3/23 - UWorld Flashcards
Possible causes of sensory ataxia (positive Romberg test with eyes closed - testing for proprioception)
Tabes dorsalis (Syphilis) Vitamin B12 deficiency (results in subacute combined degeneration due to abnormal myelin)
What are the hormonal effects of functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (e.g. amenorrhea in response to stress, weight loss, or illness)
Underlying cause is decreased Leptin levels (leptin is usually secreted by fat cells in order to decrease appetite; decreased Leptin inhibits pulsatile GnRH release) Decreased GnRH from hypothalamus Decreased LH and FSH Decreased estrogen
Immune response of hyperacute transplant rejection (min-hours)
Preformed antibodies (type II hypersensitivity reaction)
Immune response of acute transplant rejection (<6 months)
Cellular response: CD8+ T cells activated against donor MHCs (type IV hypersensitivity) Humoral response: Similar to hyperacute except antibodies develop after transplant
Immune response of chronic transplant rejection (months-years)
CD4+ T cells respond to APCs presenting donor peptides Both cellular and humoral components (type II and IV hypersensitivity)
What structure is best used to identify the appendix during surgery?
Teniae coli The 3 distinct longitiduinal bands converge at the root of the appendix
Treatment options for C. Diff
Metronidazole Oral Vancomycin Fidaxomicin (macrocyclic antibiotic that inhibits RNA polymerase) - It inhibits the sigma subunit of RNA pol, which is needed for RNA pol to bind to its promoter - Useful for recurrent C. Diff
What type of elimination occurs when the rate of elimination is constant regardless of drug concentration (e.g. constant amount of drug eliminated per unit time, regardless of concentration; e.g. enzymes have been maxed out)
Zero-order elimination
What type of elimination occurs when the rate of elimination is directly proportional to drug concentration (e.g. a fixed proportion of the drug is eliminated per unit time)
First-order elimination
What is the Hawthorne effect?
Aka observer effect Tendency of study subjects to change their behavior as a result of their awareness that they are being studied Think: Hawthorne = hawk, observing from above
What is Berkson’s bias?
Selection bias created by choosing hospitalized patients as the control group Think: Dr. Burk = picked from within the hospital (Burk and Christina fo lyfe)
Pygmalion effect?
Researcher’s belief in the efficacy of treatment can change the outcome Aka self-fulfilling prophecy
Drugs that are substrates of CYP450
Always Think When Outdoors Anti-epileptics Theophylline Warfarin OCPs
Drugs that are CYP450 inducers
Chronic alcoholics Steal Phen-Phen and Never Refuse Greasy Carbs
Chronic alcohol use
St. John’s wort
Phenytoin
Phenobarbital
Nevirapine
Rifampin
Griseofulvin
Carbamazepine
Guiness, Coronas, ‘n PBRS, induce chronic alcoholism
Griseofulvin
Carbamazepine
Nevirapine
Phenytoin
Barbiturates
Rifampin
St. John wort
Chronic alcoholism
Drugs that are CYP450 inhibitors
SICKFACES.COM Sodium valproate Isoniazid Cimetidine Ketoconazole Fluconazole Acute alcohol abuse Chloramphenicol Erythromycin (macrolides) Sulfonamides Ciprofloxacin Omeprazole Metronidazole
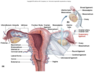
Structures of the female pelvis

How does dexamethasone suppression test help in the diagnosis of Cushing’s
Dexamethasone (corticosteroid) will exert negative feedback and cause decreased ACTH in Cushing’s disease (ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma) Dexamethasone will have no effect with ectopic ACTH production (e.g. small cell lung cancer)
How does CRH stimulation test help in the diagnosis of Cushing’s
CRH will cause increased ACTH and cortisol in Cushing’s disease (ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma) CRH will have no effect on ACTH and cortisol in ectopic source of ACTH
What is the difference between Cushing’s Syndrome and Cushing’s disease?
Syndrome - increased cortisol due to a variety of causes Disease - ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma
How do nitrites cause poisoning?
Nitrites induce the conversion of Fe2+ to Fe3+, creating methemoglobin which binds tightly to cyanide but cannot carry oxygen Methemoglobinemia does not change pO2 (this is a measure of O2 dissolved in plasma and unrelated to Hb function)
What is the protein-targeting mechanism that marks proteins destined for lysosomes
Proteins destined for the lysosome require phosphorylation of specific mannose residues to ensure proper transit through the golgi apparatus
What is the term that describes presence of both normal and mutated mitochondrial DNA, resulting in variable expression in mitochondrially inhereted disease
Heteroplasmy
What is the term that described phenotypes that vary among individuals with the same genotype
variable expressivity
What is it called when mutations at different loci can produce a similar phenotype
Locus heterogeneity