[B] 1.62 Actinobacillosis, actinomycosis Flashcards
Bacteriology of Actinomyces bovis
- Gram + Rod - Forming filaments
- Blood agar:
- Slow-growing
- Produces wrinkled “molar tooth” colonies
A. bovis: Location and route of entry to the body
- Oral cavity
- Intestines
- Urogenital system
Enter the body through injuries:
- Changing of teeth
- Sharp parts of plants
A. bovis: From the point of infection
- Invasion of deeper tissues
- Characteristic alterations - usually in bones (jaw)
A. israeli affects which species?
Human
Formation of lumpy jaw from the point of infection
- Infection
- Bacilli divide → Serous exudate & neutrophil → Lysis
- Incorrect osteoclast & osteoblast activity
- Spongiform bone formation + Purulent softening “Sulphur granules”
“Sulphur granules”
- A. bovis: In the centre network of filamentous branching threads
- Gram +
- Radially arranged clubs

Actinobacillus lignieresi: General bacteriology
- Cattle & other ruminants
- Gram -, rods or filaments
- Facultative pathogen - present on mucousa
Actinobacillus lignieresi: Injuries of the oral cavity/skin
- Injuries of the oral cavity/skin
- Invasion, carried by the lymph
- Characteristic alterations in soft tissues (Udder, tongue, skin etc)
Actiobacillotic/actinomycotic nodule
- Multiple, pea-sized nodules, sharply demarcated
- Yellow/brown granulation tissue (colour by lipoid granule containing histiocytes)
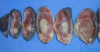
A. lignieresi: Lesions formed
- Actiobacillotic nodule
- Tumour like growth
- Abscess formation
- Sclerotising form
A. lignieresi: Tumour-like growth
Actinobacilloma
- Consequence of extreme granulation
- Egg-sized
- Cut surface:
- Soft
- Grey-yellow
- Bulging out
- Miliary foci of pus
- Firm connective tissue capsule

A. lignieresi: Abscess formation
Histiolysis increases
- Capsule
- Granulation tissue
- Dense & viscous pus containing sulphur granules

A. lignieresi: Scleroitc form
Healing
- Diffuse
- Overgrowth of connective tissue
- Grey-white, Firm
- Scattered foci (Sulphur granules)

Actiobacillotic/actinomycotic nodule: Steps of formation
Site of infection:
- Bacilli divide
- Serous exudate & neutrophil → Lysis
- Granulation tissue → Connective tissue
- Capsule
Actinobacillar nodules: If pathogens afe killed
- Graduation tissue penetrates towards the centre
- Small fibrotic connective tissue or complete healing
Glanders: Overview
“Malleus”, “Farcy”
Caused by Burkholredia mallei
- Gram -, strict aerobic, non-motile
- Zoonotic (Biological warfare agent)
Glanders: Location
- Asia
- Eastern Europe
Glanders: Susceptible species
- Horses,
- Carnivores
- Small ruminants
- Human
- Guinea pig
Glanders: Route of infection
- Per os, skin, conjunctiva, aerogenic
- Contaminated food, carcasses of infected animals
Glanders: Pathogenesis
- Per os uptake: Primary complex in the alimentary tract
- Early generalisation: Lung, spleen & liver
- Late generalisation: Septicemia, nasal mucosa, skin
- Death
Glanders: Forms
- Acute form
- Chronic form
Glanders: Acute form
- Donkey, mule, certain horse breeds, carnivores
- Septicaemia, pneumonia
Glanders: Lesions on the nasal mucosa

Glanders: Chronic form
- Certain horse breeds
- Granulomatosis lesions in the lung, nasal mucosa and skin
Glanders: Lesions
- Granulomatosis form
- Granuloma - Necrotised centre with calcium salt deposition
- Exudative form: Bronchopneumonia
Glanders: Forms
- Predominantly proliferative form
- Predominantly exudative form
Glanders: Predominantly proliferative form
- Proliferative process
- Collagenous connective tissue
- Histiocytes and giant cells
Glanders: Predominantly exudative form
- Mostly in the lungs
- Exudative process
- Serofibrinous inflammation around the pathogens
- Necrosis soon after (caryorhexis)


