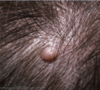
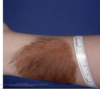
Workshop: Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions Flashcards
• What is the primary morphology of the lesion?
A. Macule B. Papule C. Patch D. Plaque E. Vesicle F. Nodule
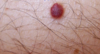
cherry hemangioma- bright red raised papule
• What is the primary morphology of the lesion? A. Macule B. Papule C. Patch D. Plaque E. Vesicle F. Nodule

PAPULE-raised, purple, small
VENOUS LAKES
• What is the primary morphology of the lesion? A. Macule B. Papule C. Patch D. Plaque E. Vesicle F. Nodule

papule. dermatofibroma. raised + hyperpigmented

• What is the primary morphology of the lesion? A. Macule B. Papule C. Patch D. Plaque E. Vesicle F. Nodule
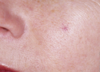
spider telangiectasia/nevi– a MACULE
• What is the primary morphology of the lesion? A. Macule B. Papule C. Patch D. Plaque E. Vesicle F. Nodule

varoucous, raised, possible a papule, maybe a plaque or nodule
seborrheic keratosis

seborrheic keratosis

seborrheic keratosis

seborrheic keratosis
primary morphology
pedunculated papule. acrochordon


erythematous and yellow umbilicated papules on places with evident pores. sebacious hyperplasia
primary morphology

macule. solar lentigo

seborrhaic keratosis

actinic keratoses. papule, maybe a plaque

actinic keratosis
$

actinic keratosis

actinic keratosis–erythematous papules/macules with scale on sun- exposed sites
treatment for actinic keratosis
cryotherapy, maybe surgery, field therapy with fluorouracil

squamous cell carcinoma

squamous cell carcinoma

squamous cell carcinoma

squamous cell carcioma

Squamous cell carcinoma – erythematous crusted papules, plaques, nodules

basal cell carcioma– erythematous, umbilicated (sometimes), papule. doesn’t spread as fast as SCC

BCC- papule, telangiectasia