Exotic reproduction Flashcards
Discuss Ferret:
Male Reproductive Disorders?
Neoplasia
ØTesticular “ similar to dog
ØPrepuce
Prostate
ØHyperplasia and cysts
ØNearly always secondary to adrenal disease
ØUrinary obstruction, tenesmus and infection
ØTreatment (obstruction) “ catheterisation, cystostomy, marsupialisation
ØTreatment (adrenal disease) “ adrenalectomy and/or deslorelin (see endocrine lecture)

Discuss Ferret:
Female Reproductive Disorders?
Neoplasia
ØOvary most common site –> may cause persistent oestrus
ØRight pic granulosa cell tumour causing bilateral alopecia
Pyometra
ØRule out/distinguish from a persistent oestrus
ØStump pyometra –> usually secondary to adrenal disease or a retained ovarian remnant

Discuss preganncy toxaemia in ferrets?
ØDue to negative energy balance in late gestation
ØUsually due to reduced food intake/provision or very large litters
ØHypoglycaemia, ketosis, hypothermia
ØAggressive medical stabilisation and prompt caesarean required
ØPrognosis very guarded
Discuss persistent oestrus in the ferret?
Ø Ferret is an induced ovulator. When it comes into oestrus physical copulation stimulates ovualtion.
Ø About 50% of females will remain in oestrus unless mated
Ø Causes a prolonged oestrus results in oestrogen-induced bone marrow toxicosis
Ø Results in pancytopaenia and eventually death
What are the clinical signs of persistent oestrus in the ferret?
Persistent Oestrus (Clinical Signs)
ØEarly stages swollen vulva
ØPale mucus membranes
ØSymmetrical alopoecia of flanks
and tail
ØIn more advanced cases get bobe marrow suppression Petichiae and/or ecchymoses
•Persistent oestrus can last only a few weeks before these severe signs seen

What is persistent oestrus prevention in the ferret?
Persistent Oestrus (Prevention)
Ø GnRH-agonist implant e.g. Deslorelin
Ø Use a vasectomised hob to go through mating process without any chance of fertilisation
Ø Proligestone injection (delvosterone) (‘jill jab’) Licensed treatment
Ø Ovariohysterectomy before first oestrus
What is persistent oestrus treatment in the ferret?
Persistent Oestrus (Treatment)
ØOvariohysterectomy BUT patients are often poor surgical candidates → must stabilise first
ØBlood transfusion may be required
ØStimulate ovulation → hCG or proligestone
ØGnRH-agonist implant e.g. Deslorelin
Discuss Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
- Hyperadrenocorticism (HAC) in ferrets results in elevated sex hormones and NOT cortisol.
- Appears to develop as a result of neutering
- Increased circulating levels of gonadotrophins due to no negative feedback from the gonads.
- Adrenal cortex is persistently stimulated leading to adrenal hyperplasia, tumour formation and raised circulating sex hormones
- Keeping ferrets indoors may result in similar physiological effected due to the lack of natural, seasonal light cycles
*
Discuss the incidence of Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
- Almost epidemic (20% incidence) in USA where ferrets are neutered at 6-8 weeks and kept indoors
- Until recently considered rare in the UK
- Is on the increase and is one of the commonest reasons for a ferret to be presented to the authors practice
What are the clinical signs of Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
Clinical Signs
- Symmetrical alopoecia & ‘rat tail’
- Vulvar swelling in neutered jills
- Sexual behaviour in neutered hobs
- Non specific Pruritus with no obvious cause
- Urinary obstruction in males due to prostate disease

How is Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism diagnosed?
Diagnosis
- Clinical signs & history are highly suggestive
- May be able to palpate enlarged adrenal
- Serum elevation in one or more of the sex hormones → Androstenedione, oestradiol & 17 α-hydroxyprogesterone
- Abdominal ultrasound → enlarged adrenal(s) (normal adrenal gland is size of grain of rice and only increases size by 50% when sick so difficult to find)
- Exploratory laparotomy
What are the differential diagnoses for Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
Differential Diagnoses
- Retained ovarian remnant
- Persistent oestrus
- Gonad neoplasia
- Allergic and non-allergic skin disease
How can you prevent Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
Prevention
- Ideally do not neuter ferrets
- Problems in entire ferrets with malodour in hobs and persistent oestrus in jills and sometimes aggression especially in jills
- Alternatives to neutering include vasectomised hob, proligestone injection (‘jill jab’), Deslorelin implant (see under treatment later)
What is the surgical treatment for Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
Treatment (Surgical)
- Left adrenalectomy relatively straightforward
- Right adrenalectomy may require vascular and or microsurgical techniques
- Some advocate partial right adrenalectomy
- Post-operative medical treatment required if partial adrenalectomy performed (see below)
What is the medical treatment Ferret Hyperadrenocorticism?
Treatment (Medical)
- Depot GnRH-agonists currently favoured (suprelorin) licensed
- Deslorelin implant (9.4mg implant has UK license for male ferrets) lasts up to 4 years. Can use on cascade.
Discuss Rabbit
Male Reproductive Disorders?
- Testicular neoplasia
- Cryptorchidism (if no scrotal sac most likley cryptorchid)
- Orchitis (most commonly due to fight wounds)
- Trauma “ result of fighting
- Inguinal hernia (middle age non-castrated males, see bladder of GI contents in it)

Discuss Rabbit
Female Reproductive Disorders?
- Uterine adenocarcinoma –> up to 80% incidence in does > 4 years of age –> metastasise by direct contact, blood and lymph
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometritis
- Pyometra
- Endometrial venous aneurisms –> potentially life-threatening haematuria
- Prevention and Treatment –> ovariohysterectomy

Discuss Rabbit
Female Reproductive Disorders?
- Pregnancy toxaemia –> last 2 weeks gestation; obesity, poor diet and stress are risk factors
- Dystocia –> rare
- Pseudopregnancy –> lasts about 17 days
What is rabbit syphilis?
Rabbit Syphilis
- Caused by the spirochete Treponema cuniculi
- Spread during copulation and close contact
- C.S: Crusting lesions on the mucocutaneous junction of nose, lips, eyelids, genitalia and anus
- Treatment = penicillin injections (do not give guinea pigs penicillin injection but in rabbits giving treatment of penicillin and resolution is proof rabbit had syphilis)

Discuss Guinea Pig
Male Reproductive Disorders?
- Inguinal hernia –> often iatrogenic following castration (use monofilament or vicryl the catgut can cause breakdown)
- Orchitis
- Testicular neoplasia
- Spermatic plugs –> on occasion cause urethral obstruction (see pic)

Discuss Guinea Pig
Female Reproductive Disorders?
- Uterine Neoplasia
- Uterine Prolapse
- Pyometra
- Ovarian Neoplasia
- Ovarian Cysts

Discuss ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
Ovarian Cysts
- >75% incidence in sows over 18 months of age
- Commonly <2cm but may exceed 8cm
- Often incidental finding
- Bilateral symmetrical alopoecia common
- Abdominal discomfort, gut stasis and anorexia

What is the treatment for ovarian cysts in guinea pigs?
Ovarian Cysts
- Ovariohysterectomy is the treatment of choice
- Attention to perioperative support is essential
- Percutaneous drainage followed by hCG or GnRH therapy may give some relief if surgery is not an option

Discuss dystocia in guinea pigs?
Dystocia
- During the last week of pregnancy –> relaxin from pituitary and endometrium causes fibrocartilage of the pubic symphysis to disintegrate –> widens to 30mm
- If do not breed before 8 months of age the pubic symphysis may be unable to separate –> dystocia
- Parturition normally in early hours –> if presented during the day –> likely dystocia
Discuss pregnancy toxaemia in the guinea pig?
Pregnancy Toxaemia
- From 2 weeks before and 1 week after parturition
- Obesity, stress and fasting risk factors
- Acute-onset depression, hypoglycaemia, ketosis
- Coma and death soon after
- Prompt, aggressive treatment required
- Prognosis poor to grave
Discuss reproductive problems in the male chinchilla?
- ‘Fur ring’ –> paraphimosis (often due to ring of fur owner should be educated how to do this. See pic)
- Inguinal hernia
- Spermatic plugs
Discuss reproductive problems in the female chinchilla?
Female
- Pyometra
- Uterine neoplasia
- Dystocia –> similar to G.pig but pubic symphysis does not separate
Discuss reproductive problems in other small mammals?
Gerbil –> cystic ovaries, neoplasia
Hamster –> cystic ovaries, neoplasia, pyometra (normal creamy vulval discharge occurs following oestrous)
Rat –> pyometra, neoplasia
Hedgehog –> pyometra, neoplasia
How can sex determination be done in reptiles?
Sex Determination
- Secondary sexual characteristics e.g. size, crests, horns, femoral pores…
- Cloacal probing
- Hemipene eversion –> manual or hydrostatic
- Cloacal palpation (crocodilians)
- Ultrasound
- Radiography
- Endoscopy
Compare a male and female bearded dragon?
Femoral Pores in Bearded Dragon
As a rule femoral pores larger in males and they have hemipene bulges

