2.1.1 Metabolism II Flashcards
Disorder associated with a defect in glycine and imino amino acid transport?
Joseph’s syndrome or glycinuria
What reactions are mediated by the enzyme serine-threonine dehydratase?

Describe the arginine metabolism pathway from arginine to L-glutamate

Classify the amino acids into three groups: glucogenic (make glucose), ketogenic, and both glucogenic and ketogenic.
Memorize the only ketogenic: Leu, Lys

Cytosolic protein turnover (non-lysosomal) characteristics
- pH near neutrality
- proteases with optimal pH around 7
- Cytosolic proteases are metal requiring
- Proteins are marked with ubiquitin
- Ubiquitin tagged proteins are attacked by proteosome complexes
- Proteosomes with high molecular weight (1500 KDa)
- Ubiquitin covalently modifies lysine residues
- Ubiquitin plays other roles in cellular signaling
Name 4 enzymes that are used in breaking down proteins. (and where they are found)
Carboxyl protease: pepsin (stomach)
Serine proteases: trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase (pancreatic secretion)

State the important transporters involved in the absorption of amino acids.
Apical: Na + Amino acid symporter
Basal: Na-K ATPase, amino acid channel

Name the 6 characteristics of lysosomal degradation in protein turnover
- lysosomal pH b/t 4 and 5
- variety of proteases with pH optima in this range
- lysosomal porteases act on proteins which are taken up via endocytosis from outside the cell or cell surface (surface receptor)
- The process of endocytosis yields endosomes which fuse with proteosomes which allows for breakdown
- Capable of breaking down proteins all the way to free amino acids
- Use the mannose-6-phosphate marker
What are some of the metabolic intermediates derived from the carbon skeletons of amino acids?
pyruvate, acetoacetyl CoA, acetyl CoA, alpha-ketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate, oxaloacetate
What are some ways that nitrogen is excreted?
Urea (30g, 86%), ammonium ion, creatine, uric acid
What enzyme is implicated in schizophrenia?
D-amino acid oxidase
Where are polyamines important in the body?
Polyamines are important in the nucleus, as they are used to neutralize the negative charges of nucleic acid
Most amino acids are converted to what two molecules?
Alpha-ketoglutarate and glutamate

The 3 characteristics of AA catbolism (portal/liver)
- After absorption across the gut the AAs are carried to liver via the portal system
- the liver is principal site of both carbon skeleton and nitrogen metabolism and most active organ in synthesis and catabolism
- most nitrogen is removed from the AAs by ezymes which either transaminate or alternatively remove the nitrogen to produce NH3
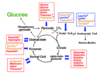
Describe how glucose can be formed from the citric acid cycle
A deficiency in what ezyme that mediates the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine is indicated in PKU?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Name the vitamin derived cofactor that plays an important role in amino acid and nitrogen metabolism
Pyridoxal phosphate

Protein is used as energy storage. How much energy is stored as protein?
6000 g
24000 kcal
How can arginine be used to synthesize nitric oxide?

Disorders associated with a defect in dibasic amino acid transport?
cystinuria or dibasic aciduria
Proteins can be broken down into amino acids. Amino acids can be catabolized into what molecules that feeds into the citric acid cycle?
Acetyl-CoA
Disorder associated with a defect in dicarboxylic amino acid transport?
dicarboxylic aciduria
Name the 4 different transporter mechanisms, the proteins they move, and diseases associated with a defect in this transport mechanism.
Neutral, Dibasic, Dicarboxylic, Glycine and imino

Describe the pathway that yields cystine from methionine?

Describe the various pathways involved in polyamine synthesis.

What sources as the main source of energy storage?
Triacyl glycerol
Describe how proteins are broken down and what they yield?

High levels of what intermediate of amino acid breakdown is associated with cardiovascular issues?
Homocysteine
Name the 5 inborn errors in amino acid metabolism.

What organisms convert N2 into NH3?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
The inborn error in amino acid metabolism that is associated with inappropriate handling of tryptophan, alanine, (etc. neutral amino acids)

Disorder associated with a defect in neutral amino acid transport?
Hartnup dz
What oxidative deamination reaction is mediated by L-amino acid oxidase?

Describe the three step process used to degrade branched chain amino acids to acetyl CoA.
- Transaminination -> 2-ketoglutarate
- Oxidative decarboxylation
- Dehydrogenation/etc.

Describe the enzymes used in propionate metabolim

Name the essential amino acids in adult humans.
Human infants and children need additional histidine and arginine during growth and recovery

What reaction is mediated by glutamate dehydrogenase?
NH4 + alpha-ketoglutarate <–> glutamate



