DIT review - Micro 4 Flashcards
What pathogens cause rash on hands and soles
- THINK: CARS
- Coxsackie A virus
- Rocky mountain spotted fever
- Secondary Syphilus
- Also Kawasaki
Pathogens that cause atypical aneumonia
Describe the 2 forms of chlamydia
- Elementary body is infectious form (elementary enters)
- Reticular body is active replicating (reticular replicates)
Why is Chlamydia a poorly staining bacteria
Obligate intracellular
Lacks classic peptidoglycan wall due to reduced muramic acid
Presentation of Chlamydia A-C
Blindness due to follicular conjunctivitis

Presentatino of chlamydia D-K
Urethritis, PID, ectomic pregnany
Neonatal disease can be acquired during birth (neonatal conjunctivitis, pneumonia)
Presentation of chlamydia L1-L3
Lympogranulosum venereum
Painless genital ulcer with painful inguinal lymph nodes that ulcerate (buboes)
Treatment of Chlamydia
Macrolides (Azithromycin)
Tetracyclines
Transmission of Coxiella
Spores form in animal droppings and get inhaled
Presentation of Q fever
Pneumonia, headache, fever, hepatitis
MOA of gardnerella vaginalis
Overgrowth of normal vaginal flora
Diagnostic features of gardnerella vaginalis
pH > 4.5
Positive Whiff test with 10% KOH prep (fishy smell worsens when adding KOH)
Clue cells - epithelial cells coated with bacteria)
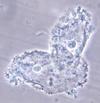
Treatment of gardnerella vaginalis
Metronidazole
Treatment of mycoplasma pneumoniae
macrolides
Why is Chlamydia obligate intracellular
Cannot produce its own ATP
Why are Rickettsia spp obligate intracellular
- Unable to produce CoA, gets it from eukaryotic cells
- NAD+ important for bacterial growth and replication
- Sketchy = Coach (CoAch) holding energy drink (NAD+) and basket of tennis balls
Classic triad of symptoms in all Rickettsia species
HA, fever, rash (vasculitis)
Diagnostic test of Rickettsia
Weil Felix test = will agglutinate if antibodies against Rickettsia are present
Treatment of Rickettsia
Doxycline
Transmission of Rickettsia Prowazeki
Lice - louse feeds on blood and defecates near feeding sites and it’s the scratching that infects patients from the lice feces
Describe the rash of Rickettsia prowazeki
+ other sx
-
Rash starts at trunk and moves out towards the extremities
- Rash spares the hands feet and head
- Myalgia and arthralgia
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis with dizziness and confusion
- Can cause COMA if really serious
Transmission of Rickettsia typhi
No sketchy
fleas
Which rickettsia causes endemic vs. epidemic outbreak (typhi vs. prowazeki)
Typhi = endemic (localized to a region)
Prowazeki = epidemia (widespread rampant outbreak)
What organism causes Rocky mountain spotted fever
Rickettsia ricketsii


