Exam 2 week 6 ppt 6 Brainstem Reticular Formation Flashcards
(24 cards)
what does the anatomy of the reticular formation subserve?
the anatomy subserves the functions of the reticular formation:
- –Integrate diverse information from a variety of sources
- –Organize generalized responses
(form goes with function)
What is the function of the reticular formation? (2)
The functions of the reticular formation
- –Integrate diverse information from a variety of sources
- –Organize generalized responses

describe the shape and orientation of reticular formation neurons
–Neurons have large highly overlapping dendritic trees
–Dendritic trees oriented perpendicular to long axis of brainstem
Reticular formation Neurons have large highly overlapping dendritic trees and these Dendritic trees oriented perpendicular to long axis of brainstem

how do the axons of the long ascending and decending tracts and the reticular formation neurons interact?
axons of the the long ascending and descending tracts traverse the brainstem & have collaterals that intermingle with the neurons of the reticular formation
Where does each reticular formation neuron receive information from?
–Each neuron receives information from a wide variety of sources
- One source may dominate input to each neuron
- But may receive both visceral & somatic
- May receive both motor (descending) & sensory (ascending) pathways
describe the output of reticular formation neurons
–Wide spread output with collaterals onto >25,000 neurons
Thalamocortical pathways from thalamic neurons that receive reticular formation input have which two forms of projection to the cortex?
Generalized (System)
- Responsible for maintaining appropriate levels of cortical activity but
- Can be modulated by specific sensory inputs
Specific (system)
- Specific sensory inputs to the cerebral cortex that
- Allows for the detailed analysis of sensory input
what are some characteristics of generalized Thalamocortical pathways?
Generalized (system)
- Responsible for maintaining appropriate levels of cortical activity but
- Can be modulated by specific sensory inputs
what are some characteristics of specific Thalamocortical pathways?
Specific (system)
Specific sensory inputs to the cerebral cortex allow for the detailed analysis of sensory input
Thalamocortical Pathways: overlapping input to cortical neurons from the generalized and specific systems can do what? (2)
- Helps determine which sensations are paid attention to and which are ignored
- Modulates sensory experiences
Functional Characteristics of RF Neurons (4)
- RF neurons are Capable of monitoring activity occurring in ascending & descending tracts
- The Greatest input from each of those pathways is dependent upon which endings are closest to neuron dendritic core & cell body
- The Magnitude of inputs is dependent upon relationship to dendritic tree
- •Subserve integrative functions individually & collectively for several reasons:
- –Input to individual neurons from wide array of input
- –Differences between different parts of RF depending upon which pathways are going thru each of those regions
- –No two RF neurons get the same input pattern
- •RF neurons work together to attain a desired functional end
- •Integrative nature of these neurons suggest that these neurons do not respond to the specific content of the input but rather the degree and pattern of activation of those inputs
Reticular neurons are Capable of monitoring activity occurring in ascending & descending tracts. The Greatest input from each of those pathways is dependent upon which endings are closest to neuron dendritic core & cell body with the Magnitude of inputs dependent upon relationship to dendritic tree.
Reticular neurons Subserve integrative functions individually & collectively for several reasons:
Input to individual neurons from wide array of input
Differences between different parts of reticular formation depending upon which pathways are going thru each of those regions
No two reticular formation neurons get the same input pattern
Reticular formation neurons work together to attain a desired functional end. The
integrative nature of these neurons suggest that these neurons do not respond to the specific content of the input but rather the degree (magnitude) and pattern of activation of those inputs
Explain details about how RF neurons are capable of monitoring activity occuring in ascending & descending tracts
RF neurons are Capable of monitoring activity occurring in ascending & descending tracts
- The Greatest input from each of those pathways is dependent upon which endings are closest to neuron dendritic core & cell body
- The Magnitude of inputs is dependent upon relationship to dendritic tree
Explain reasons why RF neurons subserve integrative functions individually & collectively (3)
- –The Input to individual neurons comes from a wide array of sources
- –There are Differences between different parts of RF depending upon which pathways are going through each region
- –No two RF neurons get the same input pattern
I think this is saying that each neuron gets input from a wide variety of sources and there are differences between the parts of the RF based on the pathways that are going through each part. Also no two RF neurons get the same input pattern. They all subserve integrative functions because each individual has a uniqe input pattern that it senses (and can integrate) and also all the neurons together get an overall input pattern that can be integrated by neurons commnicating. ??
Name 5 functions of the reticular formation
- •Control of the level of consciousness
- •Modulation of pain
- •Regulation of motor activity
- •Coordination of vision
- •Control of autonomic & automatic activity
Explain the reticular formation control of the level of consciousness generally
- •Wide variety of diffuse modulation of cerebrocortical activity
- •Reflected in electroencephalogram (EEG)
- •Ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) for widespread activation of cortex
- •Bilateral damage to this system produces a comatose state
- •Two routes
- –Direct
- –Thalamocortical
The role of the Reticular Formation in the modulation of the Level of Consciousness is due to the Wide variety of diffuse modulation of cerebrocortical activity that the reticular formation provides. This wide range of cerebrocortical activity is Reflected in electroencephalographic (EEG) activity
Ascending reticular activating system (ARAS)is responsible for widespread activation of cortex and Bilateral damage to this system produces a comatose state
There are two routes from the reticular formation to the cerebral cortex:
Direct
Thalamocortical
The Two Direct routes from the reticular formation to the cerebral cortex in the modulation of consciousness are:
Two Direct routes
- –Noradrenergic neurons – locus coeruleus
- –Serotinergic neurons – midbrain & pontine raphe nuclei
The Two Direct routes from the reticular formation to the cerebral cortex in the modulation of consciousness are the
Noradrenergic pathways from neurons in the locus coeruleus
Serotinergic pathways from neurons in the midbrain & pontine raphe nuclei

