Topic 100: General characteristic of the spinal cord, neural networks, Rexed zones, Dermatomes Flashcards
(22 cards)
Words to include in neural networks
- Convergence
- Synapsing
- Divergence
- Simple reflex (monosynaptically organized)
- Polysynaptic
- Interneuron
- Disfacilitation
- Excitatory neuron (inhibition)
- Disinhibition
- Inhibitory neuron (inhibition)
- EPSP (Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential)
- Depolarization
- Excitation
- IPSP (Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential)
- Hyperpolarization
- Inhibition
- Interneuron
Words to include in general characteristics of the spinal cord
- Upper CNS units
- Segmental level
- Intersegmental level
- Nerve cells
- Grey matter
- Nerve fibers
- White matter
- Vertebral canal
- Cervical intumescentia
- Forelimb movement
- Lumbal intumescentica
- Hindlimb movement
- Bulbar origin
- Thoracic region
- Cervical region
- Filum terminale /cauda equina
- Lubar region
- Sacral region
- Receptor
- Sensory neuron
- Spinal cord
- Relay neuron
- Motor neuron
- Effector
- Muscle
Words to include in Reced zones
- Grey matter
- Lateral horn (ø)
- Laminas
- I-IV - Upper horn
- II-III - Interneurons
- VII-IX - Lower horn
- IX - α-motor neurons
- Renshaw cells
- Recurrent inhibition
- IX - α-motor neurons
- I-IV - Upper horn
- Somatotropic arrangement
- Cells of grey matter
- Excitatory interneurons
- Inhibitory interneurons
- Renshaw cells
- Associational neurons
Words to include in dermatones
- Sensory nerves
- CNS
- Demarcated skin area
- Referred pain
- Demarcated stripes (human)
- Skin sensitivity disturbances
- Anesthesia
- Vegetative fibers
- Spinal ganglia
- Somatosensory, pseudounipolar cells
- Substantia gelatinosa Roladi
- Synapse
- Interneurons
- Sensory tract
- Vegetative tract
- Head zones
- Skin zones
- Visceral organs
- Reticular peritonitis (cattle)
Words to include, general
- Electrochemical nerve impulses
- Axons
- PNS
- Tract
- CNS
- Afferent nerves
- Efferent nerves
- Mixed nerves
- Neuron polarity
- Unipolar
- Bipolar
- Multipolar
- Pseudounipolar
Neural network
Define neural network
Neural networks are units based on simple neural connections and organized for complex tasks
Neural network
Name the different types of organization between neurons
- Convergence
- Divergence
- Simple reflex (monosynaptically organized)
- Polysynaptic
- Disfacilitation
- Disinhibition
Neural network
Convergence
The function of one neuron may be influenced by the function of more, on this neuron synapsing neurons together.

Neural network
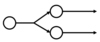
Divergence
The axon of one neuron may run to many other neurons through branches of the axon
Neural network
Simple reflex
- Monosynaptically organized
- One synapsis is responsible for the essential functions

Neural network
Polysynaptic
More than two neurons participate in the reflex
Interneurons may inhibit or excite, collaterals between parallel neural pathways may generate returning signals (reverberation)

Neural network
Disfacilitation
Inhibition of excitatory neuron

Neural network
Disinhibition
Inhibition of inhibitory neuron

Neural network
How does neural networks function?
- Neural networks can function basically through two main effects:
-
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
- Depolarization (excitation)
-
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
- Hyperpolarization (inhibition)
-
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
General characteristics of the spinal cord
Division of the nervous system
- Nervous function can be classified into:
-
CNS
- Brain
- Spinal cord - upper CNS
-
PNS
- Efferent (executional, motor)
- Afferent (sensory)
-
CNS
General characteristics of the spinal cord
Which part of the nervous system does the spinal cord belong to?
- The spinal cord is subordinated to the upper CNS units, but it also has its own coordinating, integrating function: at segmental and intersegmental level processes occur that are carried out without the control of the CNS
- Segmentally: inhibition, excitation and habituation ensure the integration
- Evideces of intersegmental integration:
- Segments of the hindlimbs send inhibitory impulses to the forelimb (Schiff-Sherrington phenomen)
- Scratch reflex
General characteristics of the spinal cord
Draw the pathway

General characteristics of the spinal cord
Structure of the spinal cord
- The spinal cord consists of nerve cells (grey matter) and nerve fibers (white matter) embedded in the bone of the vertebral canal and in protective coverings
- On cross-section nerve cells and fibers are arranged into functional groups
- In grey matter, Rexed’s zones can be found
- Fibers leave the spinal cord through the dorsal and ventral roots that are united before stepping out from the vertebral canal and form the spinal nerves
- Afferent, spinal sensory ganglion: dorsal root
- Efferent, motor fibers: ventral root
-
Cervical intumescentia:
- Plays a role in the movements of the forelimb
-
Lumbal intumescentia:
- Plays a role in the movements of the hindlimb
-
Cervical and thoracic region:
- Nerves leave the vertebral canal perpendicularly to the bulbar origin
-
Lumbar and sacral region:
- Fibers are collected when running down in the vertebral canal (filum terminale or cauda equina)
Rexed zones
Define Rexed zones
- Rexed laminae are layers of neurons within the spinal cord that perform specific functions
- Grey matter (with exceptions of the lateral horn)
- Ten layers of grey matter (I-X)
Rexed zones
Give the laminas
-
I-IV: upper horn
- II-III: mostly interneurons
-
VII-IX: lower horn
- IX: area of large (alpha) motor neurons, smaller motor neurons and of the Renshaw cells responsible for recurrent inhibition
- Motor cells show a somatotropic arrangement similarly to cerebral motor areas

Rexed zones
Give the cells in the grey matter
- Cells inside the grey matter are:
- Excitatory and inhibitory interneurons
- Renshaw cells and associational neurons that establish connection between the given segments

Dermatomes
-
Dermatome: the sensory nerves belonging to a given segment relay the information from particularly demarcated skin areas to the CNS
- Can also use the term referred pain
- These skin areas form clearly demarcated stripes in humans and irregular but well distinguishable patterns in animals
- Helps in determination of the origin of skin sensitivity disturbances and in surgical anesthesia
- Vegetative fibers belonging to the same segment are found in the same place in spinal ganglia as the somatosensory, pseudounipolar cells. Central fibers of these run together towards the substantia gelatinosa Roladi, where they synapse to interneurons. After this sensory and vegetative tracts are separated
- Head zones: Skin zones belonging to a visceral organ
-
reticular peritonitis (cattle)
- Veterinary clinical significance of the head zones


