1.4.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Flashcards
What can be the symptoms of galactosemia?
Failure of neonates to thrive - vomiting and diarrhea result from ingestion of milk
Can also develop blindness - due to precipitation of byproduct in the lens
What is lactose intolerance

Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and its role in gluconeogenesis, is inhibited by?
ADP
Why is gluconeogenesis important?
Because hours after a meal the blood glucose levels in a person will return to a fasting state, and there needs to be a means of getting glucose to the brain
Draw an overview map of metabolism

What reactions occur in the mitochondria matrix?
Citric acid cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation
Beta-oxidation
How is glucose an example of a futile cycle?
Glucose enters a cell and is phosphorylated by hexokinase. The phosphorylation leads to the inability of glucose-6-p molecule to exit the cell. The enzyme G-6-Pase can then dephosphorylate the molecule and it just goes around and around and around
UDP-galactose-4-epimerase deficiency can result in?
Similar to the transferase deficiency - treatment is restrict dietary galactose
What is heriditary fructose intolerance?
Lack of aldolase B - severe hypoglycemia
Liver failure can result - treat with avoiding fructose
What are the components of sucrose?
1-2 linkage between glucose and fructose
What is the first reaction in the formation of glucose from lactate?
Lactate to pyruvate
Formation of NADH

Under anaerobic conditions pyruvate is converted into?
Lactate
What are the 3 principle forms of sugar transport?
Facilitated diffusion
Hormone sensitive transporters
Na coupled transport
What is this an image of?
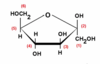
β-D-Fructose
Can G-6-P inhibit both glucokinase and hexokinase?
No
It can inhibit hexokinase but not glucokinase
Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase, and its role in gluconeogenesis, is stimulated and inhibited by?
Stim - Citrate
Inhibited - F-2,6-BP, AMP, ADP
How will F-2,6-BP affect gluconeogenesis?
It will inhibit gluconeogenesis
Inhibits the reaction of F-1,6-BP to F-6-P
What are the 3 components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
E1 - decarboxylase
E2 - dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
E3 - dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
What is essential fructosuria?
Lack of fructokinase
Describe the process of galactose metabolism?

F-1,6-BP can also act as an allosteric regulator, how?
F-1,6-BP can also “feed forward” in the reaction to stimulate the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate.
The GLUT-4 transporter is sensitive to what? What tissues is it found in?
Sensitive to - insulin
Found - muscle, heart, and adipose tissue
What will inhibit the reaction of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate?
ATP and alanine
Insulin will inhibit
gluconeogenesis







