Rheumatology Review Flashcards
fill out this flow chart


lab factors that make you think it’s RA
rf factor and Anti-CCP
for RA:
• Swelling and tenderness in ___ joints of
___ and __ are most common
presentation
• Symptoms present for > ___weeks with > ___joints and prolonged ___ stiffness
should make you consider RA
• Swelling and tenderness in small joints of
hands and feet are most common
presentation • Symptoms present for > 6 weeks with > 3
joints and prolonged morning stiffness
should make you consider RA
what part of this picture would. make you think it’s RA rather that OA

small joint swelling appearnace is common in both, but OA also has large joint involvement. OA is also less symmetrical, where as in RA, both hands are likely to b affected at the same time.
which diseases are causing each pattern of arthritis?

- RA= symmetric, affecting small joints and the knees
- Psoriatic: very asymmetric
- ankylosing spondylitis: spondilitis/axial involvement and large peripheral joints in an asymmetrical fashion.
- Osteoarthritis: affected some small joints in the hands but LARGE ones too like knees, hip, big toe (compared to MCP)
out of RA, psoriatic arthritis, AS and OA, which one has a more symmetrical presentation?
RA. the rest have fewer joints being affected at once (usually) and are often asymmetrical.

which one is more likely to be OA vs RA

left = OA = bony prominence– it’s hard
right = synovial swelling = RA. Inflammation is soft.
• 3 swollen joints
- MTP/MCP involvement
- Positive squeeze test
• Morning stiffness> 30 mins
most likely diagnosis
rheuamtoid arthritis

how would these lab values look in someone with RA?


Bouchard nodes affect ___ joints in OA, and heberdens nodes affect ____ joints in OA
treat OA with acetaminophen and nsaid pain relief
- Bouchard = pip
- heberden = dip

management of OA
weight managmenet
light exercise (activity may increase the pain but certain activities might help strengthen areas)
T/F ANA is good for lupus detection screenign
false. • The ANA test is not specific to a single disease. It should NOT be used as a
screening test
• A strongly positive ANA test means that it is more likely that a person may have an autoimmune disease. However, positive test results do not tell what type of autoimmune disease it is.
if you suspect lupus, check an ENA profile and anti-smith or anti-dsDNA
note:


what types of arthritis comprise seronegative classifications
AS
psoriatic arthritis
reactive arthritis
IBD related or enteropathic arthritis

what part of the body does spondyloarthritis (rF negative) affect?
spine
what is spondyloarthritis?
• Group of diseases with chronic inflammatory arthritis predominantly affecting the _____
- variable peripheral joint disease that is often ___, involving oligoarthritis of ___ joints and associated with extra articular manifestations such as (___, ___ and ___)
- usually ____ and _____ antibody negative.
- assocaited with the ____ gene
what is spondyloarthritis?
• Group of diseases with chronic inflammatory arthritis predominantly affecting the spine
- variable peripheral joint disease that is often asymmetrical, involving oligoarthritis of large joints and associated with extra articular manifestations such as ibd, psoriasis, and iritis
- usually rf and anti-ccp antibody negative.
- assocaited with the hla-b27 gene
what type of arthritis does this person have
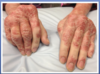
psoriatic arthritis. it’s an inflammatory seronegative arthritis associated with psoriasis. 30% of people with psoriasis have arthritis
associated features and comorbidies of psoriatic arthritis
associated features; dactylitis, asymmetric joints affected involving the spine, plaque psoriasis, enthesitis, uveitis and IBD
comorbidites: CVD, diabetes, NAFLD, depression
Patients with ____ disease more likely to develop PsA
Patients with nail disease more likely to develop PsA4
usual sites of enthesitis

dactylitis is associated with which types of arthritis?
psoriatic arthritis and reactive arthritis


























