Spine Head and Neck Imaging Flashcards
What are some basic principles of SA radiography?
Always need GA or at least heavy sedation to allow good positioning
Always need at least 2 orthogonal views
Need to avoid/consider magnification, rotation and beam divergence effects
Appropriate exposure for region of interest
How should the area of interest be related to the x-ray plate?
Area of interest should be nearest to the plate
Label the blue squares on this image of the spine

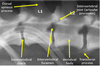
What is this yellow arrow showing as an example of pathology?

Intervertebral disc prolapse (narrowed space)
What are the yellow arrows pointing at with regards to pathology?

Intervertebral disc calcification
What is this radiograph showing with regards to an example of pathology?

Intervertebral disc prolapse and spondylosis derformans
What pathology is this radiograph showing?

Discospondylitis - an infection of the intervertebral disc space
What pathology can be seen on this radiograph?

Vertebral fracture
What is spondylosis deformans?
Where is it considered ‘incidental’?
Spondylosis deformans is a condition that affects the vertebral bones of the spine and is characterized by the presence of bony spurs or ‘osteophytes’ along the edges of the bones of the spine
SD on the ventral and lateral aspects of the vertebral end plates is usually incidental - unless it becomes excessive and extends dorsally when it can affect nerve roots
What is pictured here on the radiograph?

Spondylosis Deformans
What are some basic principles of equine spinal radiography?
Some basic principles
- Always need at least 2 orthogonal views –not always realistic or possible
- Always need anaesthesia or at least heavy sedation to allow good positioning –often done under sedation
- Need to avoid/consider magnification, rotation and beam divergence efffects
- Appropriate exposure for region of interest
What is myelography?
- Myelographyis the injection of water-soluble iodine contrast medium into the subarachnoid space
- Non-ionic contrast medium (as opposed to ionic) should always be used to reduce side effects
- Contrast can be injected into the cisterna magna or into the caudal lumbar subarachnoid space
- Myelographyis generally safe. However, it can lead to short term side effects, such as inco-ordination, and injection of contrast into the spinal cord itself can result in permanent paralysis or, rarely, death!
What type of contrast medium should be used in myelography to reduce side effects?
Non-ionic contrast medium (as opposed to ionic)
What are some side effects of myelography?
It is generally safe. However, it can lead to short term side effects such as inco-ordination, and injection of contrast into the spinal cord itself can result in permanent paralysis or, rarely, death!
What are some sites for spinal lesions?
Why is this important for myelography?
Each location gives a typical myelographic appearanmce depending on where the lesion is in relation to the contrast in the subarachnoid space

What is a cisternal puncture?
a diagnostic procedure that can be performed in order to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for biochemical, microbiological, and cytological analysis, or rarely to relieve increased intracranial pressure.
Technically easier than lumbar puncture
Less useful for thoracolumbar lesions as contrast may not reach that far or accurately delineate them

Where do you do lumbar puncture in a dog and a cat?
L5 - 6 dog
L6 - 7 cat
When is CT useful?
What can CT be combined with?
Same information as routine radiography but slice detail avoids superimposition
Can be combined with myelography
Can be useful in circumstances where MRI not feasible, e.g. metal implants
May be better for information from osseous structures cf. MRI
What can CT be combined with?
Myelography
Why is MRI good?
Cross sectional imaging avoids superimposition
Excellent soft tissue definition
What can be seen here?

- Mid sagittal T2 weighted image of cervicothoracic junction in mature adult dog
- There is dorsal deviation of ventral subarachnoid space (hyperintenseline) with compression of the overlying spinal cord and loss of dorsal sub-arachnoid space.
- Diagnosis: Extrusion of disc C6-7
What can be seen here on this MRI?

Fibrocartilagenous embolism (FCE)
- T2 weighted mid sagittal and transverse images from the cervical spine of of a mature dog.
- Focal discrete region of intraparenchymalspinal cord hyperintensitywhich is lateralisedto the left and affecting the central region of the spinal cord parenchyma (arrows). Consistent with a focal region of oedema, which with supporting signalmentand history is consistent with FCE.
What can be seen on this MRI?

Neoplasia
- Sagittal and transverse T1 weighted post-contrast images from the atlanto-occiptal region of a mature dog.
- There is large focal space-occupying mass lesion dorsolateral to the spinal cord on the right between the dorsal lamina of C1 and the occipital bone. The mass has enhanced strongly with gadolinium consistent with neoplasia and is producing considerable compression of the adjacent cervical spinal cord. (Histopathology confirmed a meningioma following excisional biopsy)
What can be seen on this MRI?

Discospondylitis
- Midline sagittal T1 and T2 weighted images from the lumbosacral region of a mature dog.
- There is loss of signal from the nucleus pulposus of the L7-S1 intervertebral disc and T1 and T2 hypointensityof the vertebral bodies and end plates of L7 and S1 adjacent to this disc. There is some dislocation of L7-S1 with ventral displacement of S1 with respect to L7.
- The imaging appearance is consistent with a diagnosis of discospondylitis
What is the problem with radiography of the skull?
Radiography of the skull is challenging as:
- Anatomy is complex
- Structures are bilaterally symmetrical and can be impossible to distinguish on lateral views
- Accurate positioning is difficult
- Other poor technique can make interpretation difficult, e.g. inadequate exposure or image contrast
What are some indications for radiographing the skull?
Indications:
- Trauma
- Malformation (e.g. hydrocephalus)
- Foreign bodies
- Neoplasia
- Dental investigation
- Intracranial pathology
- Ear disease
- Nasal disease
Trauma
- Fractures of the cranium –Difficult to diagnose
- Fractures of the mandible/maxilla –Easier to detect Zygomatic arch fracture
What do you see on imaging of the skull with hydrocephalus?

What can you see on radiographs with ear disease?

What are some things you can see on a radiograph with nasal disease?
Examples include:
- Increased nasal cavity radiopacitywith retention of underlying turbinate pattern in rhinitis
- Increased radiopacitywith loss of turbinatesin neoplasia
- Decreased radiopacity with loss of turbinatesin fungal rhinitis (e.g. Aspergillosis) Rhinitis Neoplasia

Define fontanelle
a space between the bones of the skull in an infant or fetus, where ossification is not complete and the sutures not fully formed. The main one is between the frontal and parietal bones.
How can ultrasound be used for imaging the skull?
Lateral ventricles may be imaged and can determine if they are enlarged e.g. in hydroephalus
US may be useful if open fontanelle
Which imaging modality is the way forward for intracranial lesions?
MRI
What is good about MRI?
Good soft tissue information
Good resolution of lesions from normal tissue
However, still does not provide a histological diagnosis
Good bone detail and some soft tissue detail - CT or MRI?
CT
What is the calvarium?
the portion of a skull including the braincase and excluding the lower jaw or lower jaw and facial portion
How should you position the animal for a lateral view of the calvarium?
- Lateral recumbency and the nose and mandible raised with lucent pads so that the saggital plane of the skull is parallel to the cassette
- Centre beam mid-way between the eye and the ear
How should you postion for a dorsoventral view of the calvarium?
Lateral recumbency and the nose and mandibe raised wtih the lucent pads so that the saigittal lane of the skull is parallel to the cassette
Centre beam mid way between the eye and the ear


