Atopic Dermatitis Flashcards
broad treatment of AD
- avoidance of triggers
- basic care of dry skin
- topical anti-inflammatory agents –> steroids
- phototherapy
- antihistamines
- systemic anti-inflammatory agents.
basic triggers to avoid for AD /eczema

basic dry skin care– lotions vs emolients
use wet wraps
- avoid fragrance and lanolin in emolients
- graesy emolients. lotions will burn irratated skin of children while ointments are less likely to do so.
corticosteroids vs calcineurin inhibitors
corticosteroids: fast acting. good for periodically for acute flares
calcineurin inhibitors: slower acting but NO ATROPHY. good for face or body foldss. less atrophy use, BETTER FOR DAILY USE.

in addition to steroids or calcineurin inhibitors, what else should be prescribed for AD to stop the pruritis?
prescribe sedating antihistamines tend to be better for night time pruritis.
- use non-sedating for daytime use or for allergic symptoms
systemic treatments for AD
- phototherapy
- methotrexate
- cyclosporin
- azothioprine
- biolgoic agents.
what other conditions are associated with atopic dermatitis
asthma or hayfever or rhinoconjunctivitis.
•Acute inflammation and involvement of the cheeks, scalp and ____ aspects of the extremities predominates in infants, shifting to chronic inflammation with ___ and a predilection for ___ sites in children and adults.
•Acute inflammation and involvement of the cheeks, scalp and extensor aspects of the extremities predominates in infants, shifting to chronic inflammation with lichenification and a predilection for flexural sites in children and adults.
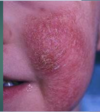
facial eczema in infants
primary and secondary morphology

AD/eczema
primary: erythematous raised plaques
secondary: excoriations

___ is a form of intense eczema where small vesicles are seen on fingers and palms
pomphylx

note:



