2.2.1 Treatment of Male Sexual Disorders Flashcards
(42 cards)
What are some of the meds indicated in causing ED?
Anti-HTN meds, Psychological meds, Hormonal meds, H2 receptor blockers, Cold medicine preparations
What is the #1 cause of erectile dysfunction?
Ateriogenic/vasculogenic
What are three causes of psychological ED?
Depression, stress, matrimonial discord
What are some of the associated conditions with retrograde ejaculation?
Diabetes, neurologic conditions, surgery, medications
What is libido?
The sexual drive or desire to engage in sexual activity
What is a common ejaculatory disorder in young men? How is it treated?
Premature ejaculation; Paxil (serotonin reuptake inhibitor)
When diabetic patients typically affected by ED?
10-15 years earlier
What is one of the terrible effects of PDE5 inhibitors?
NAION (non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy)
43 cases to date
What is the treatment of high flow priapism?
Embolization of high flow priapism
How can libido be evaluated?
AM testosterone, general medical evaluation, psych evaluation
What is the prevelance of ED?
30 million men in US
52% of men b/t 40 and 70
How does a boner occur?
More blood going into the penis than going out
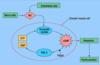
What is the MOA of viagra (PDE5 inhibitor)?
Where did priapism get its name?
Priapus - the god of fertility and nature
What are some of the things that can affect libido?
Testosterone levels (most important), chronic dz, depression, fatigue
What are the roles of the sympathetic and parasympthetic system in penis physiology?
Parasympathetic: vasodilation for erection (P for point)
Sympathetic: responsible for ejaculation (S for shoot)
What are some of the risk factors for ED?

What are the characteristics and causes of high flow priapism?

What is the mechanism of ED in diabetic patients?
Small vessel dz affects inflow into penis
Small vessel dz to the cavernosal nerves affects sympathetic input
What are some of the treatment options?
oral agents, constriction device/VED, intracavernosal injections
What are some of the oral treatments for ED?
PDE5 inhibitors (viagra, levitra, cialis)
Testosterone, “The Ropes”, Yohimbine
Apomorphine
What is ED? What is its other name?
The persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for intercourse
Impotence
What are the 4 types of erectile dysfunction?
Arteriogenic/vasculogenic
Neurologic
Venous outflow
Psychogenic