Orthopedic Principles: Hand and Wrist Flashcards
which fingers give the hand “grip strength”
the ulnar digits. the thumb gives dexterity.

SOCRATES pain history acronym

SEADS physical exam acronym

a man presents with
– Left wrist pain and numbness for 1.5 – 2 years
– Worst at night
– Shooting pain
– Numbness to fingers
Pt: ‘I shake it out and it goes away after a few minutes’ Dr: ‘Like when you fall asleep on your arm’ Pt: ‘Exactly’
what could this be?

thenar eminence is wasting. this is possibly a carpal tunnel syndrome.
carpal tunnel causes pain because of compression of the -__ nerve
median
nonsurgical and surgical treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome
- non surgical. night time splinting with wrist in neutral position. Injections
- surgical
- carpal tunnel releease.

Kanavals signs can indicate Flexor Tenosynovitis. What are the 4 hallmarks?
- fusiform swelling
- pain on proximal palpation
- flexed posture
- pain with passive stretch.

first treatment for Flexor Tenosynovitis
GET THE PUS OUT

post op complications for purulent Flexor Tenosynovitis
HIGH incidence of post-operative stiffness. we need aggressive rehabilitation starting immediately post op
which bones does the scaphoid articulate with?
radius
lunate
capitate
trapezoid
trapezium

T/F the scaphoid ridge has muscle and tendon attachments
false. however, the radial artery will move up the scaphoid to the dorsl bracn and to the volar scaphoid branch.

which arteries provide most of wrist blood perfusion
branches of the radial artery
- dorsa carpal branch over the top of the scaphoid : 7-80% of blood supply
- volar (superfiical palmar branch): 20-30% of blood supply.

main cause of scaphoid fracture
usually because of wrist hyperextension.
causes radial-side wrist pain.
the scaphoid can be broken at the tubercle, distal pole, waist, or proximal pole.

a person presents with swliing and pain in the antomical snuff box. it hurts more on the volar tuberosirty. pain with ulnar deviation.
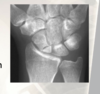
recall these hand movements in terms of what ulnar deviation is lol.
- this is probably a scaphoid fracture. cast for 2 weeks. repeat physical exam and x ray.

the more ___ the scaphoid fracture, the higher risk of non union and compromised/ tenuous blood supply
the more PROXIMAL the fracture
ex/ the fracture below will have a higher risk of non union

pattern of a SNAC (scaphoid non-union advanced collapse)
progressively degenerative arthritis
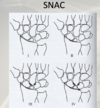
what happens if the scaphoid fracture becomes a SNAC wrist?
basically you just gotta remove the scaphoid and majority of first carpal row. that sucks.
if there is a laceration to the flexor tendons, what should you check for?
if there is a tendon laceration, make sure you chekc neurovascular status, it’s easy to rupture the arteries of the finger. also, after surgery, get into rehab or else you will get stiffness and reduced dexterity/avoid tenolysis

a skiiers thumb damages the __ ___ ligament.

the ulnar collateral ligament.

a skiiers thumb injury in which the UCL is fully torn off is called a ___ lesion; the ligament tears off and doesn’t sit where it’s supposed to– it gets flicked up over another layer of connective tissue instead of sitting on the bone. It won’t heal onto the bone, creating chornic instaiblity of the joint.
stennes lesion

treatment of a partial or complete UCL injury to the thumb
partial– cast/spline
complete tear – surgery to repair












