6/15 UWorld Flashcards
What is the source and function of ANP and BNP
- Released from atrial (ANP) and ventricular (BNP) myocytes in response to increased blood volume
- Acts via cGMP
- Causes vasodilation and decreased Na+ reabsorption at the renal collecting tubule
- Dilates afferent arteriole and constricts efferent arterial, promoting diuresis
Adverse effects of Digoxin
- Hyperkalemia (recall that dysfunctional Na+/K+ ATPase blocks K+ from entering the cell, so it builds up in the serum instead)
- Premature ventricular contractions and other arrhythmias
- Digitalis effect = T-wave changes, QT interval shortening, ST depression
- = taSTy scoop of ice cream = “scooped”/concave ST depression of EKG
- Bradycardia due to parasympathetic activity at SA node
- à SA music “note” (node) on top L of dancefloor
- à dangling heart watch = bradycardia
- Heart block due to excess parasympathetic activity of AV node in digoxin toxicity
- à AV music note
- à heart shield pendant on girl = heart block
- Contraindicated in heart block (or other drugs that depress SA or AV nodes e.g. beta-blockers)
- à sign over door: “remain unblocked”
- à blocked is spelled with a ‘beta’ B
- GI symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abd pain)
- à nauseated kid
- Neuro sx (confusion and weakness)
- Alteration in color vision
- Xanthopsia (objects appear yellow)
Factors that exacerbate Digitalis toxicity
- Hypokalemia (hypokalemia increases Digoxin binding to Na+/K+ ATPase)
- Can be caused by loop diuretics or diarrhea
- Renal insufficiency
- Increased the serum half life of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity
- Many antiarrhythmics inhibit renal clearance of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity
MOA of Milrinone
- Sketchy = “One in a million” sign
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitor, leading to decreased breakdown of cAMP, leading to a positive inotropic effect
- = “Don’t phoster disinterest” sign
- = CAMPaign
- = big muscles of donkey = positive inotropic effect
- Also causes arteriolar dilation and decreased afterload
MOA of Nesiritide
- Sketchy = “Turn the tide” elephant
- Synthetic form of BNP, which increased cGMP in smooth muscles, leading to venous and arteriolar dilation (reducing afterload and preload)
- = BuMP
- = dilated red ears and blue legs
- Also causes natriuresis
Describe the effects of prostaglandins and ATII on GFR
Prostaglandins dilate the afferent arteriole = increased GFR
ATII constricts the efferent arteriole = increased GFR
Coadministration of NSAIDs and ACEi will lead to significantly decreased GFR due to contricted afferent and dilated efferent arteriole - can precipitate kidney injury
MOA of Aliskiren
- Sketchy = “High risk” slots
- Mechanism of action
- Direct Renin inhibitor
- Prevents conversion of angiotensinogen to ATI
What drugs improve mortality in chronic CHF patients vs. drugs that treat symptoms?
- Improved survival:
- ACEI
- ARBs
- Aldosterone antagonists
- B-blockers
- Symptomatic relief:
- Diuretics
- Digoxin
- Vasodilators
Cause, CO, SVR, and Rx of Septic/Anaphylactic shock
- Sepsis/anaphylaxis
- Sepsis and anaphylaxis cause vasodilation and leaky capillaries
- Skin will be warm and flushed to do vasodilation
- SVR = Decreased (this is part of the cause of septic shock)
- CO = Increased (compensatory tachycardia)
- Rx = Antibiotics, IV fluids, vasopressors (norepinephrine)
- Sepsis and anaphylaxis cause vasodilation and leaky capillaries
Cause, CO, SVR, and Rx of Neurogenic shock
Brain is not communicating properly with the heart – e.g. brain injury, spinal cord injury
CO = Decreased
SVR = Decreased
Rx = IV fluids
On a pressure-volume loop of the LV, describe where on the graph the mitral valve and aortic valve close and open
Volume on the X-axis and pressure on the Y-axis

Adverse effects of Milrinone
Hypotension
Due to arteriolar dilation
In the cardiac cycle graph, show were mitral and aortic valve opening and closing occur


