Cutaneous Manifestation of Systemic Disease Flashcards
2 key neutrophilic dermatoses
sweets syndrome
yoderma gangrenomsum
• 56yo M
• 4 day history of mild lower leg swelling and painful spots on his legs
How do we describe his skin lesions? what could be happening?

erythematous raised papules that are coalescing into plaques. looks like petechiae. distributed over the lower extremities.
palpable purpura are heavily associated with vasculitis–could be solely cuteaneous but we should look also for systemic symptosm– claudication, lung and kidney problems (ANCA associated vasculitis)
where does palpable purpura manifest?
in the dermal vasculature layer. neutrophil inflammation in the papillary dermis causes prupura.
treatment for cutaneous small vessel vasculitis
- supportive care (leg elevation/rest)
- identify trigger and labs– ANCA associated? be aware of the systemic implications specifically glomerular neprhitis or pulmonary infiltrates or alveolar hemorrage.
- NSAIDS, antihistmaines for a skin limited disease
- if systemic, remission requires high dose of systemic steroids followed by biologics or DMARD therapy like azothiaprine
palpable purpura with central necrotizing erosion

palpable purpura

palpable purpura
note:
vasculitis involving medium or large vessels does not usually present with palpable purpura
You are the dermatology resident on call and are called to see a patient in the emergency room.
She has felt unwell for several days and developed new skin lesions
this morning

erythematous tender patches that are showing signs of epidermal sloughing or necrotization. did she take any drugs? this might be SJS or sweet syndrome.
outline the morphology and dx

sweet syndrome
tender non-prurutic erythematous plaques with uneven mamillated surface, pronouned edema
- pseudovesicular or pseudopustular appearance
- favors head and neck and upper extremities
- 20% have internal malignancies.
this is a clue to serach for a systemic disease
•They tell you the patient developed what started as a bug bite two days ago and now is progressing rapidly with extreme pain
- presents with this erosion

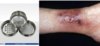
necrotizing borders with large erosions/ulcerations. pyoderma gangrenosum.
ulcer with necrotic undermined grey colored border. very painful. need to rule out infection. this might not be necrotizing fascitis– if we debride and it turns out to be PG instead of NF, it can turn out worse.
key lesion in diagnosing pyodermal gangrenosum
sieve like cribiform lesions
disease associations with pG

treatment of PG

- The next day your neighbor, who knows you are a medical student, approaches you when you are out walking with your family.
- They are feeling fine but have been getting these very itchy welts on their arms and body for a couple of days.
- They’d like to know what it is and if they should be worried!

erythematous raised plaques. almost annular.it is short term– maybe urticaria

urticaria

if urticaria is fixed for more than 24 hours, tink ___ ___ rather than hives
sweet syndrome rather than hives.
- most poeple wiith hives are well, it’s not a systemic conditions

key thing to rule out when someone presents with urticaria
make sure it’s not anaphylaxis– presents with angioedema, difficulty swallowing, breathing
a huge chunk of acute urticaria is due to
URTI

lines of therapy for urticaria
first line: non-sedating antihistamine like cetirizine
second line: if symptoms persist after two weeks, increase dose to as much as four times the standard dose
- third line; add on to second line treatment omalizumab or cyclosporine

is this cellulitis?

probably not, cellulitis is not usually bilaterla. this is probably Erythema Nodosum
in erythema nodosum, there is an acute eruption of tender, erythematous subcutaneous nodules over
____ areas (can also be on __ and __).
Associated ____, ___, _____, malaise
• Delayed hypersensitivity to variety of antigens (___, ___,
___ agents, etc)
- Acute eruption of tender, erythematous subcutaneous nodules over pretibial areas (can also be on thighs and forearms)
- Last days-weeks then slowly involute without scarring
- Associated arthritis, arthralgia, fever, malaise
- Delayed hypersensitivity to variety of antigens (bacteria, viruses, chemical agents, etc)





