Common Pediatric Lesions Flashcards
definition
primary morphology
secondary morphology
etiology
symptoms
treatment

definition: infantile hemangioma. COMMON INFNATILE Benign endothelial cell neoplasm characterized by early proliferation and then spontaneous involution (grey/purple) patch.
primary morphology: can vary in size
secondary morphology
etiology: girls, preemies, low birthweight, older mothers who had villus sampling
symptoms: most self resolved, but periocular hemangiomas can lead to blindness.
treatment: most are self resolved but severe IHs can be managed with propranolol
an infantile hemangioma is a
COMMON INFNATILE Benign ____ cell neoplasm characterized by early proliferation and then spontaneous involution (grey/purple) patch.
endothelial

vascular malgormation (port wine stain)
- wine-red colored lesion with sharp midline demarcation secondary to vascular malformation. present at birth and grows proportionately and persists into adulthood.
complications of vascular malformation
- struge-weber syndrome: vascular malformation in trigeminal distribution can lead to a seizure disorder.
- soft tissue hypertrophy causing growths and swelling.

Definition: small firm white papules with keratin Epi: 40-50% of infants will have milia, usually on the face. Management: resolves within 1 st 4wk of life (infants), resolves spontaneously (children)
What is this?

milia
How does miliaria come up?
miliaria is a heat rash. small vesicles of retianed sweat trapped under a swollen stratum corneum due to occlusion of sweat duct.
- can happen at any age group

Definition
- what is the general form of the childhood version of this disease?
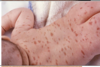
mastocytosis
- excessive collection of normal mast cells. in children, limited to skin. but in adults, can involve BM, liver, spleen and LN.
the childhood version of mastocytosis is URTICARIA PIGMENTOSA.1+ tan-brown papules/plaques. Large lesions in children–>excessive histamine–>diarrhea/wheezing
darier’s sign
urtication of mastocytosis lesion

what is this lesion associated with?

this is a halo nevi. it’s a mole surrounded by white ring/halo
- epi: incidence rate of <20 yo is 1%. average age is 15.
- 20% of patients have VITILIGO. They are also more likely to have melanocytic nevi.
management?

dermal melanosis (mongolian spot)
- grey-blue spots present at birth usually on lumbosacral region
management: self-resolve in early childhood
definition
etiology
investigation
complications

Alopecia Areata
Definition: non-scarring patterned alopecia, usually presenting with circular areas of alopecia
Epi: 1.7% lifetime risk, 1-in-5 pt have a FHx
Etiology: organ-specific autoimmune disease (T-cell mediated) Investigation: exclamation point hair which narrows proximally as it exits the hair follicle
Complications: chronic relapse, alopecia totalis (complete baldness)


