Genital Lesions Flashcards
Primary morphology • Secondary morphology

1- varousocus skin colored pedunculated papule
- hyperkeratosis/scale
this is HPV
What are potential long term sequelae of this condition?

long term genital warts:
- cervical cancer
- local SCC
- if pregnany, baby can get HPV in oropharynx of child (if vaginal birth)
What treatment modalities would you recommend?

hpv
- cryotherapy
- topical treatments with antivirals—but doesn’t really work
- vaccine- even after HPV vaccination, the vaccine has benefit to reducing flares.
Primary Lesion? these have been here for 4 weeks

- vesicle clusters. erythematous. coalesing together. possible umbilication
- it looks like hsv but hsv doesn’t usually last this long. it can eitehr be hsv or most likely MOLLUSCUM– WHICH IS SEXUALLY TRANSMITED IN ADULTS
diagnosis and treatment

molluscum. the natural history of molluscum is self limited but it is often treated because of cosmetic and stigma issues.
- cryotherapy and vessicants– can just be picked at/currettage/nitrogen
- DUCT TAPE to pull out molluscum bodies.
- in AD, there can be autoeczematization that can occur- eczema around the molluscum regions.
19 year old male with a 4 month history of spreading and increasing numbers of these lesions

molluscum

HPV in an immunocompromised host. nned a biopsy to make sure theres not another infiltrative process going on. look for HIV serology– this person probably has a high viral load
this person tested negative for tinea and candida.67 year old male with a 6 year history of this eruption. It burns and is often pruritic. what is the diagnosis and appropriate first line treatment?

there is an erythemaous patch with defined border. possibly plaque. excoriation with possible fissure going into the skin fold. can rule out candida intertrigo. therefore it is either seb.derm or INVERSE PSORIASIS.
both seb derm and inverse psoriasis have the same basic treatment– dry skin care, and low steroid dose (use less potent because it’s in inguinal area)
Which would be the most appropriate first line treatment?
- Systemic Tetracycline 500mg BID
- 1% Hydrocortisone ointment
- 0.05% Clobetasol ointment
- Topical tretinoin 0.01%

bright red erythematous patch with sharp demarkation and white secondary scaling.
this is a sensitive area. use 1% hydrocortisone ointment
description and most likely diagnosis

violaceous or erythematous plaque with secondary scaling or lichenification. finger nailes are displaying onycholysis and possible oil drop sign.
this is consistent with lichen planus OR psoriasus.

atrophy of labia minor and majora. lichen sclerosis
description and differential diagnosis

brown patch and erythema with white erosion and scale. irrecular borders. the head of the penis is very poorly defined– possible scarred down.
you need a biopsy of the darkly pigmented region and the lateral white aspect
Ddx: melenoma, or possible lichen sclerosis post inflammatory hyperpifmentation.
lichen sclerosis can lead to SCC
lichen sclerosis can lead to ___
scc
what two kinds of cancers can HPV lead to
cervical cancer and local SCC
description and differential diagnosis

sharply demarcated ulceration/erosion. could be either inflammatory or neoplastic, but this is probably syphillus. also could be HSV.
description

small erosions in clusters/ herpetiform
- erythematous with secondary erosions. scalloped border. these were probably from previous vessilcs.
this is HSV. but we should biopsy/swab for viral identification
description and ddx

erythematous plaque with secondary crusting and scale with white borders
- possible psoriasis, lichen sclerosis, candida.
treat with corticosone and canesten cream
what is the white material

the penis is red and swolllen– more inflammatory than just smega
- candidiasis!
- need yeast treatment therapy; nystatin or canestin.
- happens more frequently with diabets
- Severe diaper rash confined mostly to the area under a cloth diaper
- 3days ago, sudden spread upward onto the abdomen and downward on proximal thighs
ddx?
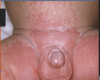
- psoriasis
- candidiasis intertrigo/diaper rash
- autoeczematousation (ID reacition) secondary to candida.
what is an ID reaction and what is it associated with?
ID reaction: also seen with candida and tinea infections
- secdonary lesions of eczema distant from primary site of exposure or involvement.
- symmetric distribution pattern.
- associated with allergic contact dermatitis or stasis dermatitis.
ddx?

candidiasis intertrigo, tinea, or psoriasis (inverse)
- less likely to be tinea because it doesn’t have an annulated border.
what is this and treatment?

looks like AV but it’s hidradenitis supperativa.
tx; get inflammation under control to prevent scarring which causes sinuses

• 3-month history of pruritic skin eruption. Associated family members are also pruritic.

scabies
dx?

the wrist is displaying koebners sign– indicative of either psoriasis or lichen planus. the oral mucosa involvement (reticularization) is more indicative of LP though.


