
- Parasympathetic:
- Increased activity
- Vagal nerves: supply intestines to the junction between colon transversus and colon descendens
- Pelvic nerves: supply colon descendens and rectum


