Lower Extremity: Acute Knee Injury Flashcards
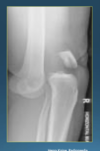
what’s going on in this xray
small bone fragment underneath the knee– a BONE CHIP.
- will change in shape and pain– needs to be taken out.

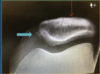
wha’ts going on in this knee scope

there is a large osteochondral fragment between the articulation of femur and tibia
T/F you can sprain your knee
false. this is an oversimplification. You can tear your ACL or PCL but you need an actual diagnosis to tailor the treatment.
treatment of ankle sprain
RICE
Rest, Ice Compression, Elevation
A person had a knee injury two years ago and was told they sprained their knee. They returned to soccer after some rest and there has been tweeks in the past where the knee just gives out, but it has never been as bad as the first injury. Now, however, he cannot straighten his knee.
Imaging is as shown. What was missed?

he most likely had a torn ACL. You can see evident meniscus trauma. The torn ACL causes bone shifting. meniscus then takes up the slack of the torn ACL and it’s not meant to have that much loading force on it at all times. it causes meniscal traring and flipping– can block motion which is why he can’t straighten his knee.
T/F a knee replacement for bone erosion is the first line treatment in a 42 year old.
false. you must buy time using screws. a 42 year old is not a candidate for knee replacement–they’ll wear through it quickly. they just support the joint and try to remove the pressure.

T/F you need an MRI to diagnose an ACL tear
false. MRI makes a dx 95% of the time, but we can’t do it on everyone. there are strict infications for urgent MRI in acute soft knee problems.

Indications for Urgent MRI in Acute Soft Tissue KNee Problem

locked vs stiff knee
lock: knee won’t fully extend. torn meniscus or torn ACL, could benefit from MRI
stiff: lack of band and strenght. Don’t need an MRI
Causes of lock knee.
a locked knee is one where there is an ACUTE MECHANICAL BLOCK to preventing extension with “normal” flexion. Pain and or weakness do not constitute a mechanical block
- a locked knee can be caused by a displaced meniscal tear, a loose body, or a prominent stump of ACL.
- a stiff knee is a knee where tehre is loss of both flexion and extension due to injury, surgery, or arthritis.
A joint swells up within the first 2 hours of injury, what is most likely in the joint when aspirating it?
blood. it’s not going to be synovial fluid. It takes a while for synovial fluid to be made. If it swells up the day after, it could definitely be synovial fliuid, but if it is an acute swelling, it’s probably blood.
how much synovial fluid does a normal knee have?
3 cc. it normally just wets the surface of the joint. if it’s swollen, it easily has enough to aspirate.
what is the contents of synovial fluid and what is it’s function
- it’s ultrafiltrate of blood plasma containing proteins from the blodo plasma mixed with proteins secreted by synovial cells and chondrocytes.
function:
1. lubrication
- nutrition
- shock absorption (rheopectic)
T/F you should aspirate a joint if you suspect hemarthrosis within 1-2 hours of injury
false. hemarthrosis is blood contained within the acapusle of a joint. there is no need to aspirate if the swelling was prestn within 1-2 hours of injury– sometimes it feels better when the blood is taken out, but that doesn’t treat the underlying cause.
you are aspirating a joint that has been swollen for over 4 hours. you see an oily substance in the aspirate. what might be occuring?
if you see fat globules in a joint aspirate, it’s from the bone marrow. there is probably a fracture leaking marrow contents into the capsule.
outline the intra-capsular structures– which ones have the capacity to cause hemarthrosis in response to trauma? (SLAMB)
S; synovium: yes
L; ligaments: yes
A; articular cartilage; no
M; meniscus; yes
B; bone yes
- when you see blood in a joint, htink about what structures can bleed when trauma to it occurs. if the articular cartilage is affected you wouldn’t see bleeidng or acute swelling.
differential diagnosis of hemarthrosis
- bleeding disorder– hemophilia A, B, Vwf
- fracture (bone)
- extensor mechanism injury
- meniscus tear
- ligament tear.
T/F if someone has hemarthrosis you should alwasy to PT PTT and INR to rule out bleeding disorder
false. first check history if you suspect a bleeding disorder– bleeding with minor injuries and dental procedures, spontaneous bleeding into joints and muscle ,family history etc. Ask about prior surgeries.
- you don’t need to test for a bleeding disorder if they have a pretty obvious cause of swelling– like fi they were snowboarding and now they have an acute swollen knee– you dont test for VWF– that’s a waste of resources
On physical exam, how would you maybe elucidate that the hemarthrosis is caused of a bleeding disorder and not due to an acute joint injury?
if there’s no bruising, point of maximal tenderness, no back story, no imaging findings.
what’re the ottawa knee rules for getting a knee xray?

would you see bruising in a tibial plateau fracture?

Proximal tibia is broken. The knee capsule might hold the blood in the joint capsule so you might not see bleeding.
you might see hemarthrosis in a tibial plateau fracture, but not in a distal tibia fracture. Why?
There will not be blood in the knee. The distal tibia is broken, the blood from shaft probably wont migrate to the knee. Might see bruising on site of trauma.

3 most common extensor mechanism injuries (stuff that straightens you knee)
- knee extensors are quads
1. patellar dislocation
2. quadriceps tendon rupture
3. patellar tendon rupture.
Bruising, PMT, Special tests and imaging for patellar dislocation?
bruising; maybe
PMT: medial
Special tests; apprehension sign
Imaging; often normal
Can be direct impact, but if there are risk factors like old age or female, it could just be from a twisting injury or getting up off the ground.