Urothelial and Renal Cancer Pathology Flashcards
What are the most common benign kidney tumors?
- Papillary adenoma
- Oncocytoma
- Angiomyolipoma
- with or without tuberous sclerosis
What are the common malignant renal tumors?
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (60%)
- Papillary RCC (15%)
- Chromophobe RCC (5-8%)
- Collecting duct carcinoma (<1%)
- Others
What is the major histologic difference between papillary adenoma and paillary RCC?
size is the main differentiating factor

What are the histological features of renal oncocytomas?
- Mahogany in color
- Benign tumor
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm (mitochondria)
- May have nuclear atypia
- May involve capsule
What are the histological findings of renal angiomyolipoma?
- 20% associated with Tuberous Sclerosis (TS complex):
- Kidney lesions: cysts and angiomyolipoma
- Brian tumors
- Heart (rhabdomyoma) and eye tumors
- Skin lesions (such as ash leaf spots)
- 80% sporadic angiomyolipoma
- Histology
- smooth muscle
- adipose tissue
- abnormal vessels

What are the pathologic features of clear cell, low grade renal carcinomas?
- Clear cell RCCs have clear cells…
- Papillary RCCs have papillae…
- Chromophobe RCCs have cells that “fear” (-phobe) “color” (chromo-)…
- RCCs with sarcomatoid features have cells that look spindle cell sarcoma…
- Collecting duct RCCs similar to collecting ducts…
- Very yellow because loaded with lipid and glycogen

Describe the histology of high grade clear cell RCC.
More likely to be high grade tumor, look for nuclear patterns

What are the Fuhrman grades for renal cell carcinoma?
- G1 - nucleoli not seen
- G2 - nucleoli high power
- G3 - nucleoli low power
- G4 - Bizarre nuclei
What are the pathologic features of low grade papillary RCC?
Tan-yellow, tumor cells and some macrophages, almost never bright yellow

What are the pathalogic features of high grade papilloma RCC?
Very uniform, granular appearance because of papillary structure

What are the histologic findings of chromophobe RCC?
Tumors don’t stain very well, fine granules that are membrane-bound vesicles

What are the pathologic features of sarcomatoid RCC?
- Large tumor, average of 10 cm with:
- normal cortex
- clear cell component
- sarcomatoid component
- Large mass (average 10 cm)
- Grossly, flashy white appearance mixed with yellow or brown nodules
- Association with low grade component
- Poor Prognosis
- Specific treatment protocol

What are the chromosomal abnormalities of clear cell and papillary RCC?
- Clear cell = -3p
- Papillary = +7, +17, -Y
What are the pathological features of urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis?
Mass in pelvis, polypoid lesion, fibrovascular core

What are the classifications of bladder tumors by pathology?
-
Urothelial carcinoma
- Flat
- Carcinoma in situ
- Invasive
- Papillary
- Noninvasive
- Invasive
- Flat
-
Other primary neoplasms
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Carcinosarcoma
- Melanoma
-
Secondary neoplasms
- Direct extension
- Metastasis
What are the pathological features of urothelial carcinoma in situ?
- CIS, tumor does not have a lot more cells
- Urothelial cells result
- Not invasive yet
- Simply high N/C ratio
- Can become invasive in short time

What are the histological findings of low grade, non-invasive papillary urothelial carcinomas?
Tissue fragments from resection, tumor cells cover a fibrovascular core, similar to urothelial lining with atypia

What are the pathologic findings of high grade non invasive papiloma UCa?
Uncommon, papillary configuration, also non invasive

What are some markers of urothelial cells?
GATA3 and S100p
What are some uncommon tumors of the bladder?
- Adenocarcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Benign stromal tumors
- Sarcomas
- Melanoma
What are some neuroendocrine tumors of the bladder?
- Small cell carcinoma
- Carcinoid tumor
- Paraganglioma
- Neuroendocrine differentiation of UCa
What are some pathologic features of primary adenocarcinoma (enteric type)?
Features similar to colon cance,r want to make sure it is not metastatic colon cancer, patients undergo colonoscopy

What are the histologic features of squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder?
Look for keratinization and large, squamous cells

What are the pathologic features of UCa with sarcomatoid differentiation (carcinosarcoma)
Tumor cell with a carcinomatous and a sarcomatous component
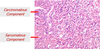
What are the features of metastatic melanoma to the bladder?
Typically have melanocytic features, can be hard to distinguish, but sometimes see pigment, use S100 melanoma marker along with HMB45 marker

What are some pathological findings of the following: prostatic adenocarcinoma of the bladder, secondary adenocarcinoma from colon, metastatic adenocarcinoma from breast?
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma stains positive for PSA
- Secondary adenocarcinoma from colon looks very similar to adenocarcinoma, and clinical findings are important
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma from breast stains positive for mammoglobin


