3.1.3 GI Hormones Flashcards
What is the oral phase of digestion?
mastication, starch digestion, swallow
Describe the duodenal phase
most pancreatic secretions, secretin release, suppression of acid production (inhibit parietal/ECL cells)

What is the small intestine phase?
absorption of nutrients and water/ions, release of peptide YY to inhibit gastric functions

What is the esophageal phase?
peristalsis, relaxation of UES and LES
Describe the duodenal regulation of pancreatic HCO3- secretions. Focus on the role of one particular enzyme and what are the stimulators

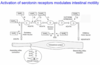
What is the role of serotonin in the GI tract?
Modulation of intestinal motility
What is the cephalic phase?
sight, small, taste, thought of food → saliva, acid, pancreatic secretions, gallbladder contractions
Where does gastrin travel to ellicit its action?
travels to oxyntic mucosa to stimulate production of acid by parietal cell
Also acts on ECL cells to activate histamine, which also activates parietal cells
Draw a chart of the gastric phase of digestion

What is the role of somatostatin in the oxyntic mucosa?
Reduce histamine release
Reduce HCl secretion
Reduce pepsin secretion

Gastrin producing G cells are where?
Antrum
What induces gastrin secretion?
Antrum distension
Gastrin releasing peptide
Fat, protein and AAs
Lumen neutralization
How does somatostatin affect insulin?
Inhibits it
What are enterogastrones? What are some examples?
Hormones that inhibit stomach processes
Ex. CCK and secretin
Fill in this chart.


Describe the activation of pepsinogen
Acid in stomach stimulates local neurons and release of secretin → Chief cell stimulated by nerve (ACh) → somatostatin inhibits it

What are suppressors of gastrin?
Somatostatin
Starvation
Lumen Acid less that pH3
What is the role of the pancrease in the intestinal phase?

What is the main cell type that releases pepsinogen?
Chief cells
Secretin is release by what cells and is stimulated by?
released by S cells, activated by chyme
What is the role of CCK on the gall bladder? Discuss the signaling pathway

What are the neurotransmitters/neurohormones that alter GI motility?
Notice the changing role of CCK when changing from small intestine and stomach

Gastrin releasing peptide is produced where and affects where?
GI nerves and effects muscle and mucosa
Describe the colonic phase.
absorption of water and ions, storage and elimination of feces

What is the gastric phase of digestion?
stimulated by stretching, acid secretion, pepsinogen, pancreas and gallbladder activation

What are the important players in the negative feed back of pancreatic secretions?
somatostatin - produced by intestinal D cells
peptide YY - Induced by fat in distal small intestine
glucagon
Pancreatic Polypeptide - stimulated by vagus
What is the gastric phase of digestion in regards to the pancreas, gallbladder and colon?

What is the role of somatostatin in the antrum?
Reduce gastrin release

What is the role of motilin?
Phase III interdigestive intestinal motility

What is this an image of?

Enterochromaffin cell producing serotonin
Describe the hormonal and neuronal regulation of gastric acid secretion?

GLP-1 does what to gastric emptying?
It slows emptying

How does histamine affect D cells?
Histamine will stimulate D cells to produce somatostatin, which can in turn inhibit the ECL and parietal cells
What is the function of gastrin?
Stimulate parietal cell acid secretion
Stimulate histamine release
Incease tone of LES
Induce mucosal growth
Induce somatostatin release
Describe the activation and action of CCK
chyme → releasing peptide by I cells → vagus signal → pancreas
Fats to duodenum → CCK release → gallbladder contraction and relaxation of sphincter of Oddi by vagus n.



