Imaging SA Repro Flashcards
(43 cards)
- A 10 year old entire male, large crossbreed dog was presented two months previously with haematuria (mostly at the end of urination) and occasional dyschezia. The dog appeared slightly stiff on its hindlegs.
- Physical examination revealed a mildly painful caudal abdomen. Rectal temp. 40.1C. Preputial/penile/perineal examination was normal. Otherwise the dog appeared well.
- The dog was treated for a presumptive lower urinary tract infection with a 7 day course of amoxycillin-clavulanate. The owner did not keep the follow-up appointment.
- The dog is represented. The owner reports that the blood in the urine settled with the treatment, although the dog still struggles to do “number twos” at times.
- In the past few days, the bleeding has returned.
- Physical exam. indicates no abdominal pain this time, but a firm rounded caudal abdominal mass is palpated just cranial to the pelvic inlet. Immediately cranial to this, a larger, tense, rounded mass is felt, and pressure on this results in a small amount of urination.
What do we do next?
Plain radiographs
Then maybe US
What is the normal radiology of the prostate?
•Located in the caudal retroperitoneum
–Caudal to bladder neck
–Ventral to descending colon / rectum
•Seen in the entire dog as a homogenous soft tissue opacity
–Occupies up to 70% of pelvic inlet
–Especially prominent in Scotties
- Smaller and often not seen in neutered males
- Not usually seen in the cat
What can be seen here?

2 ST sections in cd abdo
Which structures do you think are affected?
Prostate
Bladder – big and tense
Urethra
Don’t forget spinal disease in a large bladder
What can be seen here?

Mineral and irregular prostate
New bone around pelvis
Spondylosis of L vert
Which prostatic conditions may be associated with intra prostatic mineralisation? (2)
–Chronic prostatitis
– Neoplasia
What can be seen here?

New bone on the ventral aspect of caudal vertebrae
Spondylosis
Between end plates – more irregular aggressive new bone
If you get this on caudal vert – pathognomic of neoplasia mets
Marked ST opacity ventralll – LN (infection, or neoplasia)
What can be seen here?

Local peritoneal dx – increase opacity
Colon – has gas in
Might be LN enlargement near colon
Inflamm vs neoplasia
What is this?
What is the most liekly prostatic disease causing this appearance?

Pneumocysto and then contrast
Contrast has produced this appearance
What is the most likely prostatic dx causing this appearace?
Neoplasia - characteristic
NB: Cystic disease (e.g. metaplasia) – but youd never get this degree of cavity communicatin with urethra!!!
Dog and dysuric
Large mass mid-cd abdomen
What is the most likely diganosis?

Bladder neoplasia
Extra parenchymal prostatic cyst
What has created this image?
What can be seen?

Pneumocystogram
Bladder normal – just displaced
Parenchymal cyst
You can see a mineral line and this is due to cyst cause mineralised lining (immediately puts this top of D/D)
Hamatouria, dysuria
What can be seen?

2 ST opacity – maybe bladder and prostate
What has created this image?
What is seen?
What is the likely diagnosis?

Positive cystogram
Normal cranial bladder
Caudally – bisected structure
Size over 70% of pelvic inlet – prostate
This is classic for BPH – benign prostatic hyperplasia (smooth)
What is this?

Smooth symmetrical enlargement consistent with BPH
What is this?
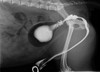
Less marked enlargement with irregular contrast leakage suggestive of neoplasia
What is the normal appearance of prostate ultrasound?
- Normal prostate is bilobed with a moderately and even granular echotexture and smooth margins
- The prostate increases in size and echogenicity with age
- Small prostatic cysts are a common incidental finding in older entire dogs

What is this appearance?

Immature Hypoechoic
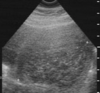
Discuss the appearance here
Mature – hard to make out margin
Smooth and rounded
Under 2cm
How does the overall echogenicity compare to the normal prostate?
What is the liekly differential?

Heterogenous
More echogenic
Bigger too
Diagnosis:
BPH
Cant rule out infection = not many cysts
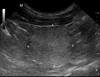
What’s going on here?

Several cystic cavities but this can be normal
How does the overall echogenicity compare to the normal prostate?
What is the liekly diagnosis?

Hypoechoic
More heterogenous (marbled appearance)
Slightly enlarged
Likely Diagnosis:
Acute prostatitis ** was this
Neoplasia possible
Note: there are not enough fluid cavities for cystic disease
What is going on here?

Abscess
Hypoenchoic
Infalmmatory disease
From the acute prostatis
Which best describes US signs?
What is the likely diagnosis?

Heterogenous
Irregular shapes
Poorly marginated
Diagnosis:
Neoplasia – so much worse than others
What is this?

This is chronic prostatitis
Care when interpreting the heterogenous appearance
What can be seen here?

Neoplasia
Prostate ventral and invading bladder neck