3/15 - UWorld CNS Flashcards
Ataxia-telangiectasia (triad of symptoms, genetic defect)
Classic triad: Cerebellar ataxia, telangiectasias, increased risk of sinopulmonary infections (IgA deficiency)
Autosomal recessive Mutation of ATM gene (ATM - Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated) -> failure to repair DNA double strand breaks
Think:
You sneeze (sinopulmonary infection), causing you to lose balance (ataxia), and knock something leading to telangiectasias on the skin
Poisoning of pufferfish
Containt tetrodotoxin
Toxin binds to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve and cardiac tissue
Prevention of sodium influx and depolarization
Symptoms: Dizziness, weakness, loss of reflexes, paresthesias of the face and extremities, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Higher exposure leads to hypotension and paralysis
Death can occur from respiratory failure and hypotension
Treatment: Supportive care Intestinal decontamination Gut lavage and charcoal
Transport proteins involved in recurrence of latent HSV
Reactivation: Anterograde axonal transport from ganglia to skin mediated via KINESIN (moves stuff away from nucleus toward nerve terminal)
Retrograde axonal transport (towards the nucleus) via DYNEIN Important in establishing the latent phase following primary infection
Vomiting center
Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) located on dorsal surface of the medulla known as the area postrema
Functions of the Midbrain
Control of eye movements, relay nuclei of the auditory and visual symstems
Functions of the Pons
Balance and maintenance of posture; regulation of breathing; relays info from the cerebral hemisphere to the cerebellum
Function of the Medulla
Contains autonomic centers that regulate breathing, blood pressure, swallowing, coughing, and vomiting reflexes
Fragile X Syndrome (physical and neuro findings; genetic cause)
Most common inherited intellectual disability
Physical findings: macroorchidism (large testes) and dysmorphic facies (long and narrow face, prominent forehead and chin)
Neuropsychiatric disorders: developmental delay, ADHD, autism spectrum disorder
Trinucleotide repeat in FMRI gene (CGG) leads to hypermethylation
Effects of botulinum toxin
Toxin causes disease by inhibition of ACh nerves
Enters the nerve terminals and prevents binding and fusion of ACh-containing vesicle (cleaves SNARE protein)
Presentation of botulism: descending paralysis that first manifests with cranial nerve abnormalities (diplopia, dysphagia, dysphonia)
Review the Brachial Plexus
. . .
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - ventromedial
Satiety Destruction leads to hyperphagia (excessive hunger)
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - lateral
Mediates hunger Destruction leads to anorexia
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - anterior
Mediates heat dissipation Destruction leads to hyperthermia
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - posterior
Mediates heat conservation Destruction leads to hypothermia
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - arcuate
Secretion of dopamine (inhibits prolactin), growth hormone-releasing hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - paraventricular
Primarily makes oxytocin
Antidiuretic hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin, thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - supraoptic
Primarily makes ADH
Secretion of ADH and oxytocin
Function of hypothalamic nuclei - suprachiasmatic
Circadian rhythm regulation and pineal gland function
Swinging flashlight test
Due to lesion of the optic tract
Eye contralateral to the lesion will appear to dilate when light is shined in it after being shined in the other eye. This is because the nasal portion of the retina contributes more input.
E.g. The L optic tract is damaged. When light is shined in the L eye (nasal innervation from R, undamaged, optic tract) there will be normal constriction. When light is then quickly shone in to the R eye (nasal innervation from L optic tract), it appears to dilate even though it is really just constricting less
Visual lesions
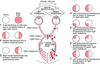
Definition of scotoma
Any visual defect surrounded by relatively unimpaired field of vision
Occur due to pathology involving parts of the retina or optic nerve (e.g. macular degeneration)