Reticular formation: control of the level of consciousness
Details about the thalamocortical pathway
- •Generalized thalamocortical system
- •Via interlaminar nuclei of thalamus
- •Largely cholinergic - pedunculopontine tegmental & dorsal tegmental nuclei
The Thalamocortical pathway from reticular formation to the cerebral cortex utilizes the Generalized thalamocortical system which projects Via interlaminar nuclei of thalamus. The reticular formation pathways responsible for this are Largely cholinergic from neurons in the pedunculopontine tegmental & dorsal tegmental nuclei

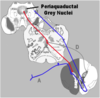
RF: Modulation of pain
explain the descending pathways
•Descending pathways release transmitters onto dorsal horn nuclei regulating transmission of nociceptive signals
- –Locus coeruleus releasing norepinephrine
- –Raphe magnus & pontine & midbrain raphe nuclei
- –All release serotonin
- –Periaqueductal gray releases enkephalins
- –Direct & indirect inhibition (red) of nociceptive pathways (blue)
The Reticular Formation also plays an important role in the Modulation of Pain. Descending pathways release transmitters onto dorsal horn nuclei and spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve neurons regulating transmission of nociceptive signals. One of these pathways descends from neurons in the Locus coeruleus which release norepinephrine. Additionally there are Descending pain modulation pathways from neurons in the Raphe magnus & pontine & midbrain raphe nuclei. Neurons from all of these structures release serotonin. Descending pain modulation pathways also arise from neurons in the Periaqueductal gray region of the midbrain. These neurons release enkephalins. There are both Direct & indirect inhibition (shown in red) of spinal nociceptive pathways (shown in blue)
RF: Locus coeruleus
about it
what does it release?
Plays an important role in the modulation of pain.
neurons from the locus coeruleus form of the descending pathways that releases transmitters onto dorsal horn nuclei and spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve neurons,
these release norepinephrine
The Reticular Formation also plays an important role in the Modulation of Pain. Descending pathways release transmitters onto dorsal horn nuclei and spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve neurons regulating transmission of nociceptive signals. One of these pathways descends from neurons in the Locus coeruleus which release norepinephrine

RF: expalin the following nuclei
Raphe manguns
pontine raphe nuclei
midbrain raphe nuclei
- descending pain modulation pathways originate in these nuclei
- Neurons from all of these structures release serotonin
Additionally there are Descending pain modulation pathways from neurons in the Raphe magnus & pontine & midbrain raphe nuclei. Neurons from all of these structures release serotonin

RF: explain pariaqeductal gray in relationship to modulation of pain
Descending pain modulation pathways also arise from neurons in the Periaqueductal gray region of the midbrain. These neurons release enkephalins.
There are both Direct & indirect inhibition (shown in red) of spinal nociceptive pathways (shown in blue)
Reticular formaiton: explain the regulation of motor activity
•Voluntary motor activity can be modulated by descending inputs from the reticular formation
- –Medial (pontine) and lateral (medullary) reticulospinal tracts project to the ventral horn of the spinal cord
- –Neurons of the reticulospinal tracts transmit integrated cerebellar, vestibular, and cortical information
Reticular Formation is also involved in the Regulation of Motor Activity. Voluntary motor activity can be modulated by descending inputs from the reticular formation Medial (pontine) and lateral (medullary) reticulospinal tracts project to the ventral horn of the spinal cord
Neurons of the reticulospinal tracts transmit integrated cerebellar, vestibular, and cortical information
Reticular formation: explain coordination of vision
•Brainstem gaze centers
- –Coordination of conjugate movement
- –Located in:
- Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF)
- Rostral interstitial nucleus (RIN) of the midbrain reticular formation
- –Regulate LMN activity in CN III, IV & VI nuclei
- §Hortizontal gaze coordination in PPRF
- §Vertical gaze in RIN
- §Via medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)
- –These centers are in turn controlled by frontal eye fields of cerebral cortex
Reticular Formation also plays an important role in the Coordination of Vision. Remember as previously discussed Brainstem gaze centers are involved in the Coordination of conjugate eye movement. As previously discussed these neurons are Located in: Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) and the Rostral interstitial nucleus (RIN) of the midbrain reticular formation
These Brainstem gaze centers Regulate LMN activity in CN III, IV & VI nuclei. Particularly the is Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) is responsible for Hortizontal gaze coordination and the Rostral interstitial nucleus is responsible for Vertical gaze coordination.
These areas of the reticular formation have their effects Via the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). Also as discussed previously these reticular formation centers are in turn controlled by frontal eye fields of cerebral cortex

Reticular formation: explain the regulation of autonomic and automatic activities
- •Centers controlling heart rate, blood pressure
- –Parasympathetic centers cranial nerves afferents & efferents and projecting to sacral spinal cord
- –Sympathetic centers as well
- •Control of automatic processes such as ventilation (inspiratory and expiratory centers)
And finally the Reticular Formation plays an important role in the Regulation of Autonomic & Automatic Activities. There are reticular formation centers controlling heart rate, blood pressure. There is reticular formation control of Parasympathetic centers regulating both cranial nerves afferents & efferents and projecting to sacral spinal cord and there is influence of reticular formation centers on Sympathetic centers as well
There is also reticular formation Control of automatic processes such as ventilation (inspiratory and expiratory centers)


