Principles of Management of Rheumatic Disease Flashcards
cardiovascular effects of NSAIS
- exacerbation of congestive cardiac failure (cause salt and water retention due to effect on renal function)
- can cause hypertension
- can increase the risk of myocardial infarcts and stroke
30 year old female complains of
– Aching joints
– Tiredness
– Can’t do her usual activities
– Blood tests ordered : • RF positive/ANA positive
What would you do now? What would you be looking for on each test?
History: duration of joint symptoms, persistence of joint symptoms (present all day every day?), pattern of joint involvement, systemic symptoms, extra-articular manifesations, functional capability.
Physical Exam: presence of weightloss, fevers, number of swollen/tender joints, nodules, other organ system invovement (ex/ oral/eyes might indicate lupus)
CBC: Hgb, WCC, platelet count
ESR, CRP
RF and Anti-CCP (ACPA) levels for RA
ENA profile for lupus
Joint Xrays
which scoring system can be used to evaluate the severity of disease in patients with RA?
DAS28. Disease activity score. takes into consideration the number of tender joints, number of swollen joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and general health status.
why is imperative that early treatment is started when someone has RA?
RA patients have joint erosions early. 40% wihtin 6 months, and 70% within 2 years.
-erosions represent permanent structural damage. joint damage may progress at a rapid rate. prevention of damage early in disease is likely to preserve patient function
primary reason why mortality is higher in peopel with RA
because there is a higher rate of coronary artery disease in people with RA.
outline the disease progression of RA
Pannus is a type of extra growth in your joints that can cause pain, swelling, and damage to your bones, cartilage, and other tissue. It most often results from rheumatoid arthritis, an inflammatory disease that affects your joints, though other inflammatory diseases are also sometimes to blame.

lifestyle adjustment for RA
rest, reduced tress, exercise (helps), weight control, quit smoking.
outline the pharmacological appraoches to treating OA, early RA, ankylosing spondylitis, and Systemic Lupus E.
certain NSAIDs are not very effective in active RA, but they are prescriped in mild OA and in soft tissue injuries. they are still often prescribed in RA still since it can be an anti-inflammatory via blocking prostaglandin synthesis.

NSAIDs are used heavily in individuals with MSK issues. What can be done to reduce the risk of GI complications?
- use gastroprotective drugs, misoprostol and PPI
- safer NSAIDS (cox 2 selective)
- identify risk factors (age, history of GI ulcertaion or GI complication, concomitant dru use like corticosteroidS), h.pylori, combo nsaid use.
- use lowest effective NSAID dose
renal side effects of NSAIDS
NSAIDS affect prostaglandin production
- prostaglandins play a key role inrenal perfusion
- in patients wiht reduced renal function, NSAIDS cause further decreased function.
- check creatinine levels routinely.
cardiovsacular effects of NSAIDS
NSAIDs can cause an exacerbation of
congestive cardiac failure
– Cause salt and water retention due to effects on
renal function
• NSAIDs can cause hypertension or affect the
control of hypertension
– Need to monitor blood pressure in patients • Can increase the risk of myocardial infarcts
and stroke
neurological effects of NSAIDS
• NSAIDs can cause neurological adverse
effects such as
– Dizziness – Confusion – Headaches
• Adverse effects are more frequently seen in
older patients
• Never use long acting NSAIDs in the elderly
patient
coagulation effects of NSAIDS
patients taking NSAIDS bruise more easily because it affects platelets–inhibits platelet aggregation and secretion by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase 1
- avoid NSAIDS in pts with anticoagulants, with PUD, or with esophageal varices.
what are DMARDS
Disease Modifying Agents in Rheumatic
Diseases (DMARDs)
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Methotrexate
- Leflunomide
- Sulphasalazine
- Cyclophosphamide
- Azathioprine
• Mycophenolate
A is for azathioprine

when to use which DMARD

early RA principle management (for disease process)
DMARDS:
methotrexate (MTX) via subQ administration and HCQ
- maybe sulphasalazine
- if mtx not effective you can switch to oral leflunomide
must monitor CBC and LFTs
this is a side effect of which drug?
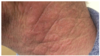
probably methotrexate.
– Common physical adverse effects
• Nausea
• Loss of appetite
• Change in bowel habit
• Hair loss
• Skin rashes, sun hypersensitivity
• Mouth ulcers
what lab abnormalities can you see when a patient is on mtx?
elevated liver enzymes
anemia because of folate inhibition
cytopenias (also because of folate)
adverse effects of HcQ


greyish discoloration of the skin due to HCQ therapy
what is the goal of DMARD therapy?
to have a 20% improvement on a DAS28 score in a patient with a rheumatoid conition (RA)
in addition to steroids and DMARDS and Nsaids for pain, what other agents are good for manageing RA
biologics – tnf-inhibitors– very effective in RA.
two types of TNF-inhibitors
antibody and receptor blocker.
- there are 5– 4 are given by s.c. and 1 by IV infusion





