4.1.3 Integrative Metabolism II Flashcards

E - gluconeogenesis
What are some of the important compounds derived from amino acids?

What types of receptors does thyroid hormone act on?
Acts through nuclear receptors

Describe the steps of synthesizing NO from arginine?
Arginine ⇒ Citulline + NO

Fill in this chart


How does cortisol act as a hormonal regulator of metabolism? How does it affect the following:
glycogen synthesis
gluconeogenesis
proteolysis

How does epinephrine act as a hormonal regulator of metabolism? How does it affect the following:
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
lypolysis
glucagon release
insulin release

Describe the pathway of the sources of energy in liver, pancreas and kidney


GLUT-4

glutamine and alanine
Describe the dependency of tissues on the various metabolic fuels. (Glucose, FAs, and ketone bodies)
Notice the tissues that are completely dependent on glucose

Draw a diagram of the sources of energy for a brain cell.


Either increase or decrease the expression
What is the role of glucagon as a hormonal regulator of metabolism? How does it affect the following:
glycogenolysis
gluconeogensis
glycogen synthesis
FA synthesis
metabolism of FAs

What are the metabolic consequences of starvation?


E - 1,2,3,4, and 5


What is the role of insulin as a hormonal regulator of metabolism?
Acts to lower blood sugar and promotes glycogen synthesis
Drugs that inhibit NOS will have what effect?
These will decrease NO - which will lead to increased BP
Draw the pathway of the sources of energy within an adipocytes

What is EDRF and Coronary Artery vasodilation?

Fill in this chart



RBCs
Which GLUT transporter is reliant on insulin?
GLUT-4
You should look at this

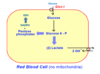
Diagram the path that glucose will take in a RBC
Thyroid hormone comes from what?
Iodinated tyrosine
Describe the pathway of the sources of energy in muscle and heart cells.

How does NO act as a mediator of erectile dysfunciton?
Drugs like cialis or viagra will increase blood flow to organs and cause relaxation