Label the jugular venous tracing graph

A wave = atrial contraction
C wave = ventricular contraction
V wave = atrial filling against closed tricuspid valve

Describe what normal heart sound splitting is
Inspiration = decreased intrathoracic pressure = increased venous return = increased RV filling = increased RV stroke volume = increased RV ejections time = delayed closure of pulmonic valve
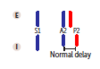
When do you see wide splitting vs. fixed splitting
- Wide splitting:
- Splitting occurs both in inspiration and expiration
- Due to conditions that delay RV emptying (e.g. Pulmonic stenosis, R bundle branch block)
- Fixed splitting:
- Occurs during right heart overload (e.g. atrial septal defect)
- ASD –> L-to-R shunt –> increased RA and RV volumes –> increased flow through pulmonic valve such that, regardless of breath, pulmonic closure is delayed
Describe paradoxical splitting
- Due to conditions that delay aortic valve closure (e.g aortic stenosis, left bundle branch block)
- Normal order of valve closure is reversed so that P2 occurs before delayed A2
- On inspiration, P2 closes later and moves closer to A2, thereby “paradoxically” eliminated the split
What maneuver enhances mitral regurg vs. tricuspid regurg
Mitral regurg enhanced by increased afterload (e.g. hand grop or squatting)
Tricuspid regurg enhanced by increased preload (e.g. inspiration)
Causes of aortic regurgitation
Aortic root dilation (e.g. syphilis or Marfan)
Bicuspid aortic valve
Endocarditis
Rheumatic fever
What murmurs are increased by inspiration vs. hand grip vs. valsalva
- Inspiration:
- This decreases intrathoracic pressure, thus increased venous return to the heart
- Increased intensity of R heart sounds (e.g. Tricuspid murmur)
- Hand grip:
- This increases SVR, this increasing afterload
- Increased intensity of mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation, and VSD
- Valsalva maneuver
- This increases intrathoracic pressure, thus decreasing preload (opposite of inspiration)
- Decreases the intensity of most murmurs EXCEPT increases intensity of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Complications/presentation of aortic stenosis
SAD:
Syncope, angina, dyspnea
Describe electrolytes responsible for each phase in cardiac myocyte fast action potential (Phase 4, 0, 1, 2, 3)
- Stage 4 (baseline negative state)
- Only “leaky” potassium channels open (K+ leaking out of cell - inward rectifier current)
- Stage 0
- Voltage gated Na+ channels open (after threshold -70 is reached by Na+ and Ca+ leaking through gap junctions)
- Na enters very quickly à fast depolarization
- Stage 1
- Initial repolarization – Na+ channels close and voltage gated K+ channels open (K+ leaves cell), causing repolarization
- Stage 2
- Plateau – Ca2+ channels open (Ca enters cells) – L-type channels
- Ca2+ and K+ channels pull voltage in opposite directions, so reach sort of plateau
- This is the phase that causes myocyte contraction (due to Ca2+ triggering more Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum)
- Stage 3
- Rapid repolarization – Ca2+ channels close, so only K+ channels open
- But eventually the voltage gated K+ channels will close, leaving only open the “leaky” potassium channels, so there is membrane stabilization

Describe electrolytes responsible for each phase of pacemaker slow action potential
- Stage 4
- Na+ channels (If – funny current) are open (Na+ enters cells) and allow depolarization (voltage gated K+ channels are closed)
- The rate of stage 4 depolarization is what sets the heart rate
- Stage 0
- Threshold reached where voltage gated Ca2+ channels open causing more rapid depolarization at threshold (-40)
- Ca2+ enters pretty quickly, but not as quickly as Na+ in stage 0 of myocytes à slow action potential
- Stage 3
- At threshold +10, voltage gated Ca2+ channels close and voltage gated K+ channels open (potassium leaves cell), causing repolarization (at -60, the voltage-gated K+ channels will close and Na+ channels will reopen)
- At certain threshold, K+ channels close, so Na+ is only channel open and cycle restarts

What is Addison disease
Autoimmune destruction of the adrenal gland
Decreased aldosterone and cortisol






