[C] 1.12 Internal Conditions of development of diseases Flashcards
Predisposition to a disease - Factors involved
Infectious/non-infectious cause + susceptibility + resistance (resistentia) → Different diseases
Predisposition and resistance are determined by…
- Hereditary characteristics (Constitiution)
- Acquired characteristics (Condition)
Constitutional characteristics (hereditary)
Connection between disease and appearance
Disease resistance
Capacity of an organism to defend itself against pathological processes or the agents of those processes
- Involves: Innate immunity
Genetic predisposition/Susceptibility
An individual may not be born with a disease but may be at high risk of acquiring it
Normal types (somatotypes)
Taxonomy to categorise the human physique according to the contribution of 3 somatotypes:
- Ectomorph
- Mesomorph
- Endomorph

Ectomorph
- Cerebrotonic
- Linear
- Thin
- Tall
- Fragile
- Delicate

Mesomorph
- Somatotonic
- Hard
- Rugged
- Triangular
- Athletically built
- Well-developed muscles

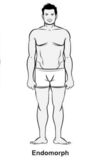
Endomorph
- Viscerotonic
- Round
- Short
- Soft
- Underdeveloped muscles
- Difficulty losing weight
Give the pathologic somatotypes
- Asthenic
- Hypoplastic, infantile
- Lymphatic
Asthenic somatotype
Describes a person who is chronically exhausted with low energy levels and easily fatigued
“Defective” constitution
Predisposition for certain diseases (diathesis)
Besides constitutional characteristics, which other characteristics of the individual play a role in the development of diseases
- Species
- Variety, race
- Sex
- Age
- Organs
Congenital disease
Harmful effects in intrauterine life
- Drugs
- Radiation
- Infections
- Avitaminosis
Acquired characteristics include…
- Condition
- Training
- Immunity


