Topic 82 - Pharmacological effect of glucocorticoids, and the physiology of the stress Flashcards
1
Q
Words to include in pharmalogical effect of glucocorticoids
A
- Anti-inflammatory effect / Antiphlogistic effect
- Phospholipase A2 blocking effect
- Color
- Dolor (pain)
- Tumor (swelling)
- Basophil degranulation
- Allergic reactions
- Masking effect
- Mesenchylam cells
- Fibroblast formation (ø)
- Collagen formation (ø)
- Cicatrisation (contraction of fibrous tissue)
- Granulation
- Osteolysis
- Ossesu matrix
- Ca2+
- Osteoporosis
- Antiallergic effect
- Histamine release
- Antigen-antibody reaction
2
Q
Words to include in physology of stress
A
- Stimuli
- Endogenous factors
- Exogenous factors
- Specific response
- Defense
- Antibody response
- Virus infection
- Aspecific response
- Noxious stimulus
- Stress-reaction
- General Adaption Syndrome (GAS)
- Stressors
- Physical stimuli
- Mechanical stimuli
- Surgical intervention
- Limitation of motion
- Temperature
- Effects of electricity
- Radiation
- Weather
- Specific pathogens
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Parasite
- Related to feeding
- Deficiencies
- Vitamins
- Micro elements
- Intoxications
- Deficiencies
- Emotional stimuli
- Psychic stress
- Pain
- Lack of stimuli
- Physical stimuli
- Stress
- Phases of stess
- Initial stage (1.)
- Cannon’s reaction
- ACTH
- Cannon’s alarm reaction
- Catecholamines
- Stage of resistance (2.)
- Adrenal cortex
- Glucocorticoids
- Immune system
- Glyconeogenesis
- Hyperglycemia
- Insulin secretion
- Amino acids
- Noxious effects
- Stage of exhaustion (3.)
- Energy reserves
- Collapse
- Death
- Stage of adaptive disorders (4.)
- Arthitis
- Chronic hypertension
- Ulcer
- Hepatic failure
- Initial stage (1.)
3
Q
Topics to include in the essay
A
- Pharmalogical effects of glucocorticoids
- Effect on mesenchymal cells
- Anti-inflammatory effect / Antiphlogistic effect
- Antiallergenic effect
- Physiology of stress
- General
- Specific response
- Nonspecific response
- Stressors
- Phases of stress
- Initial stage
- Stage of resistance
- Stage of exhaustion
- Stage of adaptive disorders
4
Q
Pharmalogica effect of glucocorticoids
A
- Glucocorticoids are utilized in veterinary practice because of their excessive anti-inflammatory effect
- The effects of continuous high level of glucocorticoids:
- On mesenchymal cells
- Anti-inflammatory effect / Antiphlogistic effect
- Antiallergic effect
5
Q
Pharmalogica effect of glucocorticoids
Effect on mesenchymal cells
A
- Inhibition of proliferation(rapid increase) of mesenchymal cells:
- Fibroblast and collagen formation is inhibited, cicatrisation (contraction of fibrous tissue) is prolonged
- Normal granulation and total healing of the wound are inhibited
-
Osteolysis is remarkable
- Osseus matrix is degraded
- Ca2+ is mobilized and excreted
- Osteoporosis developes
6
Q
Pharmalogica effect of glucocorticoids
Anti-inflammatory (antiphlogistic) effect
A
- The most important effects of glucocorticoid treatment in veterinary practice, which are due to the phospholipase A2 blocking effect of glucocorticoids are the following:
- The decrease of inflammatory color, dolor and tumor:
- Inflammatory processes go along with changes of:
- Color (color)
- Pain (dolor)
- Swelling (tumor)
- Glucocorticoids drastically moderate all three symptoms.
- Inflammatory processes go along with changes of:
- They decrease basophil degranulation (significantly decrease allergic reactions)
-
Masking effect
-
Since corticoid treatment only decreases inflammatory symptoms, it is not meant to be a causal treatment
- The inflammation inducing bacteria can proliferate in the tissue and the treatment with them can hide the real etiology of the disease.
-
Since corticoid treatment only decreases inflammatory symptoms, it is not meant to be a causal treatment
- The decrease of inflammatory color, dolor and tumor:
7
Q
Pharmalogica effect of glucocorticoids
Antiallergenic effects
A
- Glucocorticoids inhibit histamine release
- They do not have a direct influence on antigen - antibody reaction
8
Q
Physiology of stress
General
A
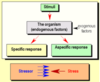
- Organisms are exposed to constant environmental effects. To maintain the internal environment the organism avoids stimuli that would shift the equilibrium. If the stimulus is very strong or disturb the internal equilibrium state (“noxious stimulus”), defense mechanisms are put into force by the organism
-
Specific response
- Is a possibility of defense
- Such specific response is e.g., the antibody response to a virus infection
- During functioning of the immune system, specific antibodies are produced against the given virus, and the organism can recover from illness
- Nonspecific response
- In case of noxious stimuli, when specific response is not available, the organism’s reaction is nonspecific
- This reaction is called stress-reaction
- This form of adaptation is called “general adaptation syndrome (GAS)”
- Stress is elicited by stressors. Every stimulus has to be considered as a stressor, if it leads to the development of GAS
9
Q
Physiology of stress
Give the stessors
A

10
Q
Physiology of stress
Phases of stress
A
- There are four phases of stress response
- Phase 1 - Initial stage (Cannon’s reaction)
- During stress, release of ACTH starts immediately
- The development of stress is often accompanied by Cannon’s alarm reaction
- The effect of catecholamines declines within a few minutes, but ACTH level remains high
- Phase 2 - Stage of resistance
- The adrenal cortex produces a high amount of glucocorticoids
- As a result unnecessary functions are rapidly reduced to the minimum
- Functioning of the immune system becomes inhibited, storing processes are terminated
- Because of the excessive glyconeogenesis, hyperglycemia is persisting, but it does not elicit insulin secretion. Within these conditions, the organism is able to resist the effects of the stressor for a longer period
- If the noxious effect persists, there are two possibilities: either stage 3 or stage 4
- Phase 3 - Stage of exhaustion
- The energy reserves of the organism expire, stage of collapse starts and the animal dies
- Phase 4 - Stage of adaptive disorders
-
Adaptive disorders, such as:
- Arthritis
- Chronic hypertension
- Ulcer
- Hepatic failure
- etc
-
Adaptive disorders, such as:



