CVPR Week 1: Heart, Lungs and Vessels Histology Flashcards
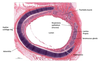
The wall of all 4 heart chambers consists of
3 layers
- Endocardium
- myocardium
- epicardium
Layers of the heart
3 listed
superficial to deep
- epicardium
- myocardium
- endocardium
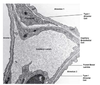
Epicardium description
Thin layer of flat to cuboidal mesothelial cells covering fibrous and adipose connective tissue (also called the visceral layer of the pericardium)
Epicardium AKA
Visceral layer of the pericardium
Identify
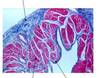

The bulk of heart tissue is?
striated involuntary cardiac muscle
Heart tissue can undergo
4 listed
- Hypertrophy
- atrophy
- necrosis
- apoptosis
Epicardium contains
- nerves
- blood vessels
that supply the heart
Identify


Identify


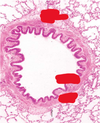
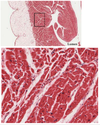
Myocardium description
- the thickest layer of the heart
- composed of bundles of cardiac muscle cells organized into spiraling fascicles that efficiently squeeze blood out of the heart chambers
The thickest layer of the heart
myocardium
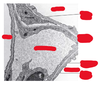
How to distinguish cardiac muscle cells
striations
intercalated discs
branched fibers
centrally located nuclei
How to distinguish myocardium
- cardiac muscle cells
- strands of connective tissue and vascular elements course through the myocardium between the fascicles
Cardiac muscle cells contents
- contractile proteins
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- T-tubules
- High density of mitochondria (40% of cytoplasmic volume)

The density of mitochondria in skeletal muscle
2% of cytoplasmic volume in skeletal muscle
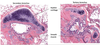
Endocardium description
Simple squamous epithelium over a layer of variable thickness connective tissue called the subendocardium
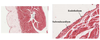
Where are the Purkinje fibers found?
In the subendocardium

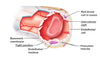
Identify

Things necessary for Cardiac muscle cell contraction
rely on a large influx of extracellular Ca2+
When asked to work harder, cardiac muscle cells undergo
hypertrophy like other muscle cells
Identify muscle types


Cardiac muscle cells have specialized junctions called
intercalated discs
Intercalated discs functional components
3 listed
- desmosomes - hold the cells together under the forces of contraction
- adherens junctions - hold the cells together under the forces of contraction
- gap junctions - facilitate the movement of signals to contract from one cell to another