1.2.3 Basic Organization of Cell Tissues of GI Tract Flashcards
What is this an image of?

Enteroendocrine cell
- enteroendocrine: endo = part of epithelium, endocrine = release hormone into blood (in contrast to exocrine which release their products outside the body, e.g., the gut lumen)
- some enteroendocrine cells project to the gut lumen where they have receptors that can sense nutrients and respond by releasing their hormone
What are some methods of stimulation of intestinal secretion?
Mast cells secreting histamine and binding to the cells
or
Submucosal neuron that releases acetylcholine

cAMP does what to the CFTR channel?
Increases Cl- secretion through it

What is this an image of? What are each of the lines pointing to?

Esophagus

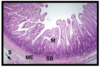
What is this an image of and what are the lines pointing at?
Small intestine crypt

What is this an image of?

Large intestine on TEM
Colonocytes
Presence of large intercellular spaces is characteristic of a fluid absorbing epithelium.
Has the capacity to secrete fluid as well
cAMP inhibits what in the intestines?
THe Na/H exchangers which can cause diarrhea
Goblet cells do what?
Secrete mucins
What is this an image of?
Small intestine with simple columnar epithelium
- villus epithelium is generally considered absorptive
- crypt epithelium is generally considered secretory
M = mucosa
SB = submucosa
ME = muscularis externa
S = serosa
cAMP inhibits what in the intestine?
Na Reabsorption

What channel secretes NaCl in the intestines?
CFTR - activated by cAMP

What are the layers of the GI tract?

What is this an image of?

Migration of the epithelial cells - how fast it occurs
What is the role of each of the labeled parts of this image?

microvilli
apical plasma membrane
actin cytoskeleton (terminal web)
ZO zonula adherens: tight junction - barrier function
ZA: zonula adherens - structural
D: desmosome or macula adherens - ‘spot weld’
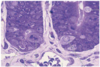
What is this an image of?

Submucosa of the stomach
arrow = muscualris mucosae
ME = muscularis externa
What is this an image of?

Left side - stomach comprised of simple columnar epithelium
Right - esophagus stratified squamous epithelium
What is this an image of?

Muscularis externa - myenteric plexus (intestine)
Arrows = neurons
Arrowheads = supporting cells
-circular layer is on the left, longitudinal layer is on the right of the image
What are the functions of the intestinal epithelium (6)?
Barrier and immune defense
Fluid and electrolyte absorption
Protein synthesis and secretion
Nutrient digestion and absorption
Fluid and electrolyte secretion and IgA secretion
Mediator production
What is this an image of?

Lamina propria of the small intestine
What is this an image of?

Lamina propria - plasma cells (small intestine) main secretor of IgA in the small intestine
What are an important parts of the small intestine?
Villi and crypts
Villi are absor
Crypts are secretory

What is this an image of?

Goblet cells
Exocrine cells
Mucins = glycoproteins
- >50% carbohydrate by mass
- principally O-glycosylation in the Golgi
- bind various microbes
- MUC2 produced by goblet cells - secreted mucin
- MUC3 produced by enterocytes - cell associated mucin
Mucus = mixture of mucins, other glycproteins, etc., fluid and electrolytes.
R = rough ER
G = Golgi apparatus
SG = secretory granules
M = microvillus of adjacent enterocyte
How is water absorbed in the intestine?
Reabsorption of solutes and H2O follows
Na/K ATPase

What is the MM and what is the red line pointing to? What is circled?

Small intestine
MM - muscularis mucosae - smooth muscle
Red line - Paneth cells
Circled - mitotic figure
Explain the difference in the cell renewal of the GI tract in the stomach and the small intestine
- stem cells in stomach at neck of glands
- stem cells in intestine in crypts
- stem cells give rise to all the differentiated functional epithelial cell types of their respective organs

What is this an image of? What are the different parts?

Large intestine - epithelium are simple columnar - absorptive with secretory potential
M = mucosa
MM = muscularis mucosae
SM = submucosa
ME = muscularis externa



