Breast Pathology Flashcards
Key Features: Central necrosis Precancerous lesion Confined to ducts & lobules
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) non-invasive
Image: ducts (black arrows) distended by pleomorphic cells with prominent central necrosis without extension

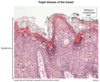
Key Features: Eczematous nipple lesion Extension of DCIS into ducts
Paget’s disease (manifestation of ductal carcinoma)
Key Features: Most common type Nests & cords of cells Firm, Rock hard mass
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma *stellate infiltration = worse prognosis
Painless breast mass
Small cells in single file (orderly row)
↓ E-cadherin expression
Mammary stroma invasion
Invasive Lobular carcinoma *Lines of cells = Lobular
Enlarged, hard lymph nodes Usually lacks palpable mass Peau d’orange Dermal lymphatic invasion Poor prognosis (Undiff)
Inflammatory Breast Cancer (Invasive) High Yield
presents with painful, diffuse breast induration, erythema, and peau d’orange (orange peel or dimpled) skin (warm, red, swollen) due to blockage of lymphatic drainage by cancerous invasion.
Inflammatory breast carcinoma (Invasive)
characterized by crusty, scaly redness on the nipple and areola with oozing and bleeding.
Paget’s disease (manifestation of ductal carcinoma)
Caused by cancerous cells obstructing lymphatic drainage after spreading to the dermal lymphatic spaces. High propensity to metastasize to the lymphatic system, (axillary lymphadenopathy)
Inflammatory Breast carcinoma (Invasive)
small, firm, and mobile breast masses that occur due to proliferation of breast stroma and ducts.
Fibroadenomas

Microscopic examination of Fibroadenoma shows ____ proliferation compressing the ducts to slits (look like septa).
stromal
presents as an irregular breast mass with no associated nipple discharge after localized trauma or biopsy.
Fat necrosis
Fat Necrosis microscopy may show adipocytes (white spots) undergoing necrosis with inflammation, including _____ and ____ cells.
lipid laden macrophages (look big, foamy, puffy, and light) Giant cells (multiple nuclei)
Typically cause cyclic (comes/goes) breast pain no nipple discharge
Fibrocystic changes of the breast
May show cysts (smooth, glassy pink globules encased) and areas of fibrous stroma (pink plain acellular sheet)
Fibrocystic changes of the breast
Paget disease of the breast occurs due to the ductal spread of atypical malignant cells to the _____
nipple epidermis (Histo looks fucked and radical with large cells that have white clearings surrounding them)
Patients may have: unilateral erythematous, intensely pruritic, ulcerative lesion over the nipple and areola. bloody nipple discharge
Paget disease of the breast
characterized by epithelial and myoepithelial cells lining fibrovascular cores in a cyst wall or duct. (finger like papillary projections with stromal plain core that may have a few scattered nuclei here and there)
Intraductal papilloma (benign)
Unilateral bloody (or clear) nipple WITHOUT a breast masses or skin changes. No enlarged axillary lymph nodes
Intraductal papilloma (benign)

the most common cause of bloody nipple discharge
Intraductal papilloma (benign)
benign tumor within the mammary duct
Intraductal papilloma (benign)
Tamoxifen Raloxifene MOA
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators: Competitive inhibitor of estrogen binding Mixed agonist/antagonist action depending on tissue where the receptor is located
_______ causes postmenopausal osteoporosis Prevention of breast cancer in high-risk patients
Raloxifene
_______ is used for adjuvant treatment of breast cancer Prevention of breast cancer in high-risk patients
Tamoxifen
Hot flashes Venous thromboembolism are adverse effects associated with:
Raloxifene Tamoxifen
Endometrial hyperplasia & carcinoma is an adverse effect associated with:
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen has a favorable effect on serum lipids: decrease in _______ cholesterol no significant change in ______ Serum triglycerides may _____ in some patients.
total and LDL HDL increase
most commonly occurs in lactating women and presents with pain, breast swelling, and erythema. Most patients also have systemic findings such as fever, malaise, and leukocytosis.
Mastitis (ie, breast infection) *keep feeding baby as normal
Histopathology demonstrates ducts distended by pleomorphic cells with prominent central necrosis withOUT extension beyond the ductal basement membrane.
Paget disease
the most common hormonally active pituitary adenoma. These tumors can cause galactorrhea (milky discharge from bood) and amenorrhea in premenopausal women.
Prolactinomas *Lactotrophs under negative regulation by Dopamine
Immobile, firm breast mass (most commonly in the upper outer quadrant)
Invasive breast carcinoma
Rupture of a silicone breast implant can lead to a foreign body REACTION of the breast with local inflammation (edema, induration), and ______ formation; can result in a palpable, tender mass.
granuloma
a breast lesion characterized by a malignant clonal cell proliferation contained by the surrounding ductal basement membrane. The (basal) myoepithelial layer of the duct is preserved and uninvolved.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
characterized by solid sheets of vesicular, pleomorphic, mitotically active cells with a significant lymphocytic & plasma cell infiltrate around and within the tumor and a pushing, noninfiltrating border.
Medullary carcinoma of breast *well circumscribed can mimic fibroadenoma

malignant cells spread from superficial DCIS into nipple skin without crossing the basement membrane.
Paget disease of the nipple
Sclerosing adenosis is characterized by _____ proliferation and compression with surrounding fibrotic tissue and peripheral ductal ___. Common finding in fibrocystic change.
central acinar
dilation

Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks _______ to disrupt malignant cell signaling and encourage apoptosis.
human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)
HER2 helps preserve cardiomyocyte function, thus Trastuzumab can cause _______ that manifests as a decrease in myocardial _______ without cardiomyocyte destruction or _______.
Cardio toxicity myocardial contractility myocardial fibrosis.
-mab that blocks human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)
Trastuzumab
Triple Negative for E, P, & HER2 indicates a ____ disease course
aggressive (Negative outcome)
Estrogen Receptor positive (overexpression) breast cancer likely responds to what drug?
Tamoxifen (endometrial cancer risk)
HER2/neu receptor positive (overexpression) breast cancer likely responds to what drug?
Trastuzumab (cardio toxic risk)
Breast cancer often presents in post-menopausal women as a palpable hard mass in the _______ quadrant.
Upper Outer
Invasive breast cancer can become fixed to the _____ muscle, deep fascia, Cooper ligament or skin (nipple retraction/ skin dimpling)
pectoral
Invasive breast cancer usually arises in the ____ lobular unit
terminal duct
African American women have an increased risk for what type of breast cancer hormone sensitivity?
Triple Negative
____ metastasis is the most important prognostic factor in early-stage breast cancer.
Axillary Lymph node
Often seen as microcalcifications on mammography Usually does not produce a mass
DCIS (not past basement membrane)

DCIS extension into lactiferous ducts
Paget’s (eczma)
Central Caseous necrosis and dystrophic calcifications
Comedocarcinoma (DCIS subtype)
↓ E-cadherin expression No mass or calcifications incidental finding on biopsy
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) non-invasive
Often presents with bilateral multiple lesions in the same location
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Firm, Fibrous, Rock-hard mass with sharp margins and small, glandular, duct-like cells in desmoplastic stroma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive breast carcinoma typically presents as an irregularly shaped, adherent breast mass, most commonly in the upper outer quadrant. Malignant infiltration of _____ of the breast can cause skin retractions.
suspensory ligaments
Peau d’orange is an erythematous, itchy breast rash with skin texture changes that resemble an orange peel. It is caused by cancerous cells spreading and obstructing ___.
lymphatic drainage
Intraductal papilloma is a benign tumor within the ___
mammary duct.


