Pediatric Trauma and Fractures Flashcards
(27 cards)
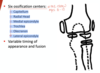
label


do adults have epiphysis
no. only diaphysis and metaphysis
what is an apophysis
a bony outgrowth that arises from a separate ossification center, and fuses to the bone later in development.
- it serves as a site of tendon or ligament attachment.
- it’s vulnerable to avulsion fractures
- the many apophysis in the body have variable appearances and are often mistaken fro fractures.
the ___ is a low pressure system that uspplies the ____ portion of the bone. it forms an extensive network of vessels that covers the entire length of the bone shaft.
the PERIOSTEUM is a low pressure system that uspplies the OUTER portion of the bone. it forms an extensive network of vessels that covers the entire length of the bone shaft.
- the periosteal vessels send small branches thorugh minute channels in cortex to supple about the outer 1.3 cortex.
type of fracture

buckle fracture. bone just bent but didn’t break. this is beacuse in peds, ht ebone is a bit softer and so may not break all the way through

greenstick fracture. broke through on e side but not the other.
type of fracture

Salter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are therefore specifically applied to bone fractures in children.
label the type of fractures


stages of callus healing
- hematoma formation
- soft callus formation
- hard callus formation
- bone remodeling
differentiate the 5 types of salter harris fractures
- through the growth plate
- through the growth plate and metaphysis
- through growth plate and nto joint and epiphysis
- through all three elements of the bone
- crush injury

most common side of pediatric fracture
elbow. distal radius (235)

which one isn’t an ossification center of the elbow?
— Capitellum — Humeral shaft -Radial Head — Medial epicondyle — Trochlea — Olecranon — Lateral epicondyle
humeral shaft. all the other sites are ossification centers.
age 7y 6m
Fall 3m from tree
Painful deformed elbow with a pale hand
- diagnosis?

supracondylar fracture.Supracondylar fractures are the most common type of upper arm injury in children. They are frequently caused by a fall on an outstretched elbow or a direct blow to the elbow.
this kid needs emergent reduction because of vascular compromise.
10 year old girl Fell off slide Refusing to use elbow painful medial aspect

the bones look in tact. this is an elbow dislocation. needs to be reduced. then splint in flexed (stable) position and xray.
boys have the highest amounts of injuries from:
girls have the highest amounts of injuries from:
Boys highest rates per 1000 hour exposure ice
hockey, rugby, then soccer.
Girls highest rates per 1000 hour exposure soccer,
basketball then gymnastics
sports with the highest frequency of injuries involving the head
highschool hockey, karate, taekwondo.
Bernice Fiscus is a 13 year old girl who fell while
hurdling during provincial track and field meet.
She caught her left leg on a hurdle and fell. She
had immediate pain to her left knee and was
unable to weight bear.
It is an isolated injury.
She did not hit her head or lose consciousness.she last ate an energy bar 1 hour before the race.
explain her xrays
her epiphysis is not on the shaft of the femur. in an adult, this wouldve been a knee dislocation.

Management of this fracture would include all of the following except:
A. Urgent reduction
B. Check neurovascular
status before & after
reduction
C. Immobilization with knee
in hyper-flexion
D. Post-reduction x-rays

C. Immobilization with knee
in hyper-flexion. Do not hyper extend the kneee, can cause compartment syndrome.
imaging rules in peds vs adults for knee injuries
if you see swollen knees in adults, you can do an xray an d a bunch of physical exams to diagnose. you do not need an MRI. unlike adults, if you cannot see anything on an Xray, it warrnats an MRI for diagnosis in kids.
Playing soccer Planted and another player hit their knee Twisted

avulsion fracture of ACL. this is an epidemic in young female athelets. we need prevention programs and epiphyseal strenghtening.
treatment for a dislocated patella.
first time: aggressive bracing and physiotherapy. but there is.a 50% re-rupture rate, and will require surgery.
if too young, may just be cartilage and can’t see on Xray, needs an MRI.
dx? tx?

fragmented patella.
Xray Immobilize (knee immobilizer in extension to allow the fragments to come together again) Crutches, safest NWB initially Ice and Follow up with Ortho Unlike Adults many of these need MRI
In the 14- to 17-year-old adolescents with
traumatic primary dislocations in whom imaging
studies show Bankart lesions, there is an
indication for ____ ____ surgery at
the time of the initial injury.
A Bankart lesion is an injury of the anterior (inferior) glenoid labrum of the shoulder due to anterior shoulder dislocation. When this happens, a pocket at the front of the glenoid forms that allows the humeral head to dislocate into it.
In the 14- to 17-year-old adolescents with
traumatic primary dislocations in whom imaging
studies show Bankart lesions, there is an
indication for prophylactic stabilizing surgery at
the time of the initial injury.
note on overuse injuries
- Repeated minor injury to the epiphyses, growth
plates and major tendon attachments may lead to
chronic inflammation and avulsion of areas of
carilage or bone (Apophyses), and microtears and
haemorrhages in tendons.
treatment for overuse injuries?
general rule is to limit activity (but not entirely) if limping or in pain.
- physiotherapy for a stretching and strengthening program.
- inadequate protection can result in avulsion fracture.



