[A] 1.51 Infiltrative processes during acute inflammation Flashcards
Cellular infiltration
Acute inflammation
- Neutrophils predominate in the first 1-2 days
- These are then replaced by macrophages
Chemotaxis
After extravasation, leukocytes emigrate in tissues toward the site of injury
- Exogenous & endogenous substances can act as chemoattractants
Exogenous chemoattractants
Bacterial products
Endogenous chemoattractants
- Components of the complement system
- Cytokines
- Arachidonic acid metabolites - Leukotriene B4
Activation of leukocyte phagocytosis: Steps
- Recognition & attachment of the particle to be ingested by the leukocyte
- Engulfment → of phagocytic vacuole forms
- Killing or degeneration of the ingested material
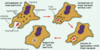
Intracellular degradation is either…
- Oxygen-dependent
- Oxygen-independent
Oxygen-dependent degradation
Production of ROS
Oxygen-independent degradation
Dependent on granule release
- Containing proteolytic enzymes such as defensins, lysozyme and cationic proteins
After phagocytosis, neutrophils undergo…
Apoptosis
- They are then ingested by macrophages
Increased erythrocyte diapedesis in dogs
Specific pathobiological inflammatory hallmark
- Responsible for the haemorrhagic appearance of the purulent inflammatory fluid (Pus/exsudate)
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) refers to…
Detecting antigens in the cell of a tissue
- Exploits the principle of antibodies binding to antigens

Myeloperoxidase (MPO)

- CD68 (Cluster of differentiation 68)
- IBA-1 (Ionised calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1)

CD3

- CD79a
- CD20

C-Kit (CD117)
Acute inflammation: Pathological tissue examples
- Tumours
- Granulation tissues = Angiofibroblast tissues
- In/around pathological tissues
Treatment of inflammation
- Antibiotics & NSAIDs
- Decreased inflammatory vascular & cellular reactions
- Weaker histopathological reactions:
- Decreased neutrophils & mast cells
- Decreased microvascular exsudation
- Decreased vasodilation & endothelial hypertrophy
Give the outcomes of acute inflammation
- Resolution
- Abscess formation
- Recurrence
- Chronic inflammation (months-years)
In which incidences does chronic inflammation arise?
- When acute inflammation fails to eliminate the inciting stimulus
- Repeated acute inflammation
- Persistent infection
- Prolonged exposure to potentially toxic exogenic/endogenic agents (silica-silicosis)
- Autoimmunity
Morphological features of chronic inflammation
- Infiltration with mononuclear cells - Macrophages, lymphocytes & plasma cells
- Tissue destruction by persistent offending agent/inflammatory cells
- Healing by connective tissue replacement of damaged tissue (Fibrosis)
- Pathological inflammatory neoangiogenesis
Hypercytokinemia
Cytokine storm
- Cytokines signal & activate immune cells such as T-cells & macrophages to travel to the site of infection
- The immune cells produce more cytokines
- This loop is kept in check by the body
- But might become uncontrolled


