DIT review - Micro 9 Flashcards
(49 cards)
What agar is used to culture fungi?
Sabouraud
What are the 4 systemic mycoses
Histoplasmosis
Blastomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Paracoccidiodomycosis
Describe histology of Histoplasmosis including size compared to RBC
- Intracellular oval bodies within macrophages
- Smaller than RBC

HIstology of blastomycosis including size compared to RBC
- Broad based budding
- Same size as RBC

Histology of Coccidiodomycosis including size compared to RBC
- Spherules (filled with endospores)
- Larger than RBC - tubleweed bigger than sombrero

HIstology of paracoccidiodomycosis including size compared to RBC
- Captains wheel
- Larger than RBC - wheel larger than red spot in center of wheel
Describe the location of each of the systemic mycoses
Histo - Mississippi and Ohio river valley (midwest/central US)
Blasto - Eastern US
Coccidio - Southwest US, California
Paracoccidio - Latin america
What is the cuase of Pityriasis versicolor
Malessezia furfur
PResentation of Pityriasis versicolor
- More common in summer (fungus survives in hot/humid conditions)
- Hypopigmented patches
- Due to degradation of lipids that produces acids that damage melanocytes
- Confined to the stratum corneum (superficial layer)
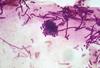
Histology of Malessezia
- Spaghetti and meatball appearance
Treatment of Pityriasis versicolor
- Selenium Sulfide aka Selsun blue
Treatmtne of tinea (dermatophyte) aka ring worm
- Topical azoles
- Griseofulvin for more severe infections
- Onychomycosis – oral Terinafine
Presentation and treatment of Sporothrix Schenckii
- “Rose gardener’s disease”
- Dimorphic
- Cigar-shaped yeast
- Presentation:
- Local pustule or ulcer at site of trauma
- Ascending lymphangitis (nodules along draining lymph nodes)
- Treatment:
- Itraconazole
- Potassium iodide (THINK: plant a rose in the pot”)
What are the only catalase positive fungi
Candida, Aspergillus
Histology of Candida at 20 C
- 20C – yeast: pseudohyphae and budding yeasts

Histology of candida at 37 C
- 37C – mold: germ tubes

Describe risk factors and pH of candida vulvovaginosis
- Vulvovaginitis
- Associated with diabetes and antibiotic use
- Normal vaginal pH (vs. Gardnerella and Trichomonas which have pH > 4.5)
Describe histology of Aspergillus
- Septate hyphae branching at 45 acute angle
- Produces conidia in radiating chains at end of conidiophore

Presentation of Aspergillus
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillus (wheezing, fever, pulmonary infiltrate) – HSR Type I
- Associated with asthma and cystic fibrosis
- Aspergillomas (solid balls of fungi) in pre-existing cavities
- Angioinvasive aspergillosis (fever, cough, hemoptysis)
- Kidney failure, ring enhancing brain lesions, paranasal necrosis
- Aflatoxin can cause hepatocellular carcinoma
Characteristics of Cyptococcus neoformans
- Heavily encapsulated
- Urease positive
- Found in soil and pigeon droppings
Presentaton of crytococcus
- Pneumonia, meningitis, encephalitis (“soap bubble” lesions in brain)
Name 3 different ways to diagnose Cryptococcus
- Bronchopulmonary washing of lung tissue
- Stain sample with mucicarmine red methanamine silver stain
- Lumbar puncture
- Stain with India ink – will show clear halo
- Latex agglutination
- Detects polysaccharide capsular antigen
Treatment of cryptococcus
- Amphotericin B + Flucytosine, followed by maintenance with Fluconazole
MOA and uses of Amphotericin B
- MOA:
- Binds Ergosterol in cell membrane and forms pores leading to fungal cell death
- Usually given IV
- Can also be given intrathecally (into spinal theca) for CNS infections
- Uses:
- Serious, systemic mycoses
- Cryptococcus, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, mucormycosis
*