Compare the male and female yemen chameleon?
Yemen Chameleon male as spurs

Compare the male and female red footed tortoise?
Red-Footed Tortoise
Male: right

Compare the male and female Herman’s tortoise?
Herman’s Tortoise
Females= shorter tail

Discuss Reptile
Male Reproductive Disorders?
Hemipene/Penile prolapse
- Traumatic separation
- Iatrogenic
- Neurological
- Hypocalcaemia
- Dysecdysis
- Tenesmus
Hemipene Impaction
- Usually husbandry-related
- Often results in infection

Discuss Reptiles
Male Reproductive Disorders?
Femoral Pore Impaction
- Caused by Inappropriate humidity?
‘Normal’ Disorders
- Aggression
- Hyperactivity
- Anorexia

Discuss Reptiles
Female Reproductive Disorders?
- Hypocalcaemia (see endocrine lectures)
- Oviduct and cloacal prolapse
- Follicular stasis (Pre-ovulatory oostasis)
- Dystocia (Post-ovulatory egg binding)
- Neoplasia

Discuss Reptiles
Female Reproductive Disorders?
Dystocia (obstructive):
- Uroliths
- Egg/foetus oversize
- Pelvic abnormalities
- Renomegaly
Dystocia (non-obstructive):
- Most common
- Hypocalcaemia
- Inadequate husbandry, diet, nesting site etc.
- Poor muscle tone
Discuss pre-ovulatory oostasis (POOS) and post-ovulatory egg-binding (POEB)?

- It is essential to differentiate whether the patient is suffering from pre-ovulatory oostasis (POOS)= ovary grows in preparation to produce eggs and then remains static can extend from weeks to years with new follicles being added and added or post-ovulatory egg-binding (POEB) or is simply undergoing normal reproduction
- POOS is a surgical condition
- POEB may be a surgical or a medical condition or husbandry management
- If POEB need to identify whether obstructive or non-obstructive

With regards to female reptiles Dystocia Surgical or Medical treatment?
Can be difficult to distinguish
Medical
- Patient fit and healthy with no obstruction
Surgical
- Patient too ill or weak to deliver clutch
- Obstruction or eggs entered the bladder
- Prolonged egg-retention
- Patients with MBD?
- Failure to respond to medical therapy

Discuss dystocia treatment in the reptile?
Dystocia (treatment):
- Correct husbandry and dietary deficiencies
- Temperature and humidity requirements may be different or at least more specific when gravid!!
- Treat any underlying disease
- Ensure access to an appropriate nesting site for the species
Discuss dystocia treatment further?
Dystocia (treatment):
- Physical manipulation?
- Percutaneous ovocentesis
- Oxytocin +/- a β-blocker (propanolol)
- Oxytocin is not physiologivally active in many reptiles. Works well in tortoises but limited efficacy in others
- Surgery
- (Endoscopy assisted)

Discuss reproductive disorder surgery in the female reptile?
Surgery
- Salpingotomy –> remove eggs only
- Ovariectomy –> remove ovaries only
- Ovariosalpingectomy –> remove oviduct and ovaries
ALWAYS remove ovary if removed oviduct
Ovaries often very close to adrenals and renal veins
Experience, good illumination and magnification are very helpful
Haemoclips and fine instruments helpful
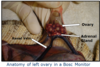
Look at these other reproductive surgeries in the reptile?



